Striated Muscles Definition Structure Types Functions Vrogue Co

Striated Muscles Definition Structure Types Functions Vrogue Co Striated musculature. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. striated musculature comprises of two types of tissues: skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. skeletal muscle is the tissue that most muscles attached to bones are made of. hence the word "skeletal". Striated muscle structure and function. striated muscles are highly organized tissues (fig. 1) that convert chemical energy to physical work. the primary function of striated muscles is to generate force and contract to support respiration, locomotion, and posture (skeletal muscle) and to pump blood throughout the body (cardiac muscle). fig. 1.
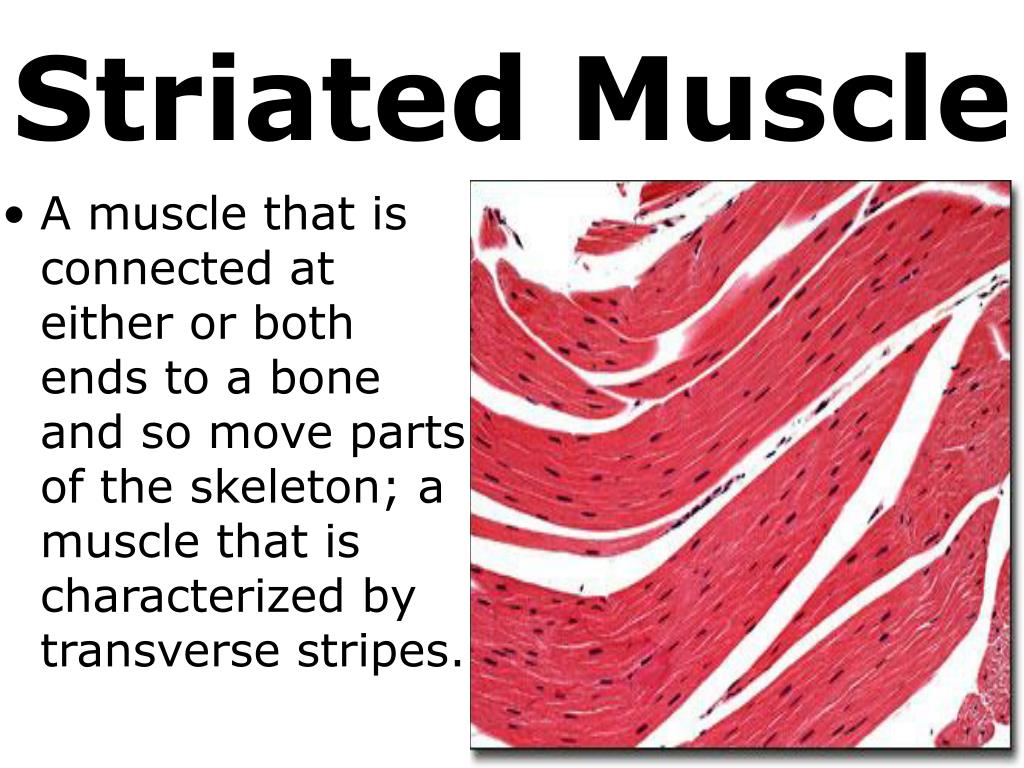
Striated Muscles Definition Structure Types Functions Vrogue Co 1. introduction. striated muscle is composed of two major muscle types—skeletal and cardiac. while the cardiac (heart) muscle functionally represents a set of self‐stimulating, non‐fatiguing muscle cells with an intermediate energy requirement, skeletal muscle represents a set of innervated, voluntary muscle cells that exhibit fatigue with high energy requirements (e.g., muscles of the. The three types of muscle cells are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. their morphologies match their specific functions in the body. skeletal muscle is voluntary and responds to conscious stimuli. the cells are striated and multinucleated appearing as long, unbranched cylinders. cardiac muscle is involuntary and found only in the heart. Striated muscle tissue is a muscle tissue that features repeating functional units called sarcomeres. the presence of sarcomeres manifests as a series of bands visible along the muscle fibers, which is responsible for the striated appearance observed in microscopic images of this tissue. there are two types of striated muscle:. Visceral striated muscle visceral striated muscle is structurally identical to skeletal muscle (i.e. looks the same in microscopic preparations). however, it is limited to a number of soft tissue structures, namely the tongue, pharynx and upper third of the esophagus. test your knowledge on the histology of the skeletal muscle with this quiz.

Comments are closed.