Supine Position Vs Lithotomy Position

Positioning Patients Georgiaemsacademy Lithotomy position vs. supine position. the two positions share similarities in the positioning of the back and head; the patient lays flat facing up and the arms placed to the sides. in lithotomy positioning, the legs are separated and raised. in supine positioning, the legs stay flat with no separation. supine position. Prone position. in prone position, the patient lies on the abdomen with their head turned to one side and the hips are not flexed. prone position is comfortable for some patients. extension of hips and knee joints. prone position is the only bed position that allows full extension of the hip and knee joints.

What Supine Means Learn Latin Language Online When laboring in supine or lithotomy position, woman's weight is mainly supported by her back , which requires woman to push against gravity and puts the fetus in an unfavorable drive angle in relation to pelvic . further, contractions are frequent but less effective in supine or lithotomy position [33,49]. Supine position. this is the most common position for surgery with a patient lying on his or her back with head, neck, and spine in neutral positioning and arms either adducted alongside the patient or abducted to less than 90 degrees. arm abduction maintained under 90 degrees prevents undue pressure of the humerus on the axilla, thereby. Supine position = lying on your back; if the head of the bed is elevated then this position might be called semi sitting or semi recumbent. lithotomy position = lying on your back in a supine position with hips and knees flexed, thighs apart, and legs supported in raised stirrups or by people holding your legs in the air. lateral position. Prone position. in the prone position, patients lie flat on their stomach. the head can be turned to either the left or right side and the legs are extended. mnemonic to remember the position: look at the word prone. take note of the word “on” and the letter “e” in the word. remember that when the patient is prone, they are lying “on.
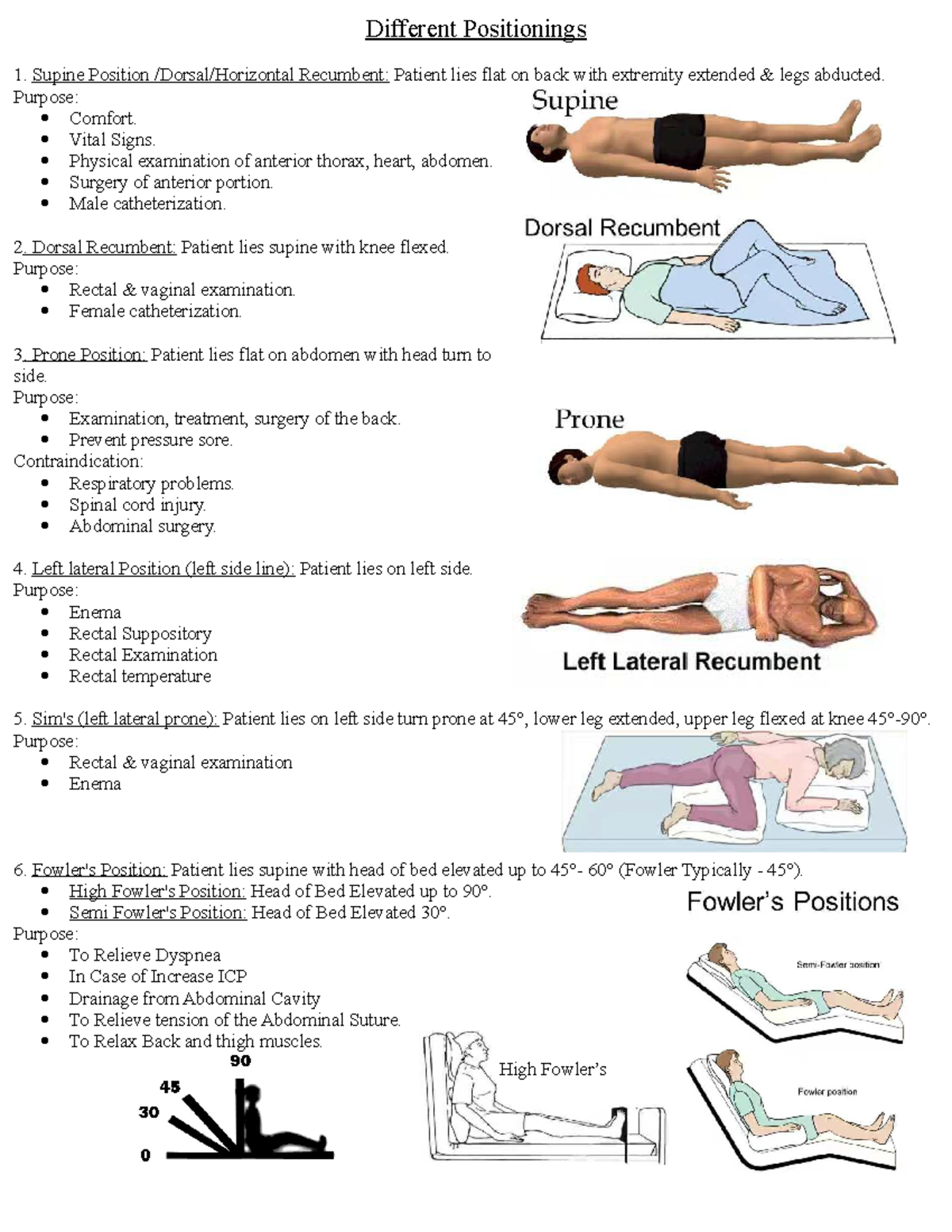
Supine Position Uses And Precautions Science 2023 47 Off Supine position = lying on your back; if the head of the bed is elevated then this position might be called semi sitting or semi recumbent. lithotomy position = lying on your back in a supine position with hips and knees flexed, thighs apart, and legs supported in raised stirrups or by people holding your legs in the air. lateral position. Prone position. in the prone position, patients lie flat on their stomach. the head can be turned to either the left or right side and the legs are extended. mnemonic to remember the position: look at the word prone. take note of the word “on” and the letter “e” in the word. remember that when the patient is prone, they are lying “on. The lithotomy position is commonly used during gynecologic, rectal, and urologic examinations or surgeries. the positioning facilitates access to specific anatomical structures, such as the organs of the urinary and reproductive system as well as the rectum and anus. for example, the lithotomy position is the preferred position for childbirth. The patient’s lower legs are parallel with the o.r. bed. hemi: the patient’s non operative leg is positioned in standard lithotomy. the patient’s operative leg may be placed in traction. high: the patient’s hips are flexed until the angle between the posterior surface of the patient’s thighs and the o.r. bed surface is 110 degrees to.

Semi Fowler Position What Is It Difference From Fowler And More The lithotomy position is commonly used during gynecologic, rectal, and urologic examinations or surgeries. the positioning facilitates access to specific anatomical structures, such as the organs of the urinary and reproductive system as well as the rectum and anus. for example, the lithotomy position is the preferred position for childbirth. The patient’s lower legs are parallel with the o.r. bed. hemi: the patient’s non operative leg is positioned in standard lithotomy. the patient’s operative leg may be placed in traction. high: the patient’s hips are flexed until the angle between the posterior surface of the patient’s thighs and the o.r. bed surface is 110 degrees to.

Patient Positioning вђ Lithotomy Prone Position Nurse Info

Comments are closed.