Transition Metal Coloured Complexes
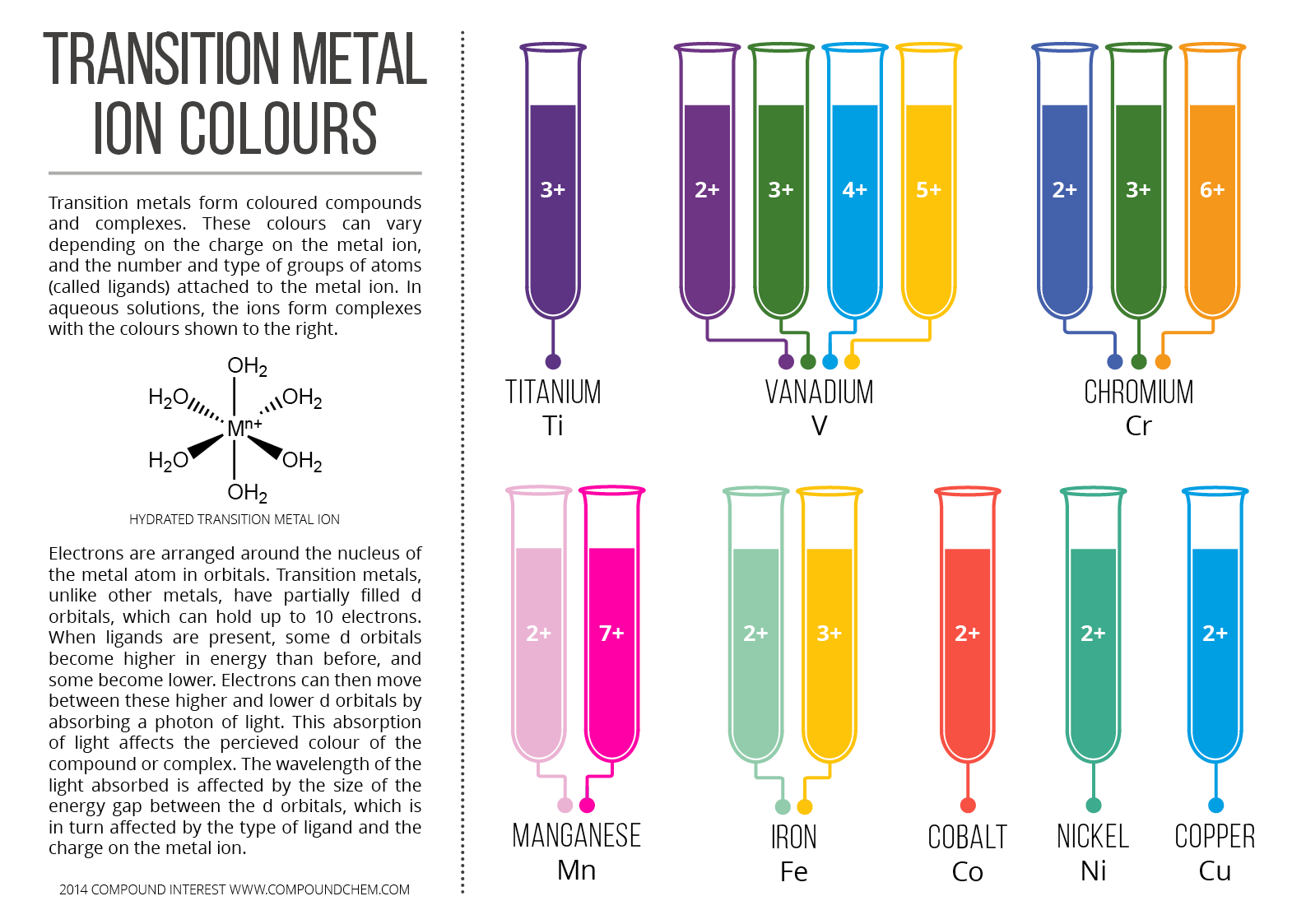
Why Compounds Of Transition Metals Are Coloured Socratic The colors of transition metal complexes often vary in different solvents. the color of the complex depends on the ligand. for example, fe 2 is pale green in water, but forms a dark green precipitate in a concentrated hydroxide base solution, carbonate solution, or ammonia. co 2 forms a pink solution in water, but a blue green precipitate in. Complex ions containing transition metals are usually coloured, whereas the similar ions from non transition metals aren't. that suggests that the partly filled d orbitals must be involved in generating the colour in some way. remember that transition metals are defined as having partly filled d orbitals.
13 Transition Metals Colored Complexes The Mad Scientist The origin of color in complex ions containing transition metals. complex ions containing transition metals are usually colored, whereas the similar ions from non transition metals are not. that suggests that the partly filled d orbitals must be involved in generating the color in some way. remember that transition metals are defined as having. The hemoglobin in your blood, the chlorophyll in green plants, vitamin b 12, and the catalyst used in the manufacture of polyethylene all contain coordination compounds. ions of the metals, especially the transition metals, are likely to form complexes. many of these compounds are highly colored (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)). Example 24.7.1 24.7. 1: colors of complexes. the octahedral complex [ti (h 2 o) 6] 3 has a single d electron. to excite this electron from the ground state t2g orbital to the eg orbital, this complex absorbs light from 450 to 600 nm. the maximum absorbance corresponds to Δ o and occurs at 499 nm. In this video, we'll explain why complex ions of transition metals form different colours through the splitting of d orbitals. we'll also use the colour whee.

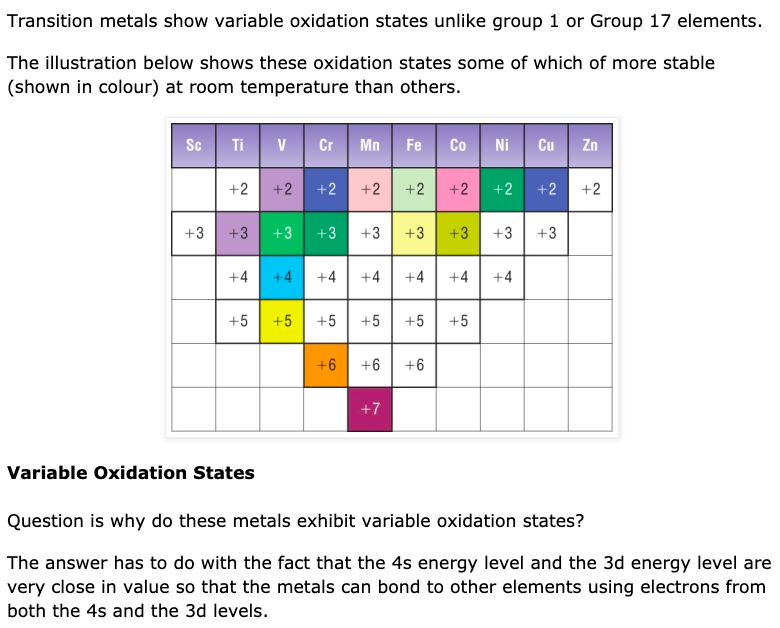
New Aqa A2 Organic Chemistry Transition Metals Formation Of Coloured Example 24.7.1 24.7. 1: colors of complexes. the octahedral complex [ti (h 2 o) 6] 3 has a single d electron. to excite this electron from the ground state t2g orbital to the eg orbital, this complex absorbs light from 450 to 600 nm. the maximum absorbance corresponds to Δ o and occurs at 499 nm. In this video, we'll explain why complex ions of transition metals form different colours through the splitting of d orbitals. we'll also use the colour whee. Topic 15: transition metals. topic 15a: principles of transition metal chemistry. 8. understand that the colour of aqueous ions, and other complex ions, results from the splitting of the energy levels of the d orbitals by ligands; scotland. advanced higher. sqa chemistry. inorganic and physical chemistry. transition metals. explanation of. Transition metals and colored complexes . a transition metal is one that forms stable ions that have incompletely filled d orbitals. by this definition, technically not all of the d block elements of the periodic table are transition metals. for example, zinc and scandium aren't transition metals by this definition because zn 2 has a full d.

Transition Metals On The Periodic Table An Overview Topic 15: transition metals. topic 15a: principles of transition metal chemistry. 8. understand that the colour of aqueous ions, and other complex ions, results from the splitting of the energy levels of the d orbitals by ligands; scotland. advanced higher. sqa chemistry. inorganic and physical chemistry. transition metals. explanation of. Transition metals and colored complexes . a transition metal is one that forms stable ions that have incompletely filled d orbitals. by this definition, technically not all of the d block elements of the periodic table are transition metals. for example, zinc and scandium aren't transition metals by this definition because zn 2 has a full d.

Comments are closed.