Steps And Procedure Of Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Overall Science
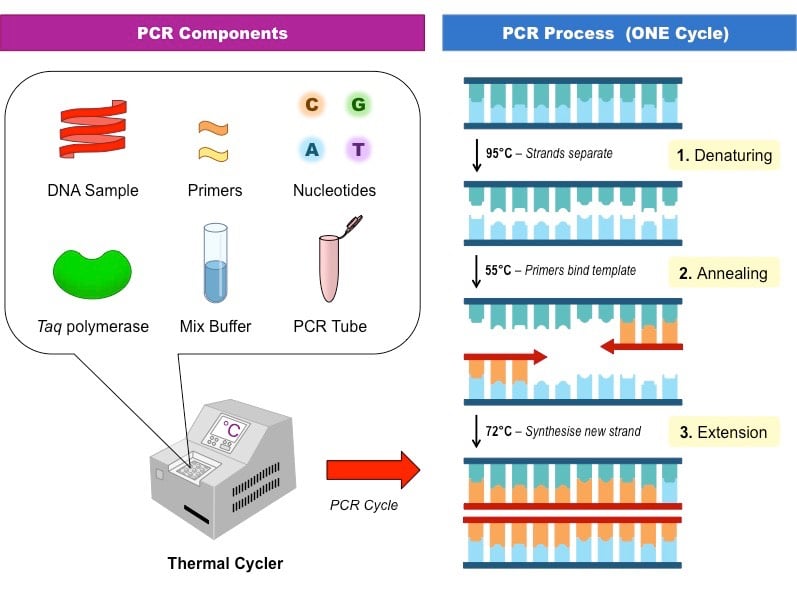
Steps And Procedure Of Polymerase Chain Reaction Pcr Overall Science Steps of pcr. many cycles of dna synthesis are carried out in pcr. these cycles are staged by controlling the temperature that reaction takes place. the various steps are: 1. denaturation of dna. the double stranded dna should be heated to 940– 960c to break a part the hydrogen bonds forming single strands. The pcr process has 4 steps:collection, preparation, amplification, and post pcr clean up. the pcr machine steps happen in the amplification step. it begins with a segment of a dna sample placed in a suitable tube along with the reagents and chemicals listed above. the tube is placed into the pcr machine or thermal cycler. the thermal cycler.
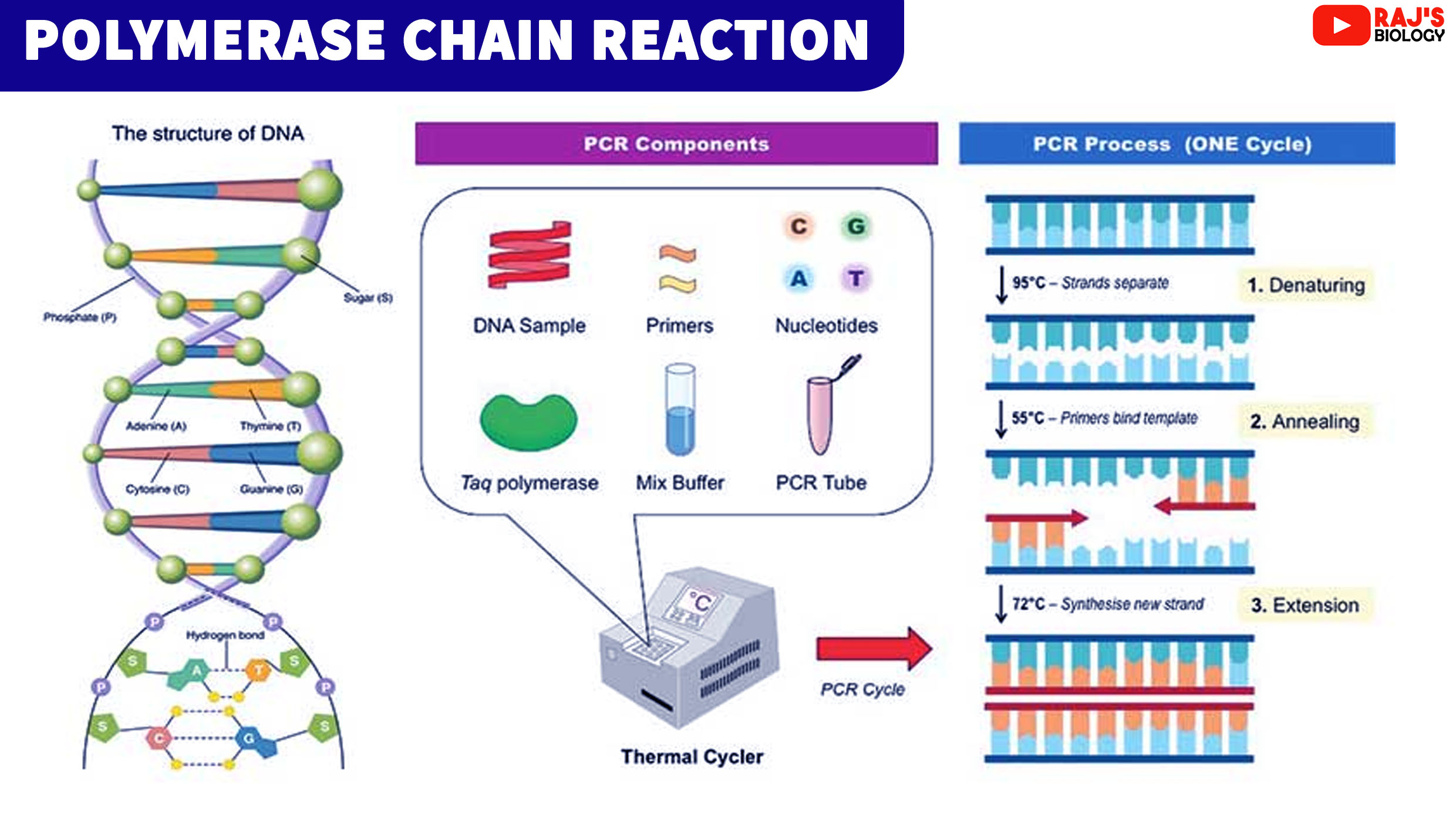
Polymerase Chain Reaction Notes Rajus Biology Polymerase chain reaction ( pcr), a technique used to make numerous copies of a specific segment of dna quickly and accurately. the polymerase chain reaction enables investigators to obtain the large quantities of dna that are required for various experiments and procedures in molecular biology, forensic analysis, evolutionary biology, and. The polymerase chain reaction is composed of four primary steps: 1. the first step is denaturation using heat. 2. the second step is annealing the primer to a specific target sequence of dna. extension 3. end of the first cycle. The polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique used to denature and renature short segments of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) or ribonucleic acid (rna) sequences using dna polymerase i enzyme, an isolate from thermus aquaticus, known as taq dna.[1][2] in 1985, pcr was introduced by mullis and colleagues for which they received a nobel prize.[3] it is a. Polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a powerful method for amplifying particular segments of dna, distinct from cloning and propagation within the host cell. this procedure is carried out entirely biochemically, that is, in vitro. pcr was invented by kary mullis in 1983. he shared the nobel prize in chemistry with michael smith in 1993.

Comments are closed.