The Cytoskeleton Microtubules Intermediate Filaments Microfilaments
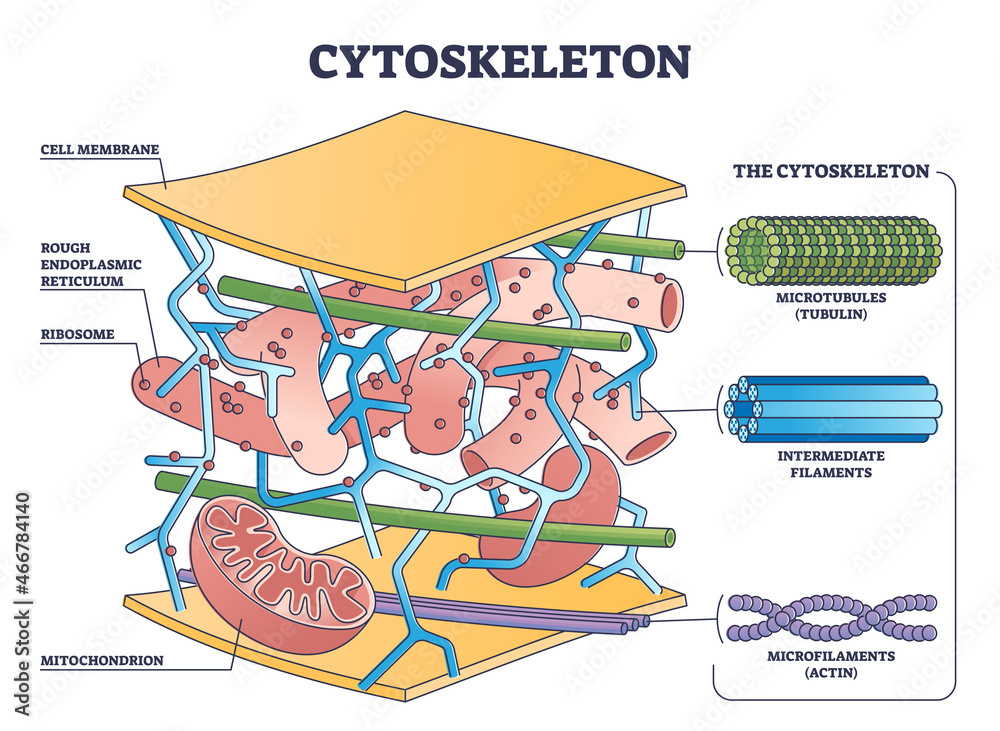
Cytoskeleton Structure As Complex Dynamic Network Of Interlinking As their name implies, microtubules are small hollow tubes. microtubules, along with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, come under the class of organelles known as the cytoskeleton. the cytoskeleton is the framework of the cell which forms the structural supporting component. microtubules are the largest element of the cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton of a eukaryote – specifically of an animal cell, has three kinds of cytoskeletal filaments, which provide structure, aid in movement, and he.
вђњchapter 1 Cytoskeletonвђќ In вђњfundamentals Of Cell Biologyвђќ On Openalg Collectively, this network of protein fibers is known as the cytoskeleton. there are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules ( figure 3.20 ). here, we will examine each. figure 3.20 microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell; like rubber bands, they resist. There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules (figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1). here, we will examine each. figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1: microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell; like rubber bands, they resist tension. The cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments. these structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell's parts. Intermediate filaments. several strands of fibrous proteins that are wound together comprise intermediate filaments (figure 4.24). cytoskeleton elements get their name from the fact that their diameter, 8 to 10 nm, is between those of microfilaments and microtubules.

Differences Between Microfilaments Microtubules And Intermediate The cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments. these structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell's parts. Intermediate filaments. several strands of fibrous proteins that are wound together comprise intermediate filaments (figure 4.24). cytoskeleton elements get their name from the fact that their diameter, 8 to 10 nm, is between those of microfilaments and microtubules. The cytoskeleton consists of (a) microtubules, (b) microfilaments, and (c) intermediate filaments. [1] the cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. [2] in eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is. Khanmigo is now free for all us educators! plan lessons, develop exit tickets, and so much more with our ai teaching assistant.

Physiology Microfilament Microtubule Intermediate Filament Biology The cytoskeleton consists of (a) microtubules, (b) microfilaments, and (c) intermediate filaments. [1] the cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. [2] in eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is. Khanmigo is now free for all us educators! plan lessons, develop exit tickets, and so much more with our ai teaching assistant.

Comments are closed.