Sulfide Ion

Sulfide Sulfite Sulfate Ions Difference And Formulas Youtube Sulfide is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the formula s2− or a compound containing it. learn about its chemical and geological properties, corrosion effects, organic chemistry, and disulfide bonds. Sulfide is a term for compounds containing sulfur, such as metal sulfides, organic sulfides, and phosphine sulfides. learn about the preparation, solubility, structure, and properties of sulfides, and their applications in chemistry and industry.

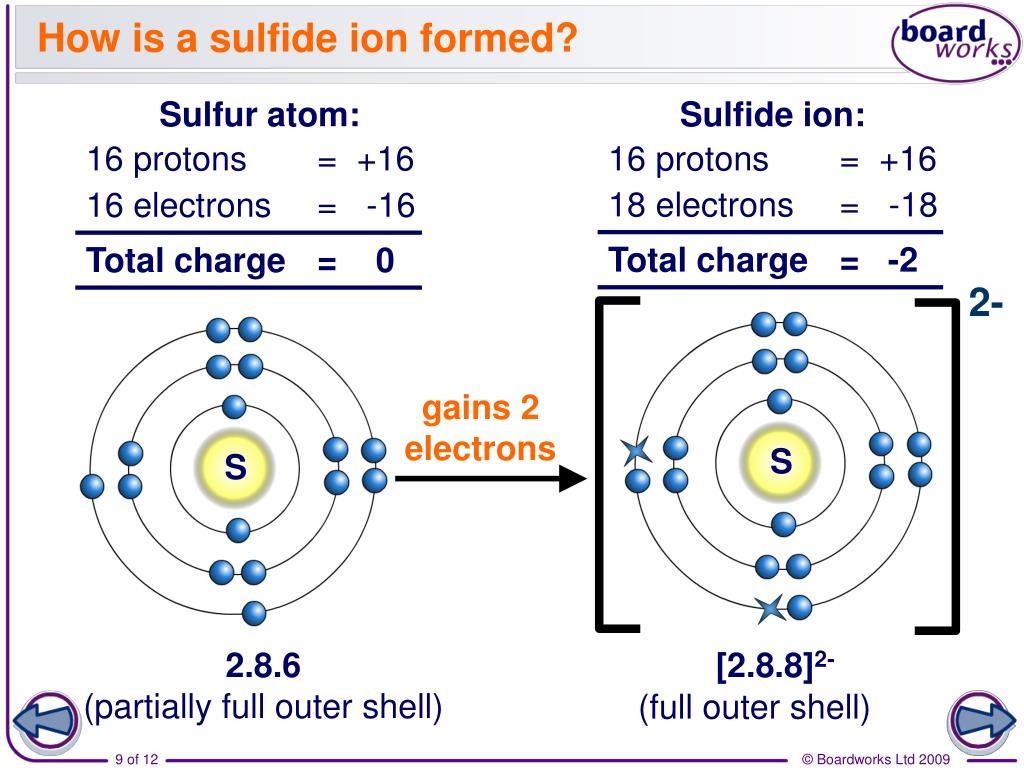
Ionic Bonding Elements Are The Simplest Substances There Learn how to write the electron configuration for s 2 , the sulfide ion, and why it is the same as argon. watch a video explanation with examples and diagrams by wayne breslyn. Learn about the properties, reactions, and tests of sulfide ion, a strong base that forms hydrogen sulfide in water. find out which sulfide salts are insoluble in acidic or basic solution and how to oxidize sulfide to sulfur. Treatment of a thiol with a base, such as nah, gives the corresponding thiolate ion (rs –), which undergoes reaction with a primary or secondary alkyl halide to give a sulfide. the reaction occurs by an s n 2 mechanism, analogous to the williamson synthesis of ethers ( section 18.2 ). Because the ammonium ion has a 1 charge and the sulfide ion has a 2− charge, we need two ammonium ions to balance the charge on a single sulfide ion. enclosing the formula for the ammonium ion in parentheses, we have (nh 4) 2 s. the compound's name is ammonium sulfide.
Ppt How Do Atoms Form Ions Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Treatment of a thiol with a base, such as nah, gives the corresponding thiolate ion (rs –), which undergoes reaction with a primary or secondary alkyl halide to give a sulfide. the reaction occurs by an s n 2 mechanism, analogous to the williamson synthesis of ethers ( section 18.2 ). Because the ammonium ion has a 1 charge and the sulfide ion has a 2− charge, we need two ammonium ions to balance the charge on a single sulfide ion. enclosing the formula for the ammonium ion in parentheses, we have (nh 4) 2 s. the compound's name is ammonium sulfide. Learn about the properties, preparation, and uses of sulfur, a nonmetallic element that forms the sulfide ion, s2−, with metals and nonmetals. find out how sulfur is mined, oxidized, and essential for life. Sulfide ion. view more sulfide (2 ) is a divalent inorganic anion obtained by removal of both protons from hydrogen sulfide. it is a conjugate base of a hydrosulfide. sulfide is a metabolite found in or produced by escherichia coli (strain k12, mg1655). sulfide is a metabolite found in or produced by saccharomyces cerevisiae.

What Is The Lewis Structure Of Hydrogen Sulfate Ion T Vrogue Co Learn about the properties, preparation, and uses of sulfur, a nonmetallic element that forms the sulfide ion, s2−, with metals and nonmetals. find out how sulfur is mined, oxidized, and essential for life. Sulfide ion. view more sulfide (2 ) is a divalent inorganic anion obtained by removal of both protons from hydrogen sulfide. it is a conjugate base of a hydrosulfide. sulfide is a metabolite found in or produced by escherichia coli (strain k12, mg1655). sulfide is a metabolite found in or produced by saccharomyces cerevisiae.

Comments are closed.