Sulfur Cycle Introduction Steps And Diagram Sulphur Cycle Sulphur
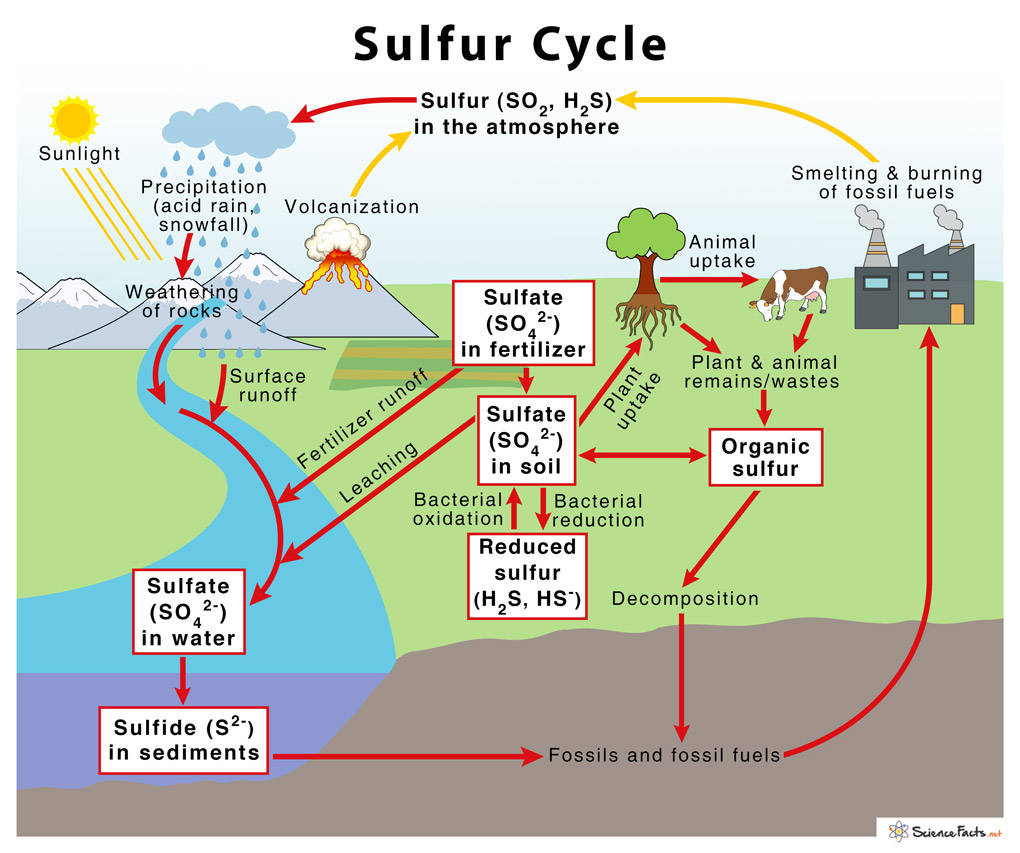
Sulfur Cycle With Diagram вђ Definition Steps And Importance Biogeochemical cycle. sulfur cycle, circulation of sulfur in various forms through nature. sulfur occurs in all living matter as a component of certain amino acids. it is abundant in the soil in proteins and, through a series of microbial transformations, ends up as sulfates usable by plants. sulfur containing proteins are degraded into their. The process of sulphur cycle is explained below: the sulphur is released by the weathering of rocks. sulphur comes in contact with air and is converted into sulphates. sulphates are taken up by plants and microbes and are converted into organic forms. the organic form of sulphur is then consumed by the animals through their food and thus.

Sulfur Cycle Introduction Steps And Diagram Microbiology Notes Sulfur cycle. elemental sulfur (s) is converted into sulfate (so42 ) by photosynthetic and chemolithoautotrophs like thiobacillus, sulfide acts as an e – source. when sulfate enters the reduced habitats, sulfate reduction is carried out by other microorganisms. for instance, during anaerobic respiration, desulfovibrio used sulfate as an. 1) formation of inorganic sulfur. it occurs through two different processes –. 2) oxidation of inorganic sulfur to sulfate (so42−) it involves two steps –. 3) assimilative reduction of sulfate to sulfide (s2−) also known as sulfur reduction, it is performed by plants, fungi and various microorganisms such as desulfovibrio and. The sulfur cycle consists of various terrestrial and atmospheric processes consisting of different oxidation and reduction reactions. the following are the steps involved in the sulfur cycle: 1. in the atmosphere. sulfur in the atmosphere is mostly present in the form of so 2. most of the so 2 in the atmosphere arises from human activities like. The sulfur cycle describes the movement of sulfur through the geosphere and biosphere. sulfur is released from rocks through weathering, and then assimilated by microbes and plants. it is then passed up the food chain and assimilated by plants and animals, and released when they decompose. many bacteria can reduce sulfur in small amounts, but.

Comments are closed.