Structure Of Spiral Deoxyribonucleic Acid Molecule Dna Molecule With
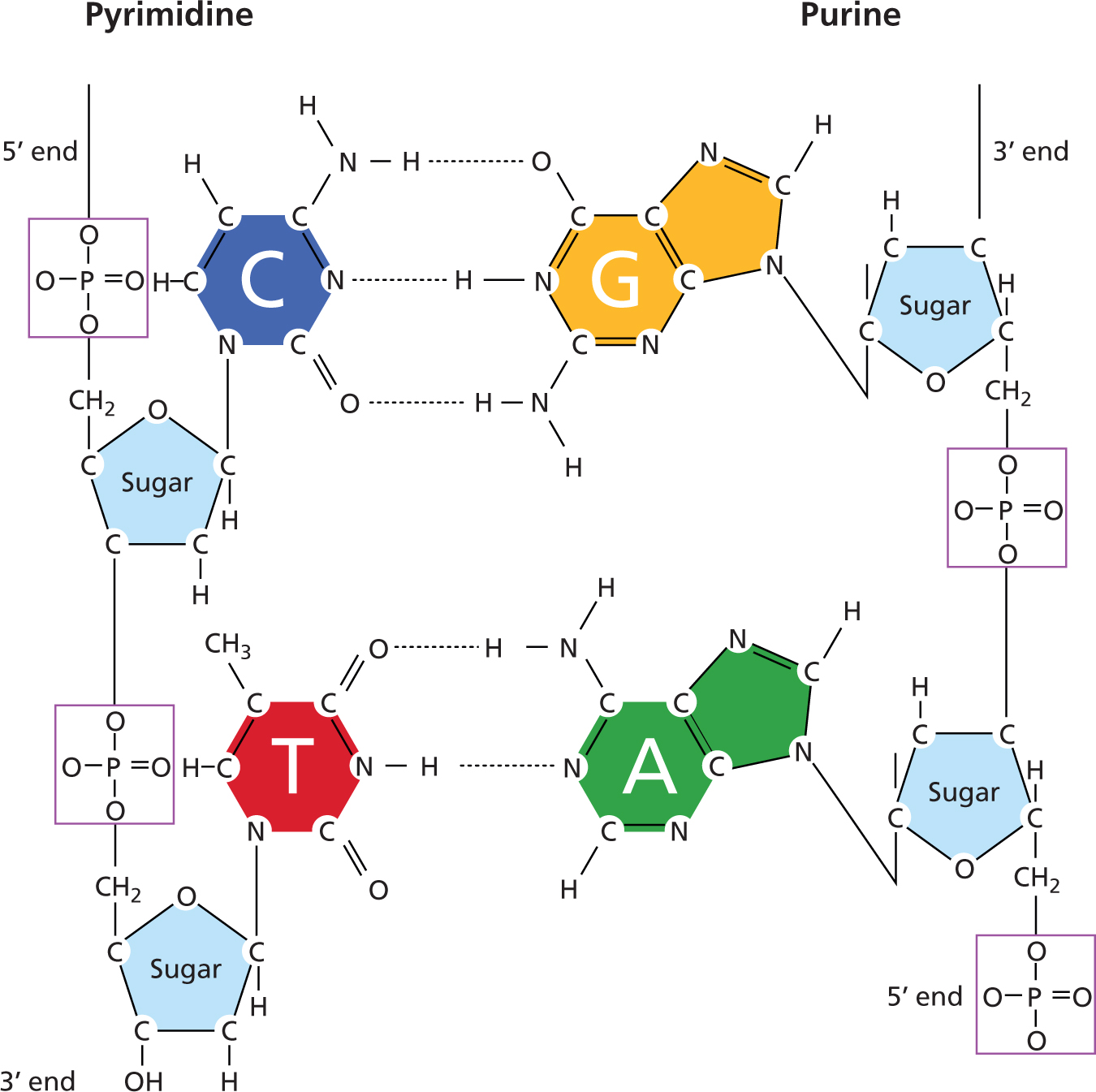
S R Fig01 07 Double stranded dna actually comes in three different forms, known as a dna, b dna, and z dna. although a dna and b dna are right handed helices, z dna is a left handed helix 10 . the twisting of the dna double helix and the geometry of the bases creates a wider gap (called the major groove ) and a narrower gap (called the minor groove ) that run along the length of the molecule, as shown. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed.
Fast And Low Cost Computational Method Can Mo Eurekalert Dna structure. dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecules are nucleic acids, which are the information carrying molecules of the cell. dna molecules are polymers and are made up of many smaller molecules, called nucleotides. each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, a sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base. Kara rogers. dna, organic chemical of complex molecular structure found in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. it codes genetic information for the transmission of inherited traits. the structure of dna was described in 1953, leading to further understanding of dna replication and hereditary control of cellular activities. The structure and function of dna. biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting dna as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. dna was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits, which resemble one another chemically. early in the 1950s, dna was first examined by x ray diffraction. Encoded within this dna are the directions for traits as diverse as the color of a person's eyes, the scent of a rose, and the way in which bacteria infect a lung cell. dna is found in nearly all.

Nucleic Acid Definition Function Structure Types Britannica The structure and function of dna. biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting dna as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. dna was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits, which resemble one another chemically. early in the 1950s, dna was first examined by x ray diffraction. Encoded within this dna are the directions for traits as diverse as the color of a person's eyes, the scent of a rose, and the way in which bacteria infect a lung cell. dna is found in nearly all. Now let’s consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). the building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( figure 9.3 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. (the term "nuclein" was later changed to "nucleic acid" and eventually to "deoxyribonucleic acid," or "dna.") that a bound to t and c bound to g within the molecular structure of dna (figure 2.

Comments are closed.