The Difference Between Rbe2 And Rbe3 Elements Using A Simple Beam

Fdr ьгэьд ьль Rigide юааrbe2юаб ьща Interpe юааrbe3юаб ъ дьэш ьдаэгэ ьъфыа Difference between rbe2 and rbe3 elements, using a simple beam example.the resulting forces and or displacements can be verified by the provided formulas. be. So, let us first start by understanding the key difference between kinematic couplings (rbe2) and distributed couplings (rbe3): rbe2 elements add infinite stiffness to the nodes being constrained; rbe3 elements provide a distributed connection, which does not influence the local (or global) stiffness of the model.
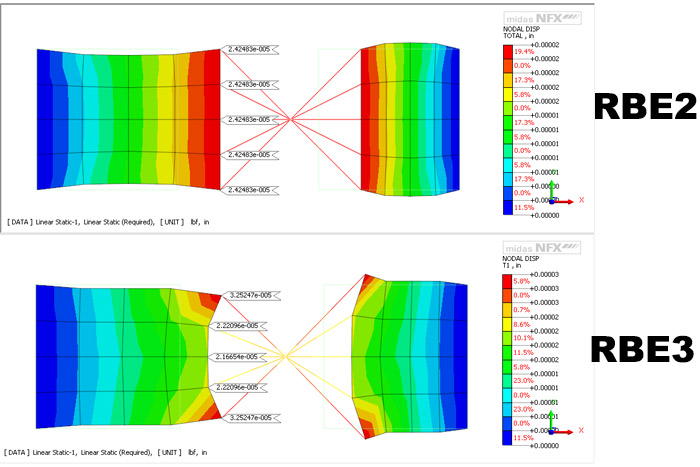
Rbe 2 Ve Rbe 3 Eleman Nedir The basics: r‐type elements {rbe2} here is a starting point to understand the rbe2. a very simple beam model with a 100 lbf load at the center of the beam. the beam is held together with a rbe2. moment & force calc. m = 2.5*50 f = 100 2 simple beam with fixed ends turn on equation force. Both elements "look" the same, in that they have a single node connected to one or (usually) multiple other nodes. the difference is that the rbe2 element adds (infinite) stiffness to the structure, while rbe3 elements "distribute forces" around the connected nodes, without adding any stiffness. a rigid element can be as simple as two nodes. Rbe2 and rbe3 are basically rigid elements that are use to connect mesh sets together. the name is similar, but there is a fundamental difference between them: rbe2 transmits the displacements and rbe3 transmits the loads (mpc forces) i made 2 videos that show: how to create rbe2 and rbe3 elements. the results in terms of displacements and forces. Comparing rbe2 vs rbe3 elements, rbe3 on the other had is not a ‘rigid’ element so to speak. the motion at the ‘dependent’ node is a weighted average of the motion at the ‘independent’ nodes. this is why it is also known as an ‘interpolation’ r element. rbe3 elements do not add artificial stiffness to the structure like the rbar.

What Is The Difference Between A Kinematic Rbe2 And A Distributing Rbe2 and rbe3 are basically rigid elements that are use to connect mesh sets together. the name is similar, but there is a fundamental difference between them: rbe2 transmits the displacements and rbe3 transmits the loads (mpc forces) i made 2 videos that show: how to create rbe2 and rbe3 elements. the results in terms of displacements and forces. Comparing rbe2 vs rbe3 elements, rbe3 on the other had is not a ‘rigid’ element so to speak. the motion at the ‘dependent’ node is a weighted average of the motion at the ‘independent’ nodes. this is why it is also known as an ‘interpolation’ r element. rbe3 elements do not add artificial stiffness to the structure like the rbar. On using this element will be discussed and also why this element is a useful as a companion to the rbe2 and rbe3 elements. 1.2 analyst recommendations r elements (re’s) are not elements but multi point constraints (mp’s) that just happen to look like elements graphically. never apply sp’s too dependent nodes. One of the most common uses for the rbe3 is to "smear" a load into a structure. the rbe2 impose stiffness and are often called "infinitely stiff", while the rbe3 is an interpolation element and does not impart additional stiffness to the model. to help illustrate this difference between the rbe2 and the rbe3 consider the following simple shelf.

Comments are closed.