The Abdominal Muscles Consist Of Several Layers Which All Carry Out

Abdominal Muscle Layers Artwork Stock Image C010 7080 Science The transversus abdominis muscle is the deepest of the three lateral abdominal muscles. it runs from the inner surface of the lower costal cartilages, thoracolumbar fascia, iliopectineal arch and iliac crest horizontally to the linea alba. caudal fibers are also involved in the formation of the cremaster muscle. The anterolateral abdominal wall consists of four layers skin, superficial fascia (connective tissue), muscles and parietal peritoneum. the muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall include flat and vertical muscles. the flat muscles are stacked on top of each other and have fibres that run in different directions, helping to strengthen the.
/GettyImages-160935664-f80d8f5e0554435cb8cb2d68a339304f.jpg)
Abdominal Muscles Location And Function Introduction. the abdominal muscles are the muscles forming the abdominal walls, the abdomen being the portion of the trunk connecting the thorax and pelvis. an abdominal wall is formed of skin, fascia, and muscle and encases the abdominal cavity and viscera [1]. the abdominal muscles support the trunk, allow movement, hold organs in place, and. Your abdominal muscles have many important functions, from holding organs in place to supporting your body during movement. there are five main muscles: pyramidalis, rectus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques and transversus abdominis. ab strains and hernias are common, but several strategies can keep your abs safe and healthy. The abdominal wall performs several vital functions. it contains and provides a scaffold for the development and functioning of abdominal viscera. all layers contribute to a degree of physical protection of the organs. the abdominal muscles may be divided broadly into anterolateral and posterior components. The muscles of the vertebral column, thorax, and abdominal wall extend, flex, and stabilize different parts of the body’s trunk. the deep muscles of the core of the body help maintain posture as well as carry out other functions. the brain sends out electrical impulses to these various muscle groups to control posture by alternate contraction.
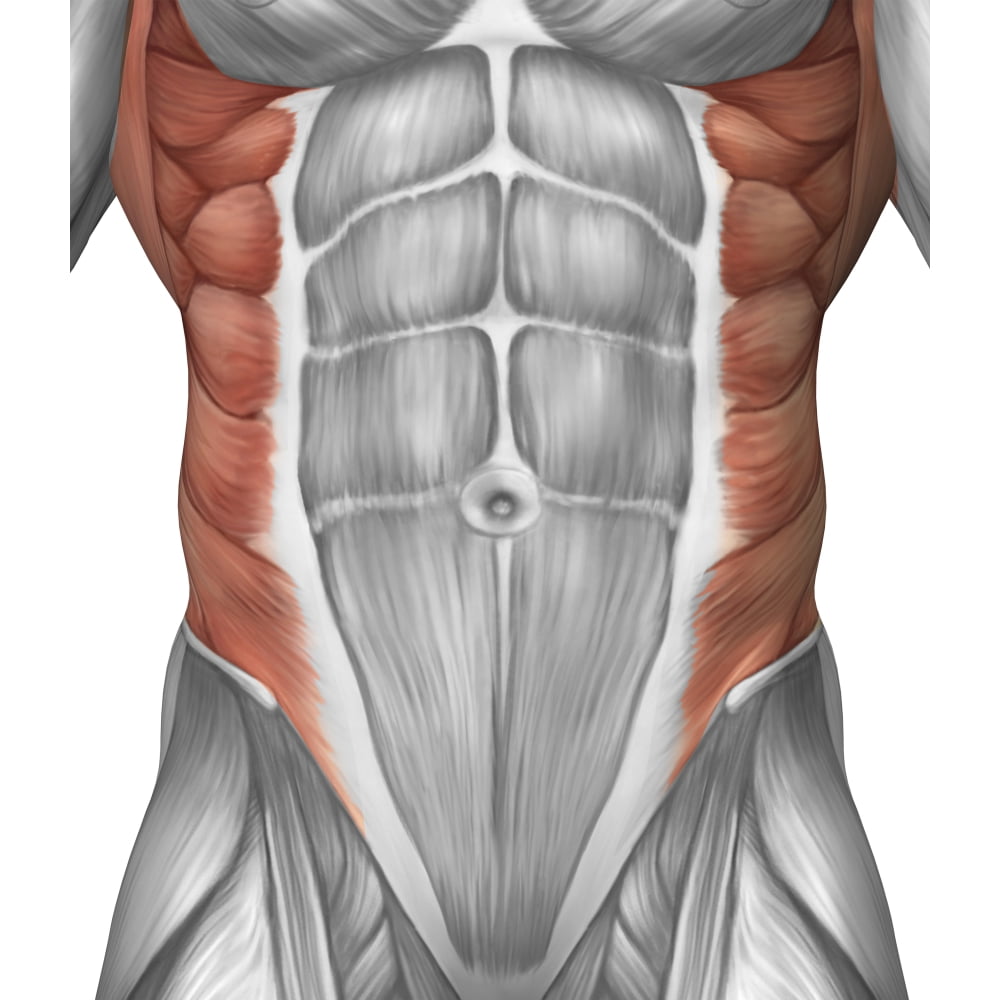
Male Muscle Anatomy Of The Abdominal Wall Poster Print 26 X 30 The abdominal wall performs several vital functions. it contains and provides a scaffold for the development and functioning of abdominal viscera. all layers contribute to a degree of physical protection of the organs. the abdominal muscles may be divided broadly into anterolateral and posterior components. The muscles of the vertebral column, thorax, and abdominal wall extend, flex, and stabilize different parts of the body’s trunk. the deep muscles of the core of the body help maintain posture as well as carry out other functions. the brain sends out electrical impulses to these various muscle groups to control posture by alternate contraction. There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero lateral wall of the abdomen. the external oblique, closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique, extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs. 1:44 muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall. 3:09 external abdominal oblique muscle. 4:58 internal abdominal oblique muscle. 6:16 transversus abdominis muscle. 8:28 inguinal canal. 9:22 rectus abdominis muscle. 11:06 pyramidalis muscle. 12:48 quadratus lumborum. 13:37 psoas major.

Abdominal Wall Anatomy Of The Abdomen Learn Surgery There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero lateral wall of the abdomen. the external oblique, closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique, extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs. 1:44 muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall. 3:09 external abdominal oblique muscle. 4:58 internal abdominal oblique muscle. 6:16 transversus abdominis muscle. 8:28 inguinal canal. 9:22 rectus abdominis muscle. 11:06 pyramidalis muscle. 12:48 quadratus lumborum. 13:37 psoas major.

Abdominal Muscles Diagram Diagram Quizlet

Comments are closed.