This Diagram Explains Why The Expansion Speed Of The Universe Is
Measuring The Expansion Of The Universe Surprising Discrepancies Hint The expansion of the universe is the increase in distance between gravitationally unbound parts of the observable universe with time. [ 1] it is an intrinsic expansion, so it does not mean that the universe expands "into" anything or that space exists "outside" it. to any observer in the universe, it appears that all but the nearest galaxies. Some 13.8 billion years ago, the universe began with a rapid expansion we call the big bang. after this initial expansion, which lasted a fraction of a second, gravity started to slow the universe down. but the cosmos wouldn’t stay this way. nine billion years after the universe began, its expansion started to speed up, […].

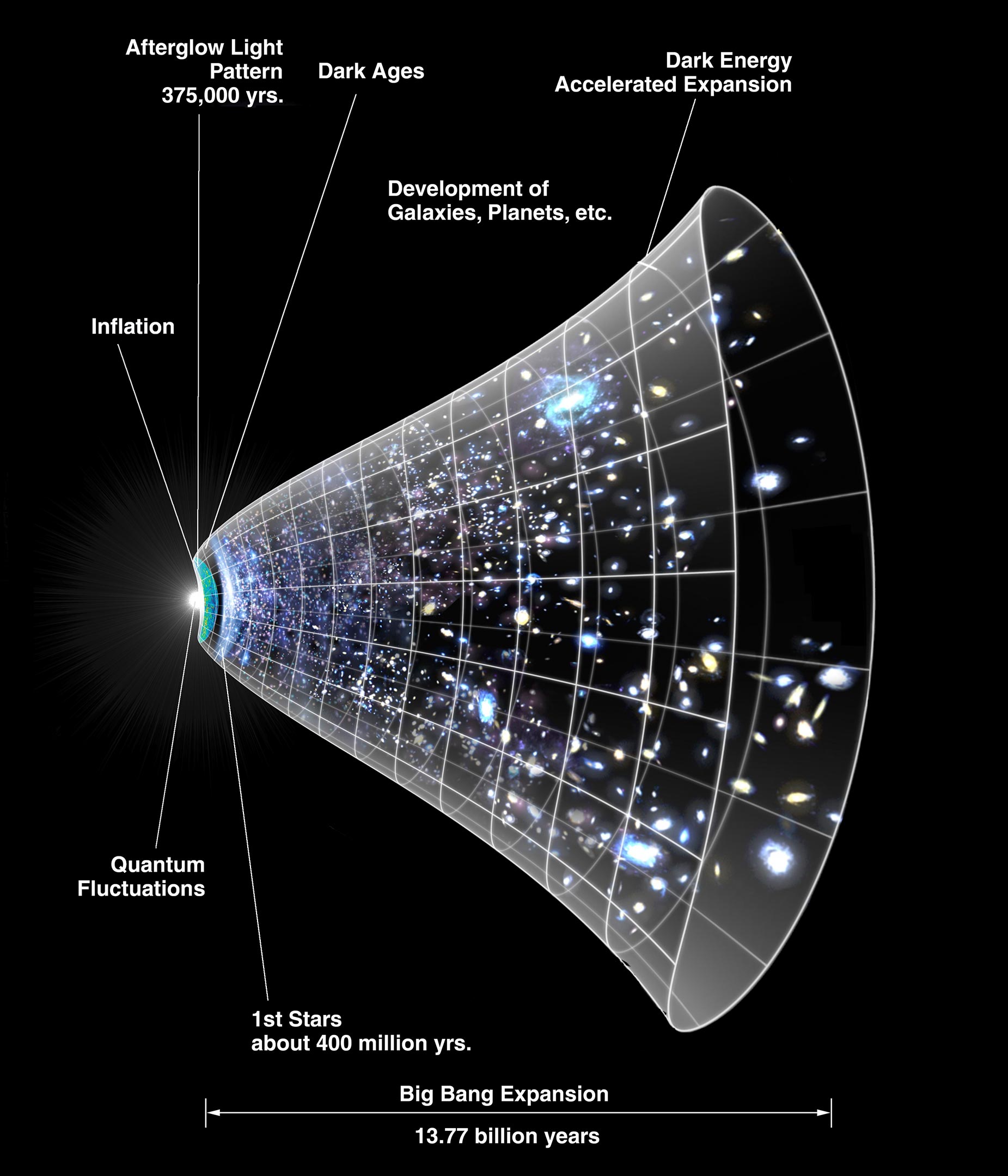
òé òâ òââòé òüöòéïòü µû òüùòüäòéªòéúòâ òâëòéªòüºúûïòüìòü òüö Expanding ççuniverse çü ççuniverse çü D The timeline in this schematic diagram extends from the big bang inflation era 13.8 billion years ago to the present cosmological time. observations show that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, such that the velocity at which a distant galaxy recedes from the observer is continuously increasing with time. Astronomers have known for decades that the universe is expanding. when they use telescopes to observe faraway galaxies, they see that these galaxies are moving away from earth. to astronomers. The energy from the big bang drove the universe's early expansion. since then, gravity and dark energy have engaged in a cosmic tug of war. gravity pulls galaxies closer together; dark energy pushes them apart. whether the universe is expanding or contracting depends on which force dominates, gravity or dark energy. What this leads to is the hypothesis that the universe is expanding. for an animation demonstrating the expanding universe, click here.the figure here by nasa shows a simplified diagram of the expansion of the universe. if you look closely at the diagram, you that on the left was the formation of the universe and the energy is quite high.

宇宙の膨張率 ハッブル定数 は時代と共に変化 物理法則の見直しが迫られる可能性も 記事詳細 Infoseekニュース The energy from the big bang drove the universe's early expansion. since then, gravity and dark energy have engaged in a cosmic tug of war. gravity pulls galaxies closer together; dark energy pushes them apart. whether the universe is expanding or contracting depends on which force dominates, gravity or dark energy. What this leads to is the hypothesis that the universe is expanding. for an animation demonstrating the expanding universe, click here.the figure here by nasa shows a simplified diagram of the expansion of the universe. if you look closely at the diagram, you that on the left was the formation of the universe and the energy is quite high. The expansion of the universe is not constant. recent measurements have shown that the rate of the universe's expansion is increasing. the evidence for this area of physics comes from observations. Before 1998, astronomers thought that, although the universe is expanding, the expansion should be slowing down, or decelerating, because the overall gravitational pull of all matter in the universe would have a dominant, measureable effect. if the expansion is decelerating, then the hubble constant should be decreasing over time.

Comments are closed.