Structure Nomenclature And Properties Of Proteins And Amino Acids
Amino Acid Study Guide Structure And Function Albert Io Chapter 5 structure, nomenclature, and properties of proteins and amino acids martha h. stipanuk, phd∗ proteins were first recognized as a distinct class of biological molecules in the eighteenth century by antoine fourcroy and others, evidenced by the ability of egg whites, wheat gluten, plasma albumin, and fibrin (from clotted blood) to coagulate when treated…. Proline is a non essential amino acid and is coded by ccu, ccc, cca, and ccg. it is the least flexible of the protein amino acids and thus gives conformational rigidity when present in a protein. proline’s presence in a protein affects its secondary structure. it is a disrupter of α helices and β strands.

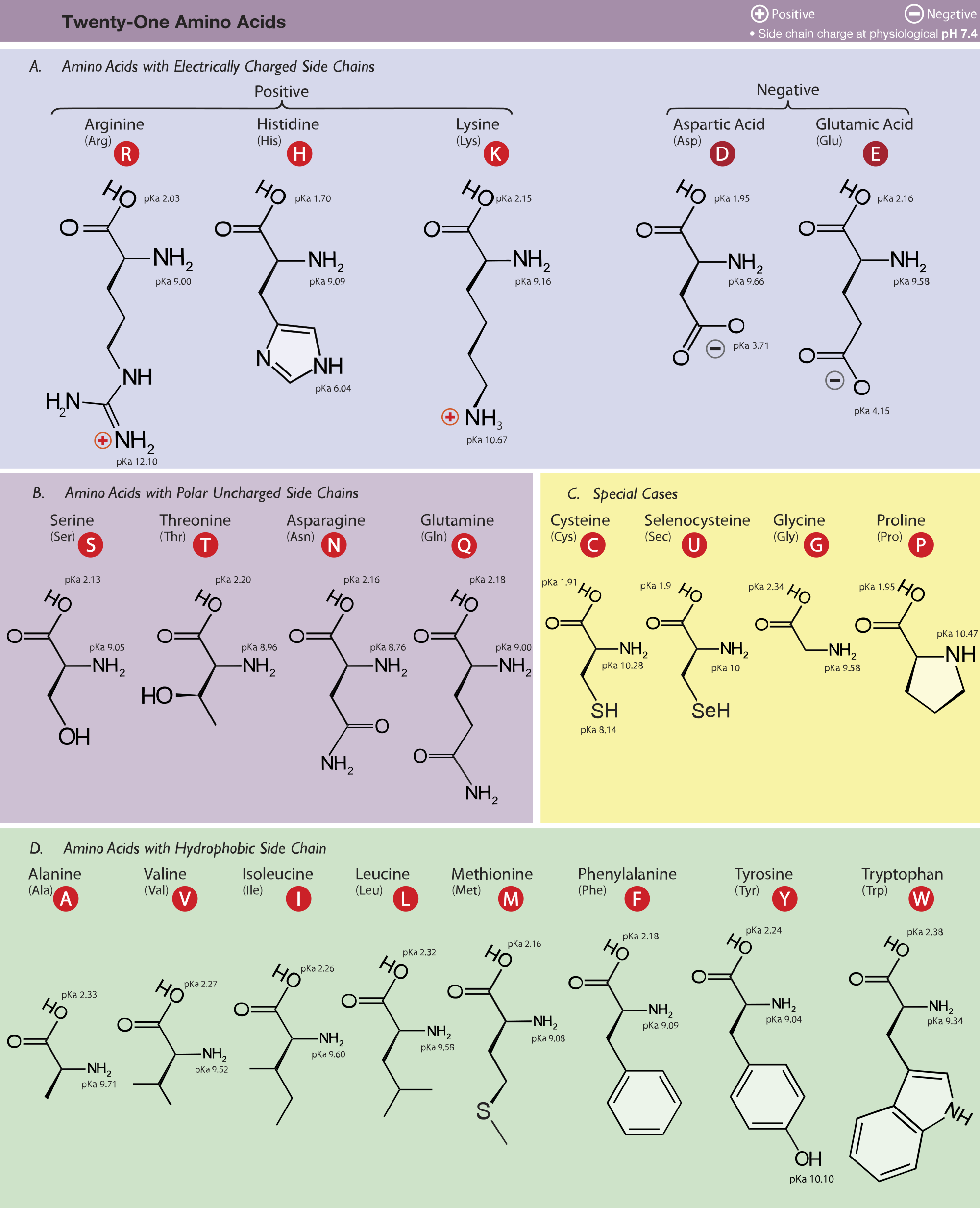
Structure Nomenclature And Properties Of Proteins And Amino Acids The structures, abbreviations (both three and one letter), and pk a values of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins are shown in table 26.1. all are α amino acids, meaning that the amino group in each is a substituent on the α carbon—the one next to the carbonyl group. Amino acid structure. amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. every amino acid also has another atom or group of atoms bonded to the. It is a component of pantothenic acid, hoch 2 c (ch 3) 2 ch (oh)conhch 2 ch 2 co 2 h, a member of the vitamin b complex and an essential nutrient. acetyl coenzyme a is a pyrophosphorylated derivative of a pantothenic acid amide. the gamma amino homolog gaba is a neurotransmitter inhibitor and antihypertensive agent. All amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in figure 2.1. at the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the α carbon and attached to it are four groups – a hydrogen, a carboxylic acid group, an amine group, and an r group, sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. the α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino.
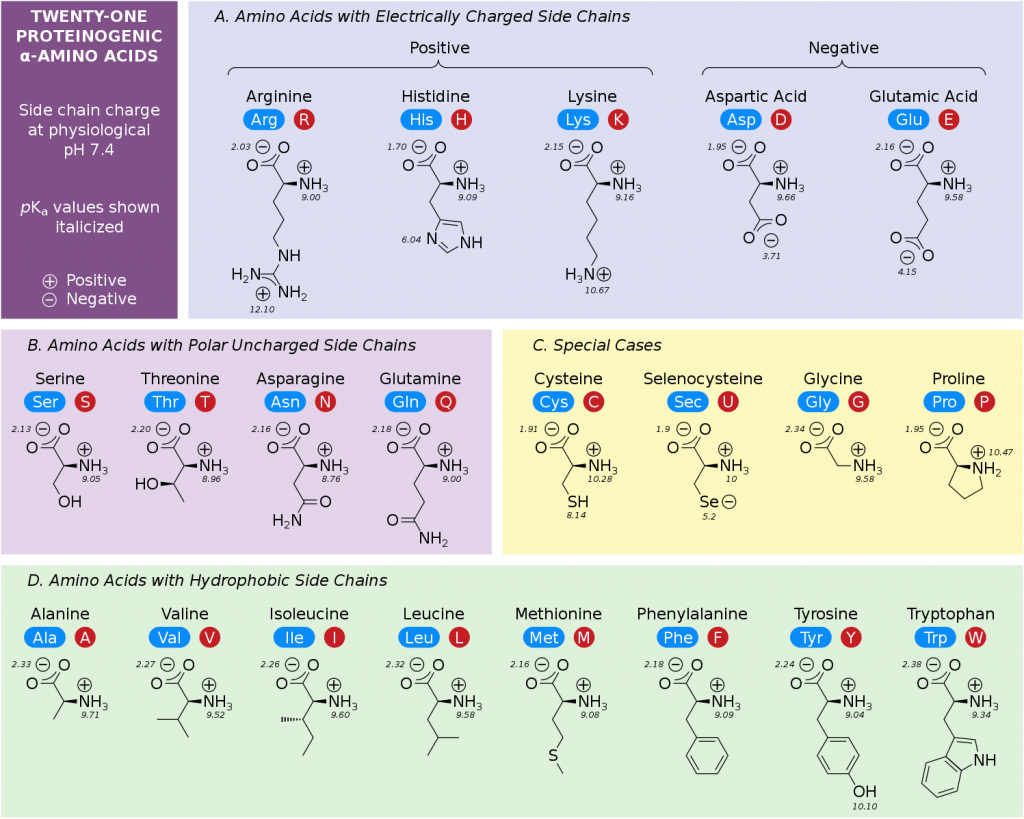
Amino Acid Chart Chemtalk It is a component of pantothenic acid, hoch 2 c (ch 3) 2 ch (oh)conhch 2 ch 2 co 2 h, a member of the vitamin b complex and an essential nutrient. acetyl coenzyme a is a pyrophosphorylated derivative of a pantothenic acid amide. the gamma amino homolog gaba is a neurotransmitter inhibitor and antihypertensive agent. All amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in figure 2.1. at the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the α carbon and attached to it are four groups – a hydrogen, a carboxylic acid group, an amine group, and an r group, sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. the α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino. Uncommon amino acids. in addition to the 20 common amino acids, there are several uncommon ones found: hydroxylysine and hydroxyproline. these are found in the protein collagen. collagen is a fibrous protein made up of three polypeptides that form a stable assembly, but only if the proline and lysine residues are hydroxylated. Properties of amino acids (pka, pkb, pkx, pl) the properties of α amino acids are complex, yet simplistic in that every molecule of an amino acid involves two functional groups: carboxyl ( cooh) and amino ( nh2). each molecule can contain a side chain or r group, e.g. alanine is an example of standard amino acid containing methyl side chain group.

Comments are closed.