The 4 Nucleotide Bases Guanine Cytosine Adenine And Thymine What Are Purines And Pyrimidines
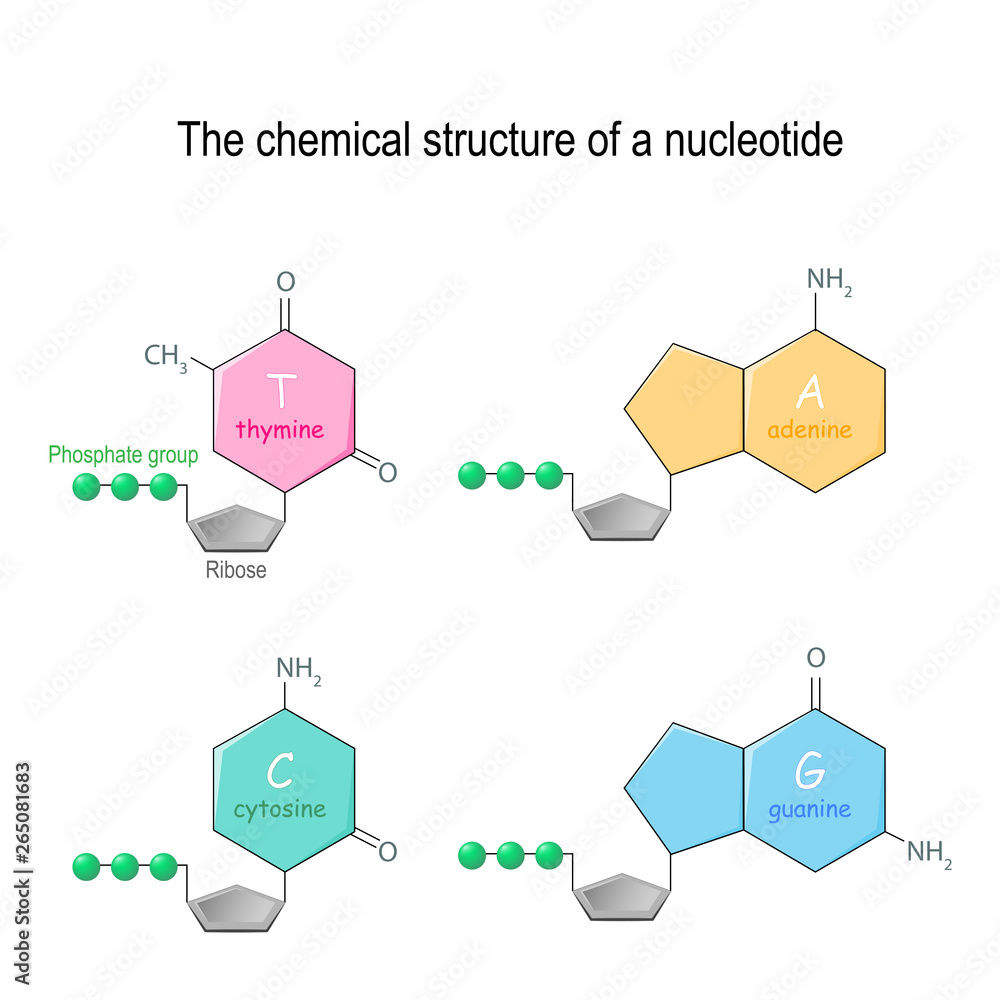
The Chemical Structure Of A Nucleotide Four Main Bases Found In Dna A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) or cytosine (c). c and t bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines , while a and g bases, which have two rings, are called purines . There are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. the nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. figure 9.3 (a) each dna nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base.
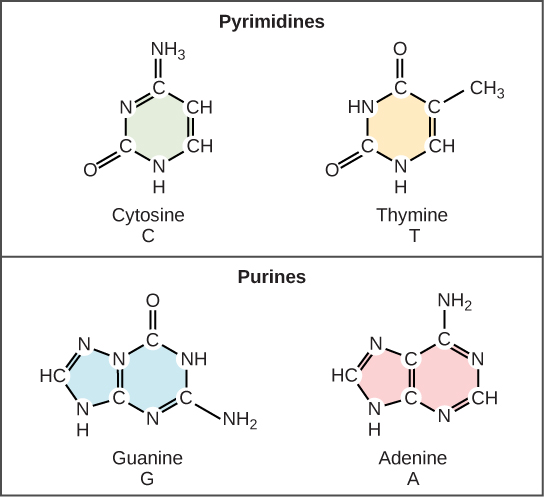
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Biology Libretexts Adenine and guanine have a fused ring skeletal structure derived of purine, hence they are called purine bases. [4] the purine nitrogenous bases are characterized by their single amino group (−nh 2), at the c6 carbon in adenine and c2 in guanine. [5] similarly, the simple ring structure of cytosine, uracil, and thymine is derived of. Join our mcat study group: fb groups 2277468099106607if you found this lecture to be helpful, please consider telling your classmates and univers. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed. Adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. the nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. figure 9.3 (a) each dna nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base.

George S Biology Blog Vocabulary Concepts Of Chapter 13 14 The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed. Adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. the nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. figure 9.3 (a) each dna nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base. Molecular structure of dna. dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. the bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. Scientists classify adenine and guanine as purines. the purine's primary structure is two carbon nitrogen rings. the purine's primary structure is two carbon nitrogen rings. scientists classify cytosine, thymine, and uracil as pyrimidines which have a single carbon nitrogen ring as their primary structure ( figure 3.31 ).

Comments are closed.