Theory Of Production And Cost

Theory Of Production Cost Theory Intelligent Economist Learn about the types of costs (fixed, variable, average, marginal, total) and how they affect production and profit. see diagrams, examples and the difference between shut down and break even points. Theory of production, in economics, an effort to explain the principles by which a business firm decides how much of each commodity that it sells (its “outputs” or “products”) it will produce, and how much of each kind of labour, raw material, fixed capital good, etc., that it employs (its “inputs” or “factors of production”) it will use.
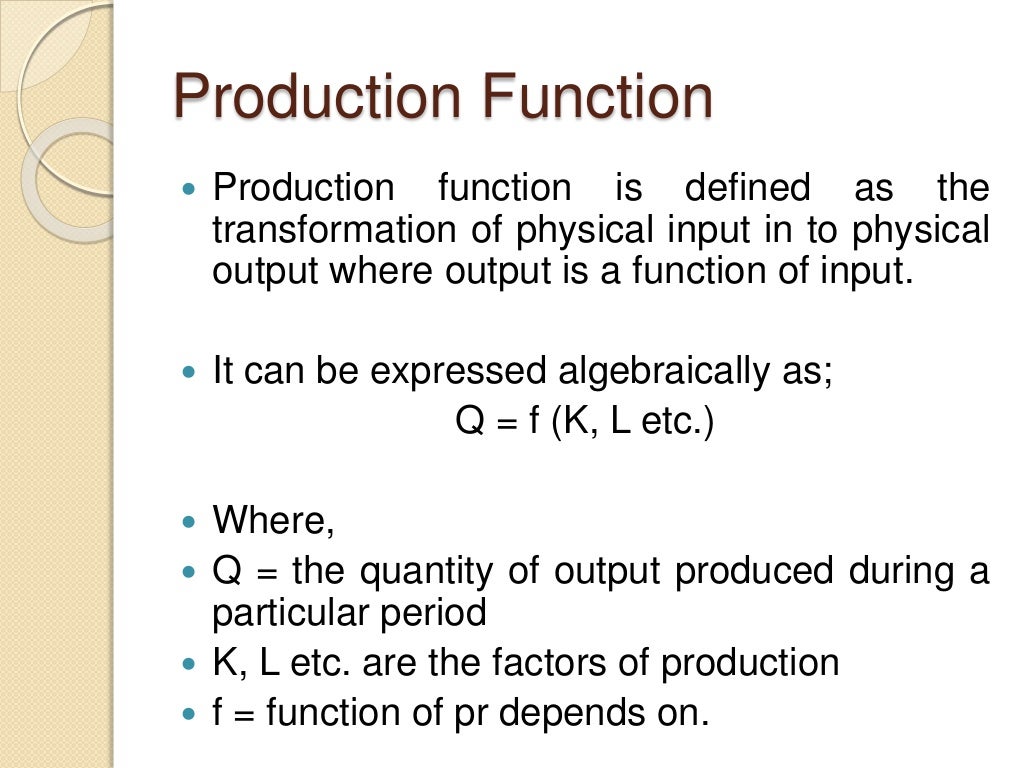
Theory Of Production And Cost Chapter outline. 7.0 introduction. 7.1 explicit and implicit costs. 7.2 theory of production. 7.3 costs of production. 7.4 relationship between production and costs. 7.5 long run costs: the advantage of flexibility. 7.6 key terms. Learn how firms calculate revenue, costs, and profits in the short and long run. explore the concept of production function, fixed and variable inputs, and the difference between accounting and economic profit. Learn how firms transform inputs into outputs using production functions, and how they face different costs depending on the inputs and the time period. explore the concepts of fixed and variable inputs, short and long run, total product, marginal product, and average product with examples and graphs. Start unit test. in economics, a "perfect" market is a theoretical market in which there are many buyers and sellers, and where no one has an advantage over others. in this unit, you'll learn how perfect markets can be used to model relationships between productivity and costs and competition between firms.

Theory Of Production And Cost Learn how firms transform inputs into outputs using production functions, and how they face different costs depending on the inputs and the time period. explore the concepts of fixed and variable inputs, short and long run, total product, marginal product, and average product with examples and graphs. Start unit test. in economics, a "perfect" market is a theoretical market in which there are many buyers and sellers, and where no one has an advantage over others. in this unit, you'll learn how perfect markets can be used to model relationships between productivity and costs and competition between firms. In producing goods and services, firms combine the factors of production—labor, capital, and natural resources—to produce various products. economists assume that firms engage in production in order to earn a profit and that they seek to make this profit as large as possible. that is, economists assume that firms apply the marginal decision. A chapter from a book series on economics and mathematical systems that explains the production function and its applications. the production function relates inputs to output and shows the possibilities of substitution between factors of production.

Comments are closed.