The Life Cycle Of A Plant
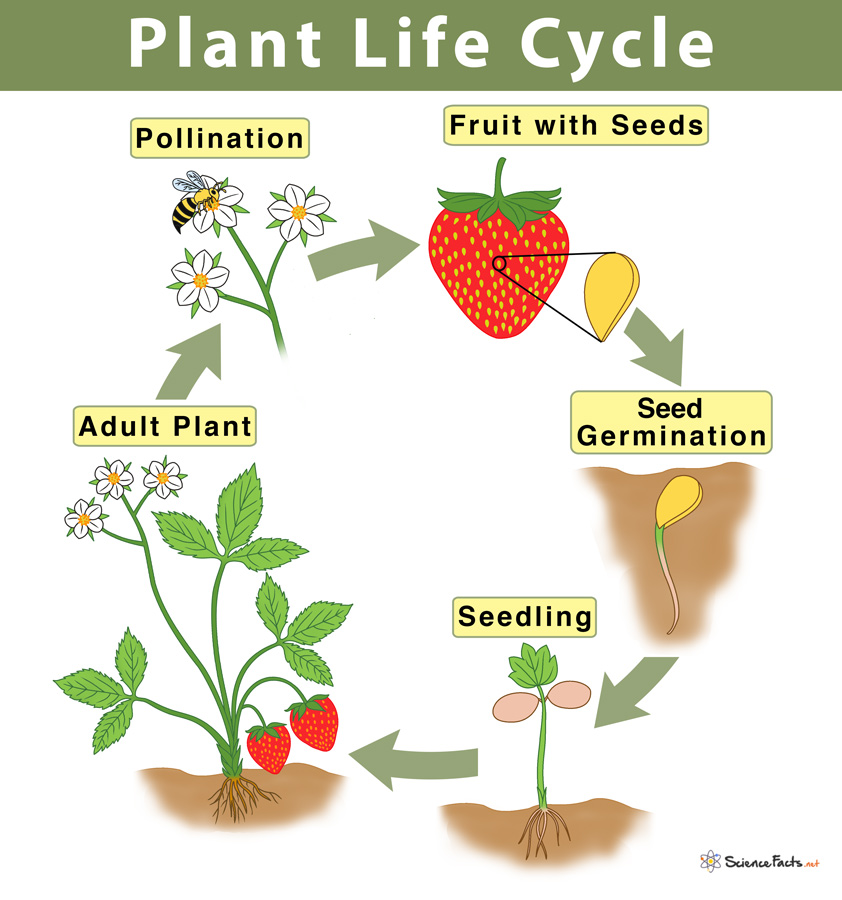
Plant Life Cycle Stages And Diagram Learn the basic life cycle of a plant, from seed to seed, in flowering and non flowering plants. see diagrams, examples, and faqs about plant reproduction and growth. Learn how plants start from seeds, grow, reproduce, and die in a continuous process called the life cycle. explore the five stages of the plant life cycle, the alternation of generations, and the differences between flowering and seedless plants.
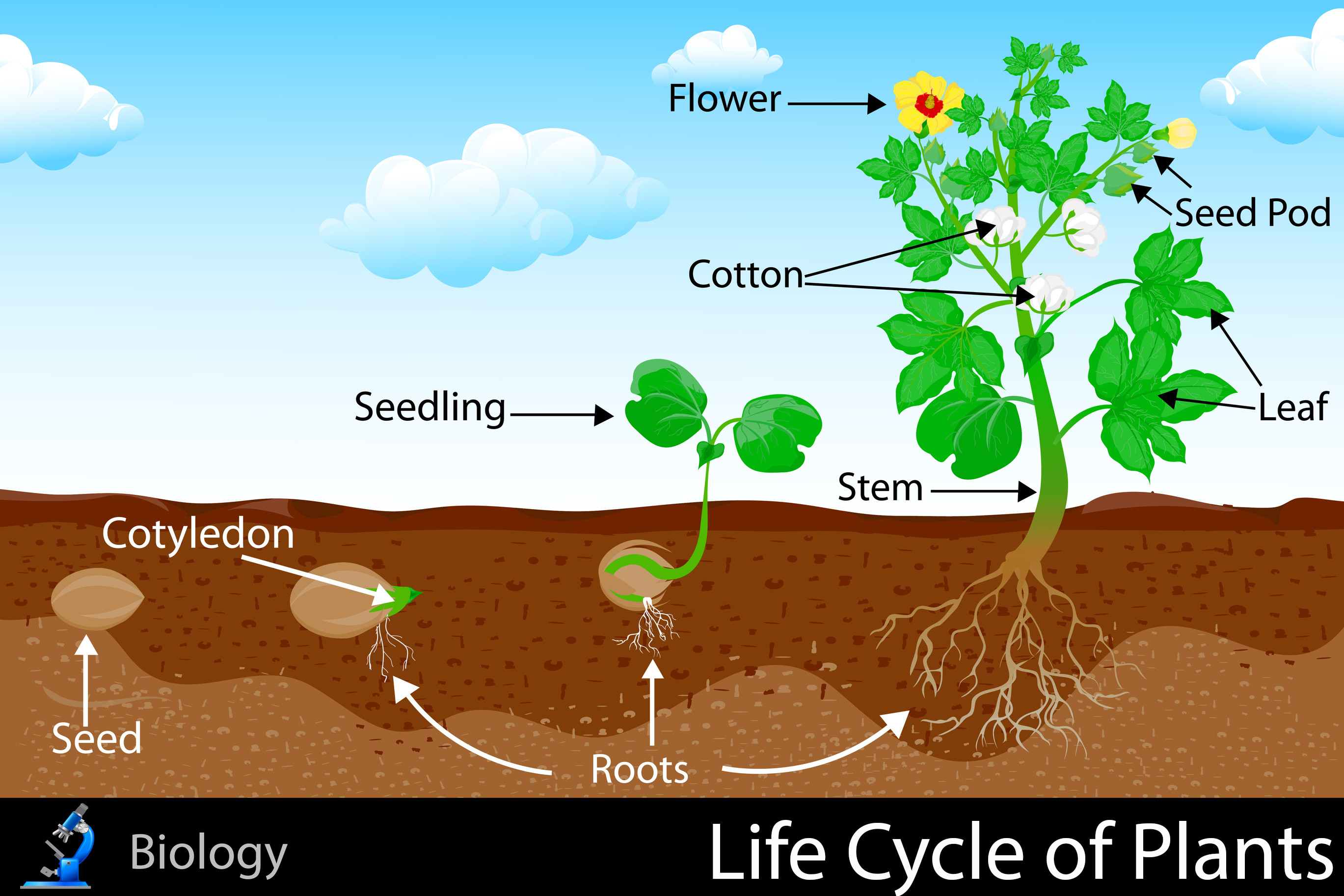
Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspressmagazine Learn how plants alternate between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte generations, and between sexual and asexual reproduction. see diagrams and examples of the general plant life cycle and its variations. Learn how flowering plants reproduce using flowers, pollen, seeds and fruits. discover the different ways of pollination, fertilisation, seed dispersal and germination with examples and illustrations. Plant life cycle: plants, like any other living organisms, have their specific developmental history. specifically, plants exhibit a so called haplodiplontic [1] life cycle wherein the gametes (sex cells) are not a direct product of meiosis. instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. A typical plant’s life cycle is diagrammed in figure below. l ife cycle of plants. th is diagram shows the general life cycle of a plant. early plants reproduced mainly with spores and spent most of their life cycle as haploid gametophytes. spores require little energy and matter to produce, and they grow into new individuals without the need.
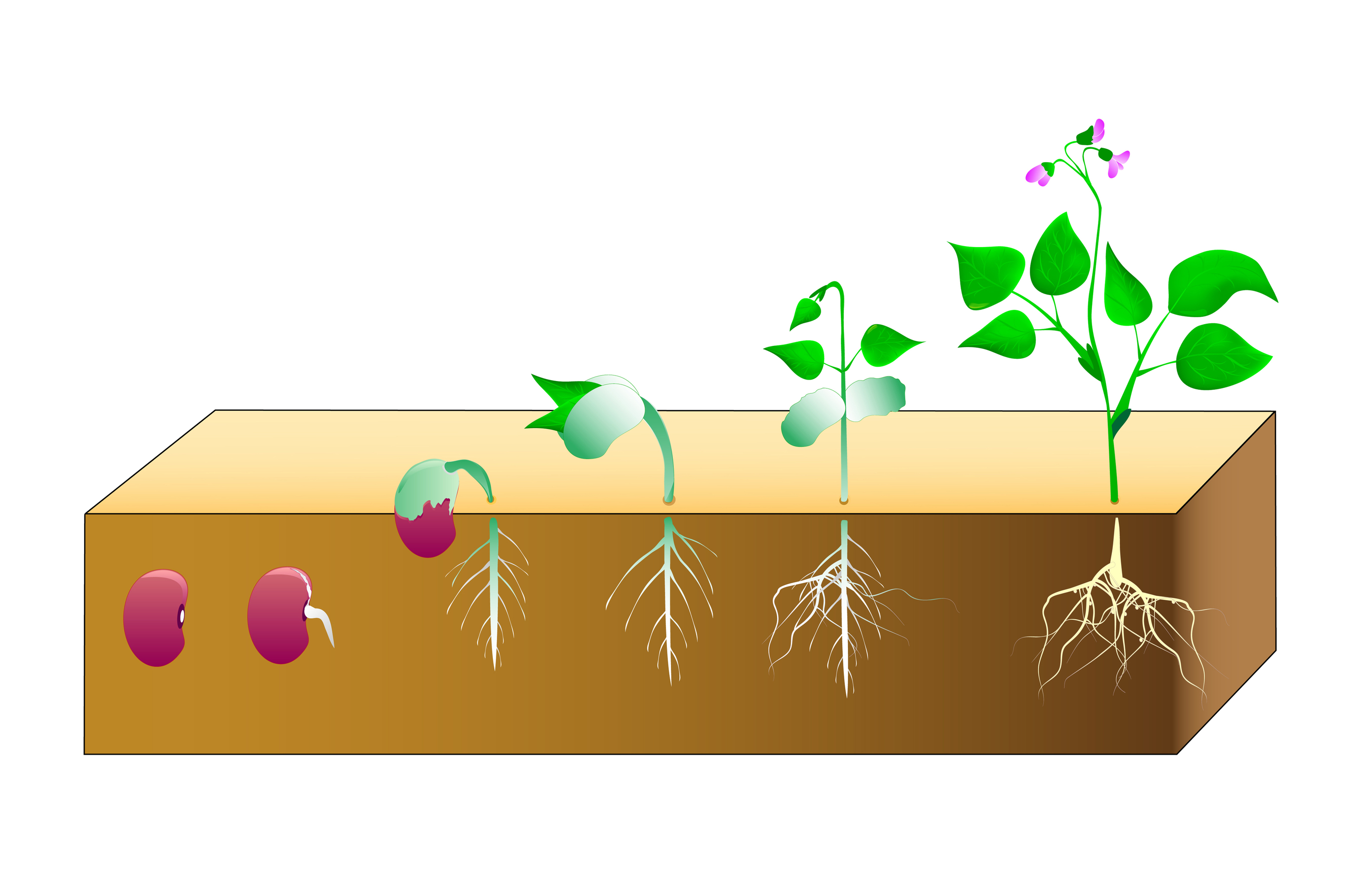
Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspressmagazine Plant life cycle: plants, like any other living organisms, have their specific developmental history. specifically, plants exhibit a so called haplodiplontic [1] life cycle wherein the gametes (sex cells) are not a direct product of meiosis. instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. A typical plant’s life cycle is diagrammed in figure below. l ife cycle of plants. th is diagram shows the general life cycle of a plant. early plants reproduced mainly with spores and spent most of their life cycle as haploid gametophytes. spores require little energy and matter to produce, and they grow into new individuals without the need. Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the gametophyte stage and the sporophyte stage. the haploid produces the male and female gametes by mitosis in distinct multicellular structures. fusion of the male and females gametes forms the diploid zygote, which develops into the . after reaching maturity, the diploid sporophyte produces. Learn about the stages of a plant's life from seed to seed in this guide for primary school students. watch a video, play a game and find out how dandelions spread their seeds.
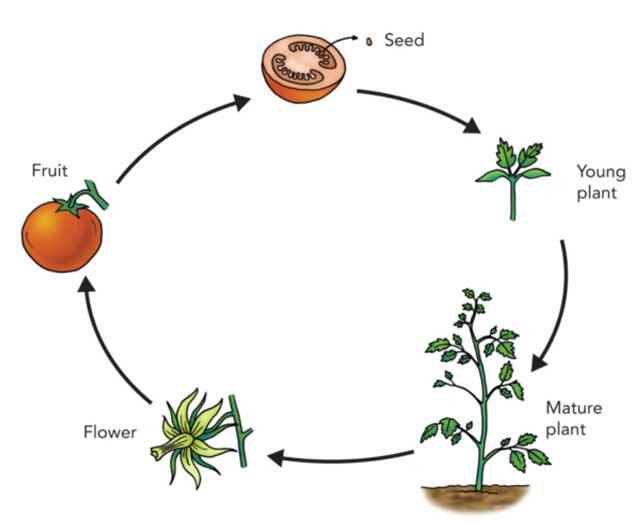
Life Cycle Of Plants Stages Types And Facts Plants have two distinct stages in their lifecycle: the gametophyte stage and the sporophyte stage. the haploid produces the male and female gametes by mitosis in distinct multicellular structures. fusion of the male and females gametes forms the diploid zygote, which develops into the . after reaching maturity, the diploid sporophyte produces. Learn about the stages of a plant's life from seed to seed in this guide for primary school students. watch a video, play a game and find out how dandelions spread their seeds.

Comments are closed.