Thermal Mass In Passive Solar Design Networx
What Unit Is Thermal Energy Measured In Printable Templates Protal Rules of thumb. some rules of thumb to consider: if your south facing window area is less than 7% of the floor area of the house, you won’t need any extra thermal mass (but you won’t be getting much passive solar heating when the sun goes down). for every square foot (sf) of south facing glass over that 7%, you need about 5½ sf of 4. In a passive solar design, the thermal mass element is what keeps things from swinging widely from hot to cold, during a typical day and night cycle. an example of how it works: when you start cooking a very large pot of water, the water is cold and the stove adds heat. the pot of water "collects" the heat until it reaches a boil, and then when.

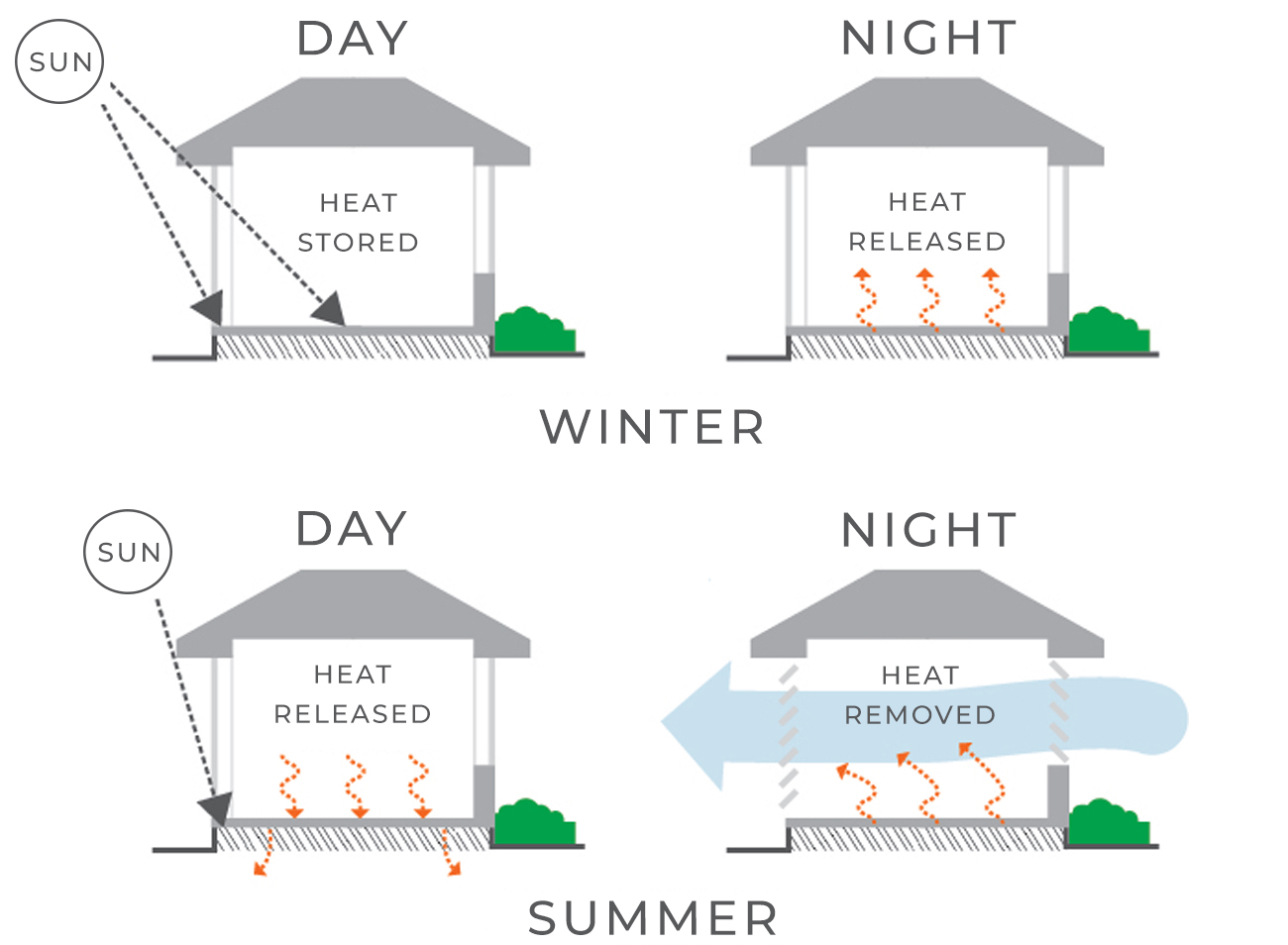
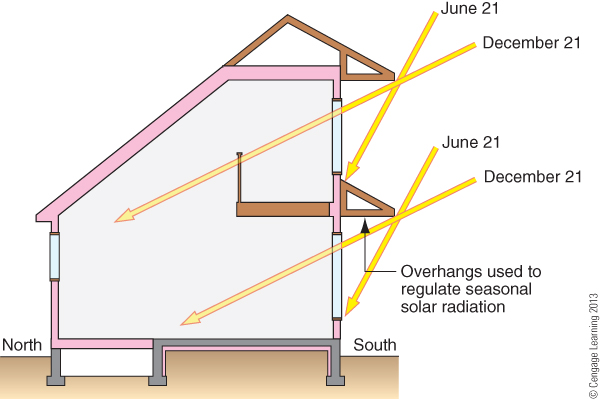
Passive Solar Design Civil Engineering Portal Optimizing sun angles and thermal mass for passive solar design in any climate. jan 07, 2024. the saying “warm in winter, cool in summer” only really works for buildings who are optimized for solar gain and make strategic use of thermal mass and insulation. most buildings are not designed to passive solar principles, even if modern. Thermal mass is another vital and complimentary component of passive solar design. a material that has thermal mass is one that has the capacity to absorb, store and release the sun's heat energy. its density and levels of conductivity help to keep the internal temperature of a building stable. objects that have thermal mass have. Reading time: 1 minute. thermal mass is a property of construction materials to absorb, store, and release heat energy. it is an important element of passive solar house design and can be utilized for passive solar heating, passive solar cooling, or both. some of the examples of thermal mass construction materials are concrete, brick, stone. In a passive solar heating system, the aperture (collector) is a large glass (window) area through which sunlight enters the building. typically, the aperture (s) should face within 30° of true south and should not be shaded by other buildings or trees from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m. each day during the heating season.
Thermal Mass In Passive Solar Design Networx Reading time: 1 minute. thermal mass is a property of construction materials to absorb, store, and release heat energy. it is an important element of passive solar house design and can be utilized for passive solar heating, passive solar cooling, or both. some of the examples of thermal mass construction materials are concrete, brick, stone. In a passive solar heating system, the aperture (collector) is a large glass (window) area through which sunlight enters the building. typically, the aperture (s) should face within 30° of true south and should not be shaded by other buildings or trees from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m. each day during the heating season. The goal of a passive solar design is to convert sunlight into ambient heat in a building or home. this is known as solar gain, which can be used to heat a building’s internal air, water supply, or thermal mass. most commonly, this is achieved by letting sunlight hit the proposed area through windows, skylights, and open concepts. The materials that act as thermal mass in a home are concrete, bricks, sand and stone. interestingly, water has a very high thermal mass, as it can absorb more energy than a masonry product. it is not effective in the fabric of a building however because it releases its energy too quickly, which does not work with the 24 hour cycle.

Using Thermal Mass In Passive Solar Design Cold Climate Housing The goal of a passive solar design is to convert sunlight into ambient heat in a building or home. this is known as solar gain, which can be used to heat a building’s internal air, water supply, or thermal mass. most commonly, this is achieved by letting sunlight hit the proposed area through windows, skylights, and open concepts. The materials that act as thermal mass in a home are concrete, bricks, sand and stone. interestingly, water has a very high thermal mass, as it can absorb more energy than a masonry product. it is not effective in the fabric of a building however because it releases its energy too quickly, which does not work with the 24 hour cycle.

Comments are closed.