The Basics Of Leds

Basics Of Leds By Kwalityphotonics Vijaykumargupta Leds began competing with conventional light sources and fixtures in general illumination applications. the department of energy expects led technology to become the preferred method of lighting in homes and offices by 2025. advantages. comparable in efficacy to cfls, gaining on fluorescent tubes, and incandescents. Leds (that's "ell ee dees") are a particular type of diode that convert electrical energy into light. in fact, led stands for "light emitting diode." (it does what it says on the tin!) and this is reflected in the similarity between the diode and led schematic symbols: in short, leds are like tiny lightbulbs.

Basics Of Leds By Kwalityphotonics Vijaykumargupta The light emitted by an led is usually monochromatic i.e. of single color and the color is dependent on the energy band gap of the semiconductor. light emitting diodes can be manufactured to emit all the wavelengths of visible spectrum i.e. from red (620nm to 750nm) to blue – violet (380nm to 490nm). There are several methods of generating white light using leds. below is 2 typical emission methods. blue led+yellow phosphor. combining a blue led with yellow phosphor, which is a complementary color, will yield white light. this method is easier than other solutions and provides high efficiency, making it the most popular choice on the market. Assuming that a single green led with 10ma forward current should have a constant operating voltage of 5v, the series resistor r v equals (5v v f,10ma ) 10ma = 300Ω. the forward voltage is 2v, as indicated by a graph of typical operating conditions found in the data sheet (figure 2). figure 1. standard red, green, and yellow leds have forward. Main article: light emitting diode physics. in a light emitting diode, the recombination of electrons and electron holes in a semiconductor produces light (be it infrared, visible or uv), a process called " electroluminescence ". the wavelength of the light depends on the energy band gap of the semiconductors used.

Back To Basics Leds Part 1 The Tech Blog Assuming that a single green led with 10ma forward current should have a constant operating voltage of 5v, the series resistor r v equals (5v v f,10ma ) 10ma = 300Ω. the forward voltage is 2v, as indicated by a graph of typical operating conditions found in the data sheet (figure 2). figure 1. standard red, green, and yellow leds have forward. Main article: light emitting diode physics. in a light emitting diode, the recombination of electrons and electron holes in a semiconductor produces light (be it infrared, visible or uv), a process called " electroluminescence ". the wavelength of the light depends on the energy band gap of the semiconductors used. A led or light emitting diode is an electrical component that produces light when current passes through it. leds are semiconductor devices, light is produced when the electrons combine with the material used as the semiconductor. leds can come in a variety of different shapes, colours and sizes. leds can produce the same amount of light around. Leds are all around us: in our phones, our cars and even our homes. any time something electronic lights up, there's a good chance that an led is behind it.
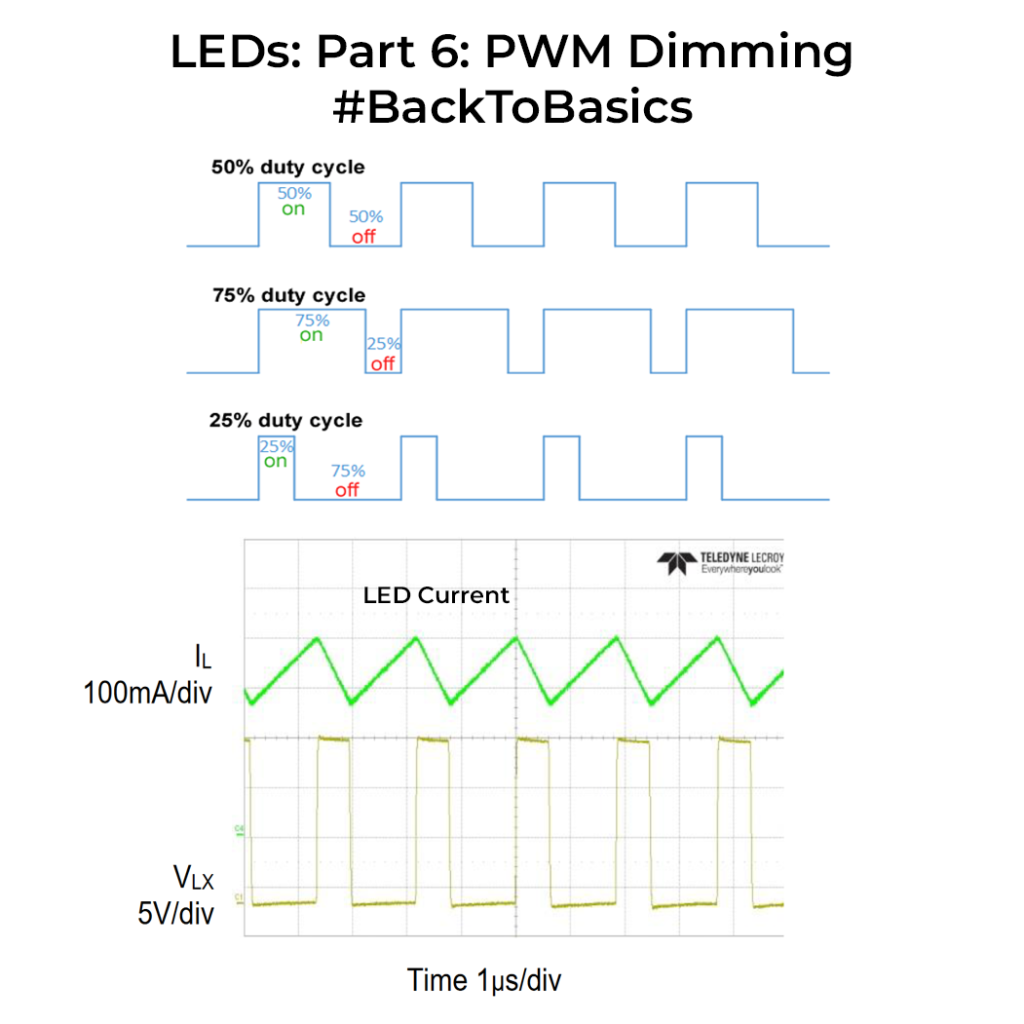
Back To Basics Leds Part 6 Pwm Dimming The Tech Blog A led or light emitting diode is an electrical component that produces light when current passes through it. leds are semiconductor devices, light is produced when the electrons combine with the material used as the semiconductor. leds can come in a variety of different shapes, colours and sizes. leds can produce the same amount of light around. Leds are all around us: in our phones, our cars and even our homes. any time something electronic lights up, there's a good chance that an led is behind it.

Comments are closed.