The Chemical Structure Of A Nucleotide Four Main Bases Found In Dna
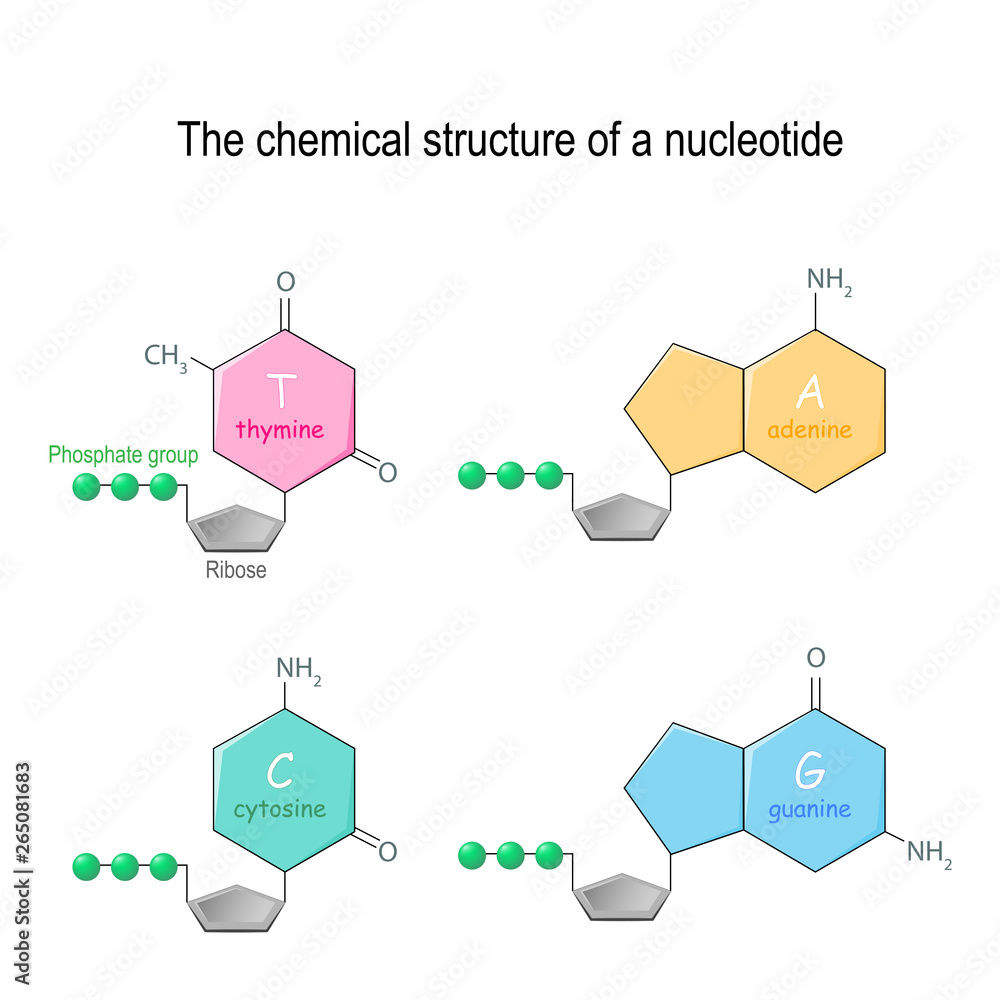
The Chemical Structure Of A Nucleotide Four Main Bases Found In Dna Five nucleobases— adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g), thymine (t), and uracil (u)—are called primary or canonical. they function as the fundamental units of the genetic code, with the bases a, g, c, and t being found in dna while a, g, c, and u are found in rna. thymine and uracil are distinguished by merely the presence or absence of a. Nucleotide definition. a nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. they also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. a nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5 carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. the four nitrogenous bases in dna are adenine, cytosine.
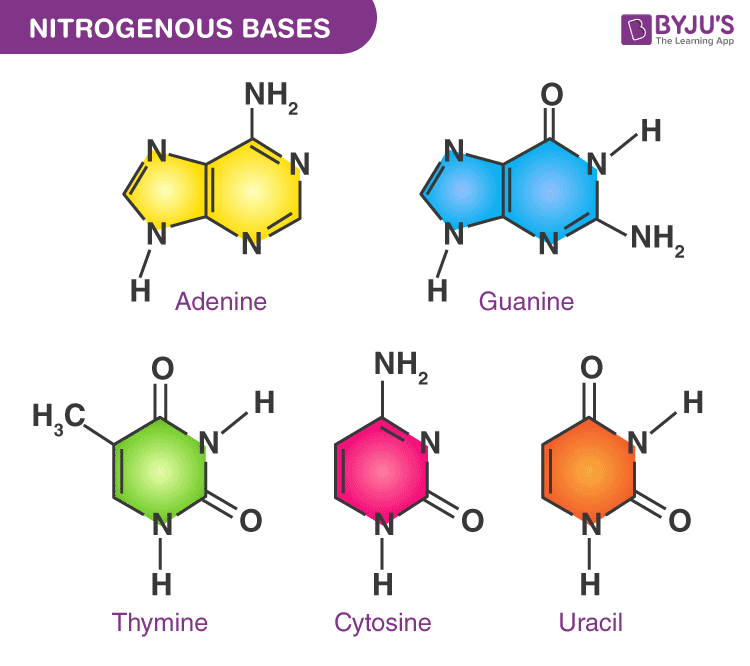
Which Best Describe The Structure Of A Nucleotide There are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. the nucleotide is named according to the nitrogenous base it contains. figure 9.3 (a) each dna nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base. Dna structure and function. dna is the information molecule. it stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. these instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. these chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of dna, called genes. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed. This nucleotide contains the five carbon sugar deoxyribose (at center), a nucleobase called adenine (upper right), and one phosphate group (left). the deoxyribose sugar joined only to the nitrogenous base forms a deoxyribonucleoside called deoxyadenosine, whereas the whole structure along with the phosphate group is a nucleotide, a constituent of dna with the name deoxyadenosine monophosphate.
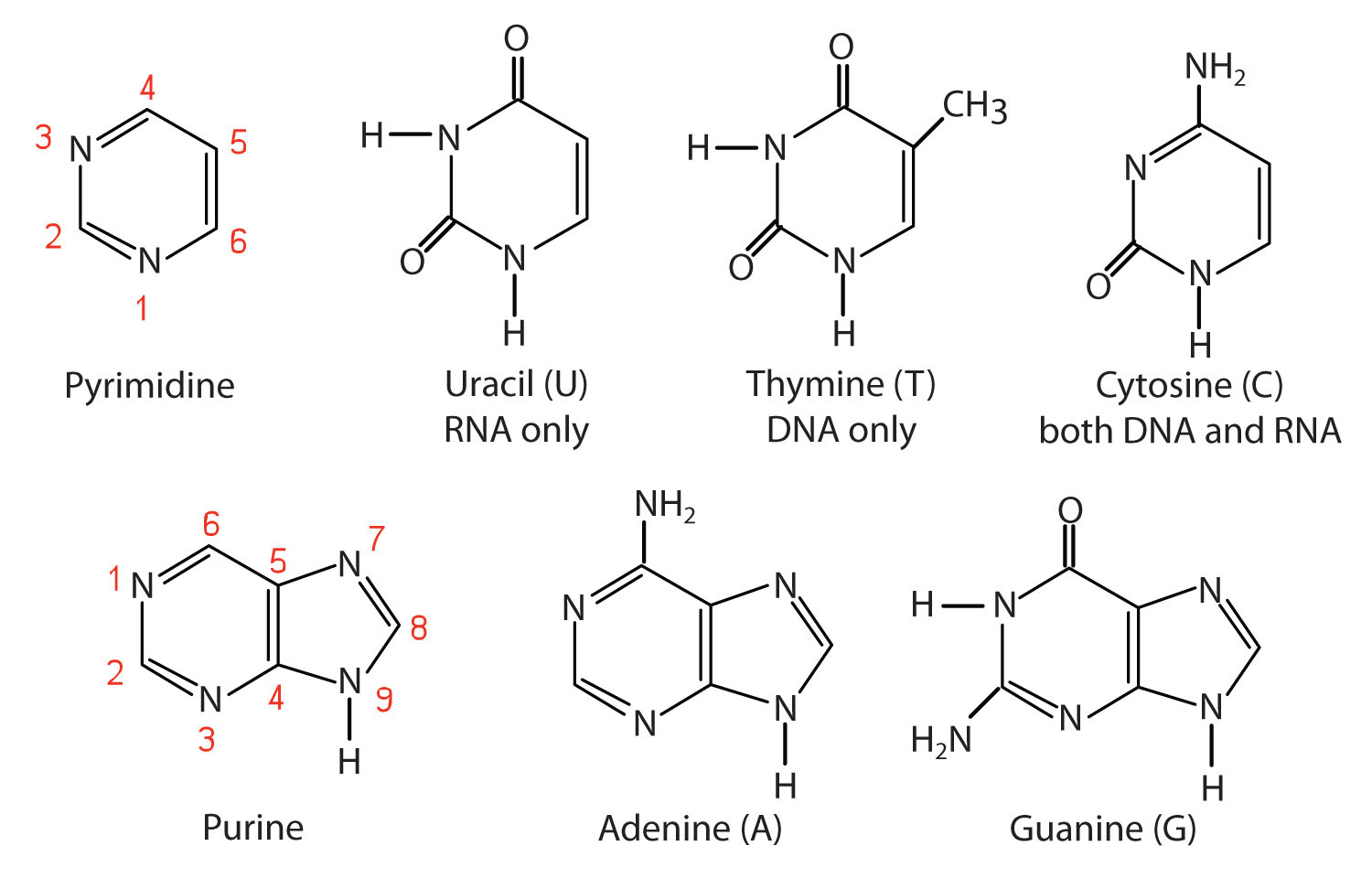
Nucleotides The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed. This nucleotide contains the five carbon sugar deoxyribose (at center), a nucleobase called adenine (upper right), and one phosphate group (left). the deoxyribose sugar joined only to the nitrogenous base forms a deoxyribonucleoside called deoxyadenosine, whereas the whole structure along with the phosphate group is a nucleotide, a constituent of dna with the name deoxyadenosine monophosphate. Deoxyribose differs from ribose (found in rna) in that the #2 carbon lacks a hydroxyl group (hence the prefix “deoxy”). this missing hydroxyl group plays a role in the three dimensional structure and chemical stability of dna polymers. nucleotides in dna contain four different nitrogenous bases: thymine, cytosine, adenine, or guanine. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that serves as the building block for nucleic acids like dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) and rna (ribonucleic acid). these molecules consist of three primary components: a nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and one or more phosphate groups. the sequence of nucleotides within a nucleic acid strand encodes genetic.

Comments are closed.