The First Three Steps For Solving Quadratic Equation By

Solve Quadratic Equations By Using The Quadratic Formula Step By A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation in a single variable where the highest exponent of the variable is 2. there are three main ways to solve quadratic equations: 1) to factor the quadratic equation if you can do so, 2) to use the quadratic formula, or 3) to complete the square. if you want to know how to master these three methods. Example of the quadratic formula to solve an equation. use the formula to solve thequadratic equation: y = x2 2x 1 y = x 2 2 x 1 . just substitute a,b, and c into the general formula: a = 1 b = 2 c = 1 a = 1 b = 2 c = 1. below is a picture representing the graph of y = x² 2x 1 and its solution.

Solving Quadratic Equations Gcse Maths Revision To solve the quadratic equation using completing the square method, follow the below given steps. first make sure the equation is in the standard form: ax 2 bx c = 0. now, divide the whole equation by a, such that the coefficient of x 2 is 1. write the equation with a constant term on the right side of equation. Solve by using the quadratic formula: 3 y (y − 2) − 3 = 0. 3 y (y − 2) − 3 = 0. when we solved linear equations, if an equation had too many fractions we cleared the fractions by multiplying both sides of the equation by the lcd. First, we need to rewrite the given quadratic equation in standard form, after getting the correct standard form in the previous step, it’s now time to plug the values of. from the converted standard form, extract the required values. then evaluate these values into the quadratic formula. solving quadratic equations by completing the square. Solve by completing the square: x2 8x = 48. solution: step 1: isolate the variable terms on one side and the constant terms on the other. this equation has all the variables on the left. x2 bx c x2 8x = 48. step 2: find (1 2 ⋅ b)2, the number to complete the square. add it to both sides of the equation.

Three Ways To Solve A Quadratic Equation Saadlong First, we need to rewrite the given quadratic equation in standard form, after getting the correct standard form in the previous step, it’s now time to plug the values of. from the converted standard form, extract the required values. then evaluate these values into the quadratic formula. solving quadratic equations by completing the square. Solve by completing the square: x2 8x = 48. solution: step 1: isolate the variable terms on one side and the constant terms on the other. this equation has all the variables on the left. x2 bx c x2 8x = 48. step 2: find (1 2 ⋅ b)2, the number to complete the square. add it to both sides of the equation. Quadratic equation in standard form: ax 2 bx c = 0. quadratic equations can be factored. quadratic formula: x = −b ± √ (b2 − 4ac) 2a. when the discriminant ( b2−4ac) is: positive, there are 2 real solutions. zero, there is one real solution. negative, there are 2 complex solutions. An equation containing a second degree polynomial is called a quadratic equation. for example, equations such as \ (2x^2 3x−1=0\) and \ (x^2−4= 0\) are quadratic equations. they are used in countless ways in the fields of engineering, architecture, finance, biological science, and, of course, mathematics.
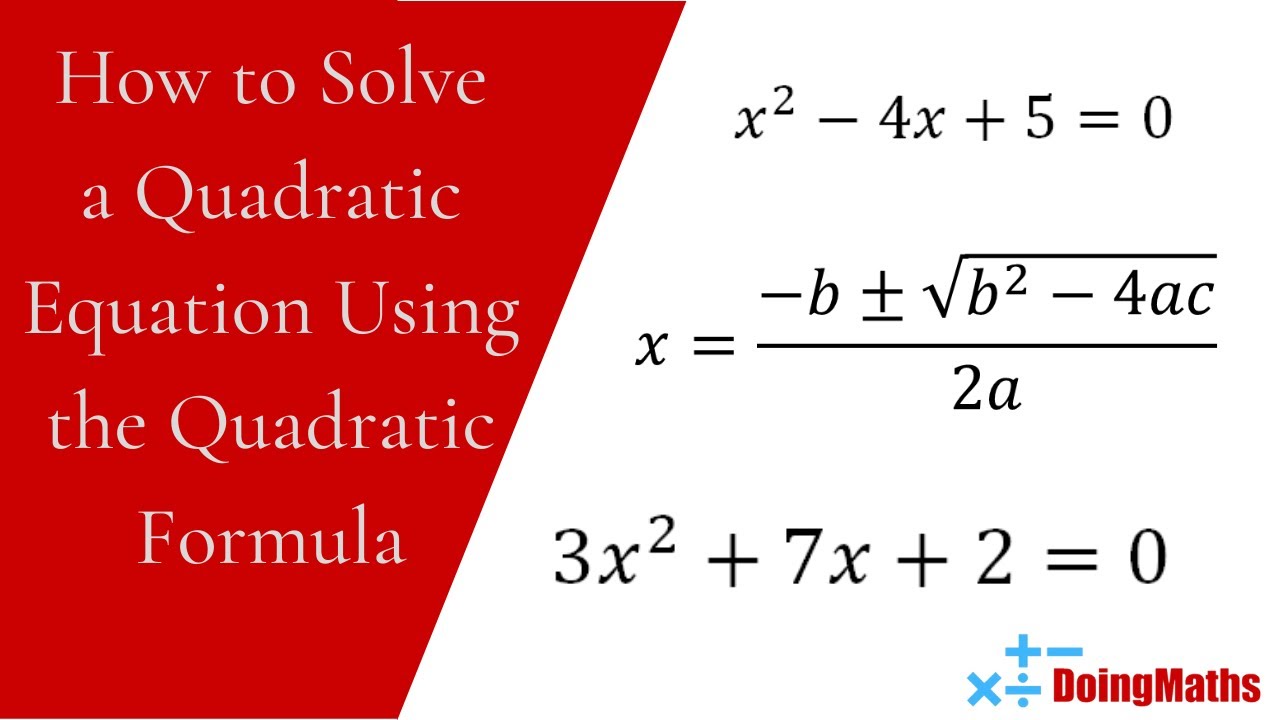
How To Solve A Quadratic Equation Using The Quadratic Formula A Quick Quadratic equation in standard form: ax 2 bx c = 0. quadratic equations can be factored. quadratic formula: x = −b ± √ (b2 − 4ac) 2a. when the discriminant ( b2−4ac) is: positive, there are 2 real solutions. zero, there is one real solution. negative, there are 2 complex solutions. An equation containing a second degree polynomial is called a quadratic equation. for example, equations such as \ (2x^2 3x−1=0\) and \ (x^2−4= 0\) are quadratic equations. they are used in countless ways in the fields of engineering, architecture, finance, biological science, and, of course, mathematics.

Comments are closed.