Sulfur Cycle Diagram Labeled World Of Reference
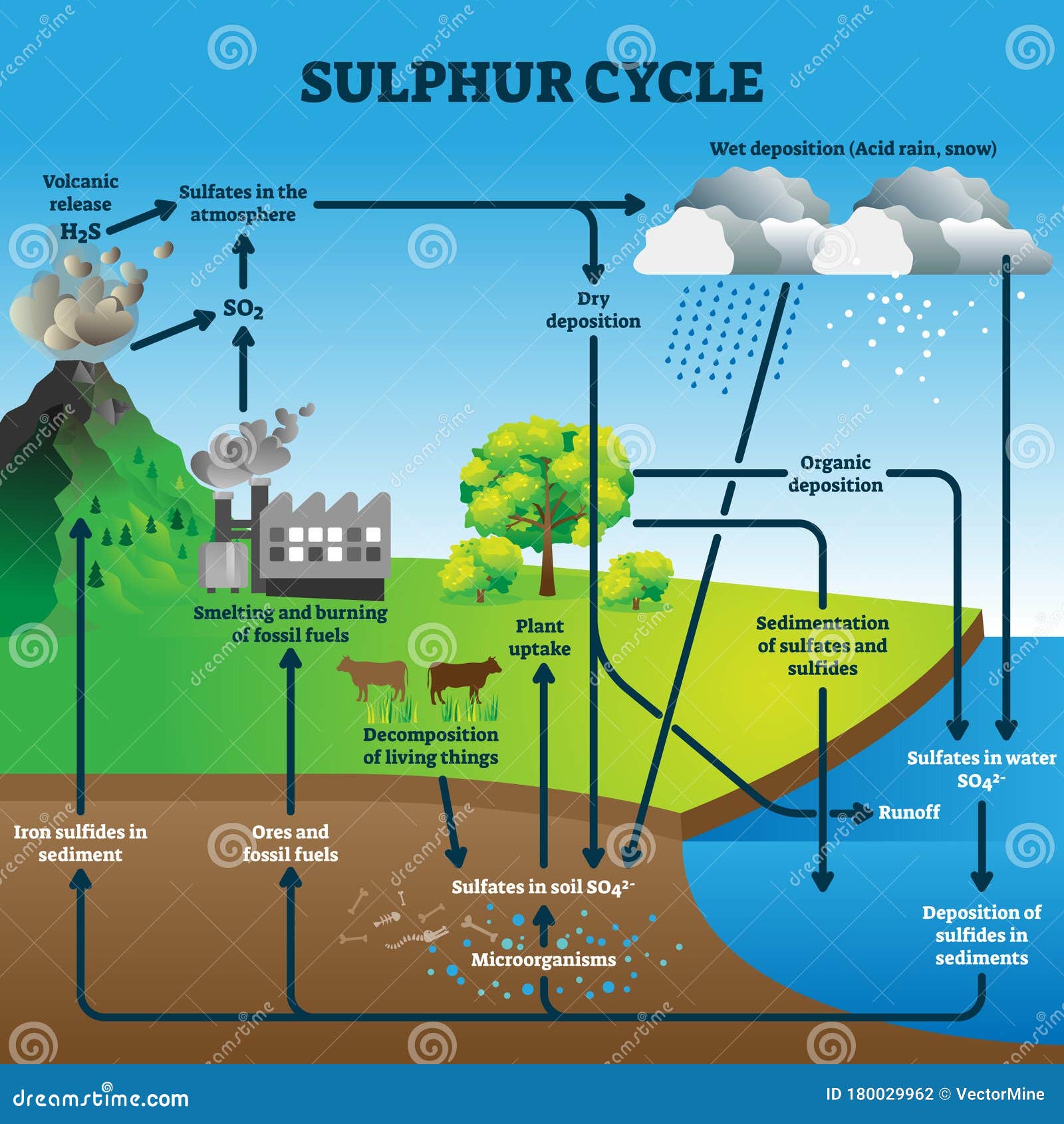
Sulfur Cycle Diagram Labeled World Of Reference Sulfur cycle, circulation of sulfur in various forms through nature. sulfur occurs in all living matter as a component of certain amino acids. it is abundant in the soil in proteins and, through a series of microbial transformations, ends up as sulfates usable by plants. sulfur containing proteins are degraded into their constituent amino acids. 1) formation of inorganic sulfur. it occurs through two different processes –. 2) oxidation of inorganic sulfur to sulfate (so42−) it involves two steps –. 3) assimilative reduction of sulfate to sulfide (s2−) also known as sulfur reduction, it is performed by plants, fungi and various microorganisms such as desulfovibrio and.
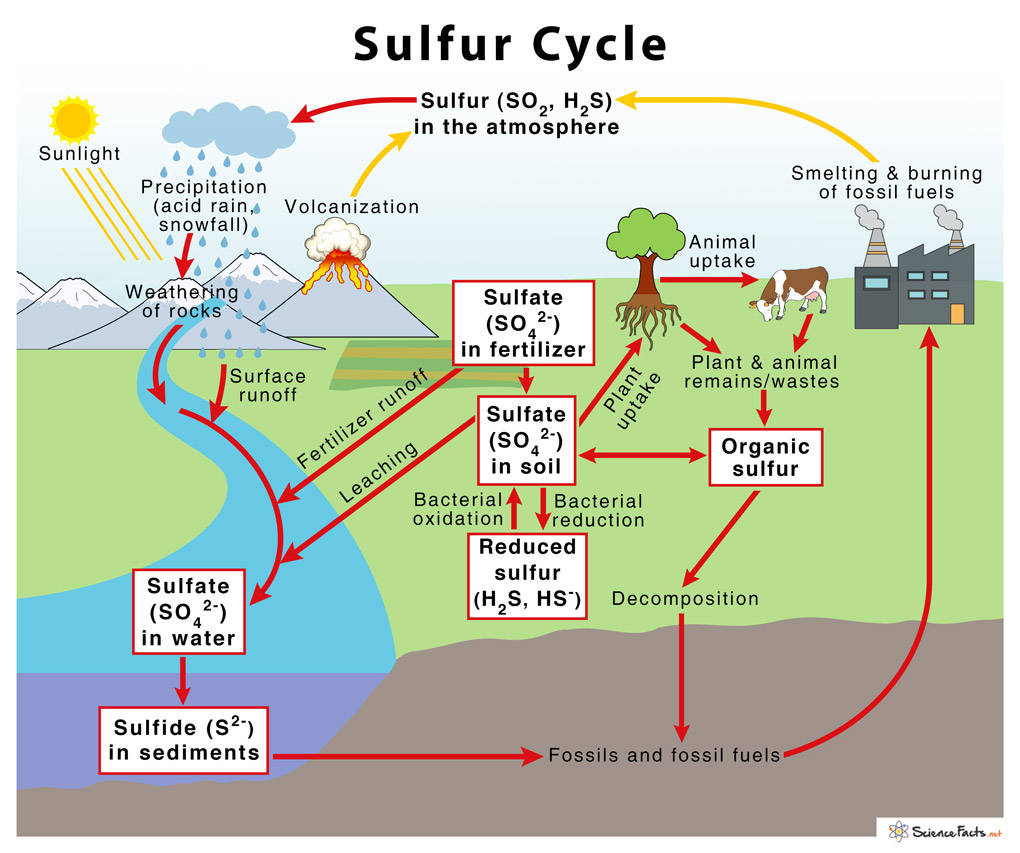
Sulfur Cycle With Diagram вђ Definition Steps And Importance The sulfur cycle consists of various terrestrial and atmospheric processes consisting of different oxidation and reduction reactions. the following are the steps involved in the sulfur cycle: 1. in the atmosphere. sulfur in the atmosphere is mostly present in the form of so 2. most of the so 2 in the atmosphere arises from human activities like. The sulfur cycle. sulfur is an essential element for the macromolecules of living things. as a part of the amino acid cysteine, it is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds within proteins, which help to determine their 3 d folding patterns and, hence, their functions. as shown in figure 20.7.1 20.7. 1, sulfur cycles between the oceans. The important sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical cycle in which the sulfur moves between rocks, waterways and living systems. it is important in geology as it affects many minerals and in life because sulfur is an essential element (), being a constituent of many proteins and cofactors, and sulfur compounds can be used as oxidants or reductants in microbial respiration. [1]. Sulfur, an essential element for the macromolecules of living things, is released into the atmosphere by the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal. as a part of the amino acid cysteine, it is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds within proteins, which help to determine their 3 d folding patterns, and hence their functions.

Comments are closed.