Structure Of Cardiac Muscle Cardiac Muscle Tissue Cardiac Physiology

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity в Anatomy And Physiology Introduction. cardiac muscle also called the myocardium, is one of three major categories of muscles found within the human body, along with smooth muscle and skeletal muscle. cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is made up of sarcomeres that allow for contractility. however, unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is under involuntary control. Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. an intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. cardiac muscle tissue. cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
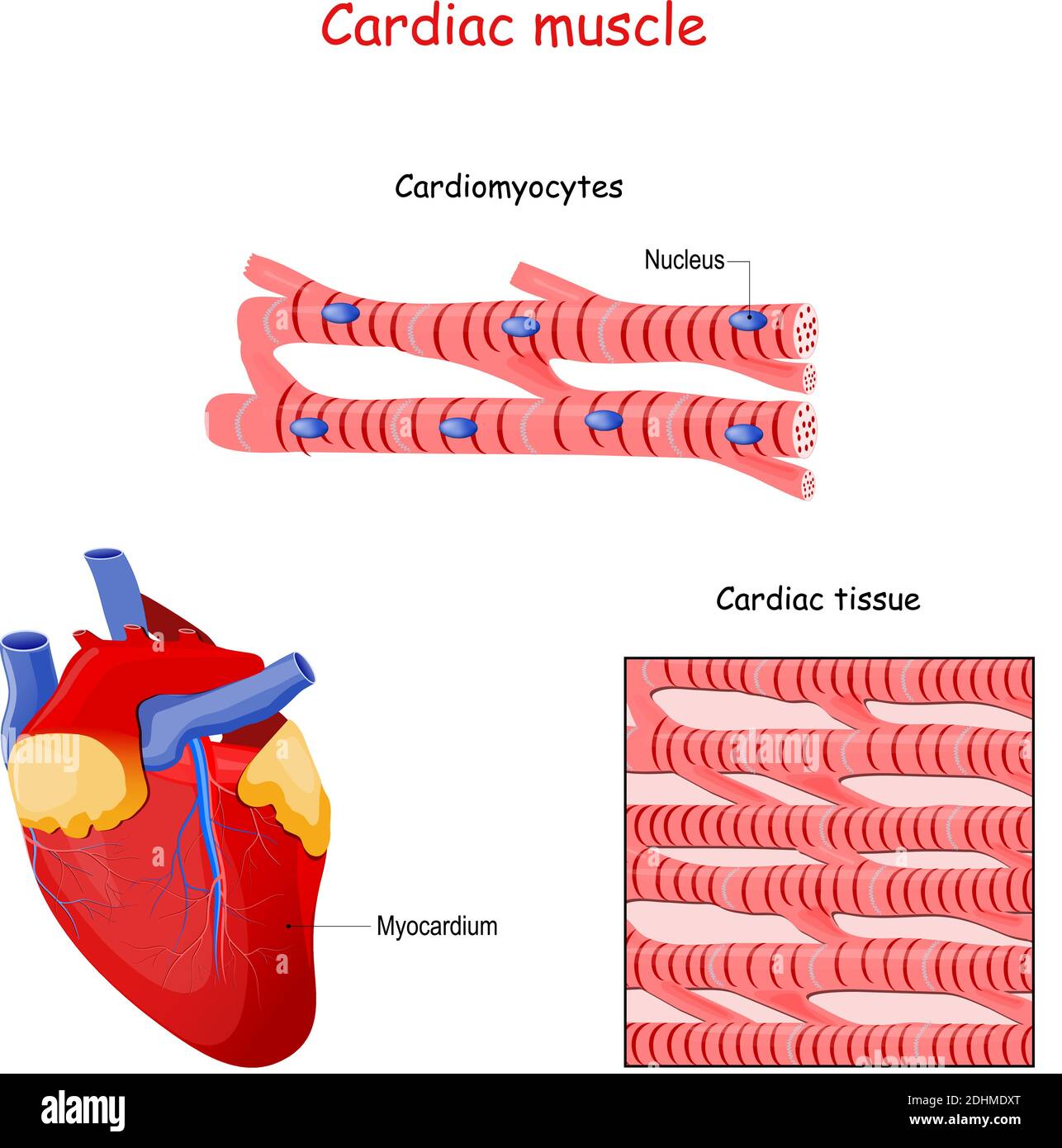
Cardiac Muscle Structure Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle ( figure 10.21 ). Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. it is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. the myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. cardiomyocytes are the. This article provides an overview of cardiac muscle physiology. we describe the structure of the cardiac myocyte, the generation and spread of the cardiac action potential, the process of excitation contraction coupling, and the metabolism and energetics of the heart. finally, we discuss the mechanics of muscle fibre contraction. Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. an intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. figure 1. cardiac muscle tissue. cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.

Labeled Diagram Of Cardiac Muscle This article provides an overview of cardiac muscle physiology. we describe the structure of the cardiac myocyte, the generation and spread of the cardiac action potential, the process of excitation contraction coupling, and the metabolism and energetics of the heart. finally, we discuss the mechanics of muscle fibre contraction. Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. an intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. figure 1. cardiac muscle tissue. cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. There are two major types of cardiac muscle cells: myocardial contractile cells and myocardial conducting cells. the myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. contractile cells conduct impulses and are responsible for contractions that pump blood through the body. Cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. the rhythmic contraction of cardiac muscle is regulated by the sinoatrial node of the heart, which serves as the heart’s pacemaker. the heart consists mostly of cardiac muscle cells (or myocardium).
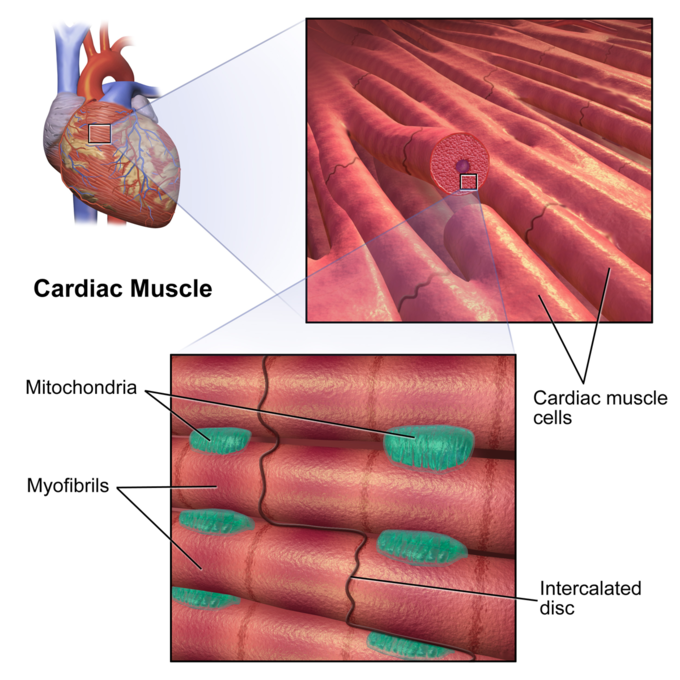
The Heart Boundless Anatomy And Physiology There are two major types of cardiac muscle cells: myocardial contractile cells and myocardial conducting cells. the myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. contractile cells conduct impulses and are responsible for contractions that pump blood through the body. Cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. the rhythmic contraction of cardiac muscle is regulated by the sinoatrial node of the heart, which serves as the heart’s pacemaker. the heart consists mostly of cardiac muscle cells (or myocardium).

Comments are closed.