Subscapularis Muscle Tear вђ Orthopaedicprinciples
Subscapularis Muscle Tear вђ Orthopaedicprinciples Kendall’s muscle testing and function 6th edition by admin leave a comment amzn.to 4c0wmts kendall’s muscles: testing and function, with posture and pain, 6th edition, transforms this landmark physical therapy classic to prepare you for unparalleled clinical success in today’s practice. The subscapularis muscle is a large muscle that originates on the anterior surface of the scapula and lies in front of the shoulder. origin subscapular fossa of the scapula. the muscle passes to its insertion into the lesser tuberosity underneath the arch formed by the cracked process and the combined origins of the coracobrachialis muscle and.

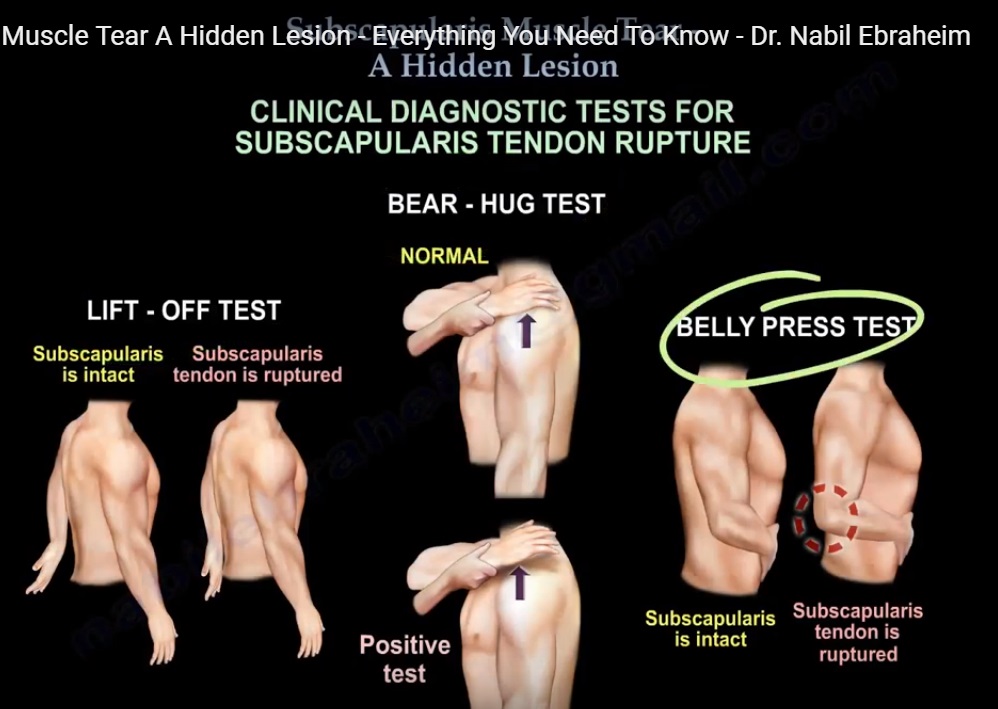
Subscapularis Muscle Tear Tear of the subscapularis tendon; 1 plete tear. surgical repair; repair may be either open or arthroscopic; biceps tenodesis during repair is associated with improved outcomes. biceps tenodesis is usually done if the biceps is involved in the process, otherwise subluxation of the biceps will stress and fail the repair; 2.chronic muscle tear. These include: pain that gets worse at night. shoulder or arm weakness. pain that gets worse when you lift your arm. other symptoms of a subscapularis tear are unique to this injury. these include. Despite being the largest and strongest muscle in the rotator cuff, the subscapularis was once the “forgotten tendon,” with tears of this tendon described as “hidden lesions.”39, 63 not uncommonly, detachment of the subscapularis fibers off the lesser tuberosity starts on the articular side and may have been missed in some patients when open cuff repair surgery was routinely performed. Subscapularis tear. one of four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, the subscapularis muscle originates at the subscapular fossa and inserts onto the lesser tubercle of the humerus. the largest and strongest of the rotator cuff muscles, the subscapularis muscle consists of 60% tendon and 40% muscle. the subscapularis muscle turns the arm.

Partial Subscapularis Tendon Tear Despite being the largest and strongest muscle in the rotator cuff, the subscapularis was once the “forgotten tendon,” with tears of this tendon described as “hidden lesions.”39, 63 not uncommonly, detachment of the subscapularis fibers off the lesser tuberosity starts on the articular side and may have been missed in some patients when open cuff repair surgery was routinely performed. Subscapularis tear. one of four muscles that make up the rotator cuff, the subscapularis muscle originates at the subscapular fossa and inserts onto the lesser tubercle of the humerus. the largest and strongest of the rotator cuff muscles, the subscapularis muscle consists of 60% tendon and 40% muscle. the subscapularis muscle turns the arm. The subscapularis is the largest and most powerful of the rotator cuff muscles and fulfills an important role in glenohumeral movement and stability. the spectrum and implications of subscapularis muscle or tendon injury differ from injury to other rotator cuff components because of its unique structure and function. diagnosing subscapularis injury is clinically difficult and assessment of. Subscapularis tendon overview. the subscapularis tendon is one of the four tendons that come together to form the rotator cuff. the rotator cuff tendon attaches to the top of the arm bone (humerus) just beyond the cartilage surface of the humeral head. the tendon wraps around, forming a cuff of tissue around the humeral head covering the front.

Comments are closed.