Transition Metals Revision For Gcse Chemistry

Transition Metals Revision For Gcse Chemistry Youtube Learn about and revise the transition metals with this bbc bitesize gcse chemistry (ocr 21c) study guide. The transition metals are much less reactive than the group 1 metals. the alkali metals react with water, oxygen and halogens while the transition metals either react very slowly or do not react at all. a classic example of this is the reaction with oxygen. a group 1 metal will tarnish in the presence of oxygen as a metal oxide is formed.
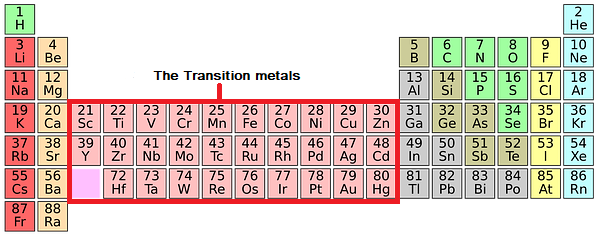
The Transition Metals Chemistry Revision Learn about and revise transition metals, alloys and corrosion with this bbc bitesize gcse chemistry (edexcel) study guide. The transition metals are placed in the centre of the periodic table, between groups 2 and 3. they are generally hard and dense, and less reactive than the alkali metals. iron, copper, silver and gold are important transition metals. this video explains more about transition metals. gcse chemistry revision science section covering transition. Gcse; aqa; transition metals aqa physical properties of transition elements. the transition elements are metals. they have high melting points and densities, and are strong and hard. they form. Have catalytic activity as a pure metal, and as a compound. compared to aluminium and the group 1 and 2 metals, transition metals typically have higher melting points, and higher densities. iron (fe) as an example. iron follows these general rules for transition metals, and also has a very high melting point (1538°c) and a high density (7.87 g.
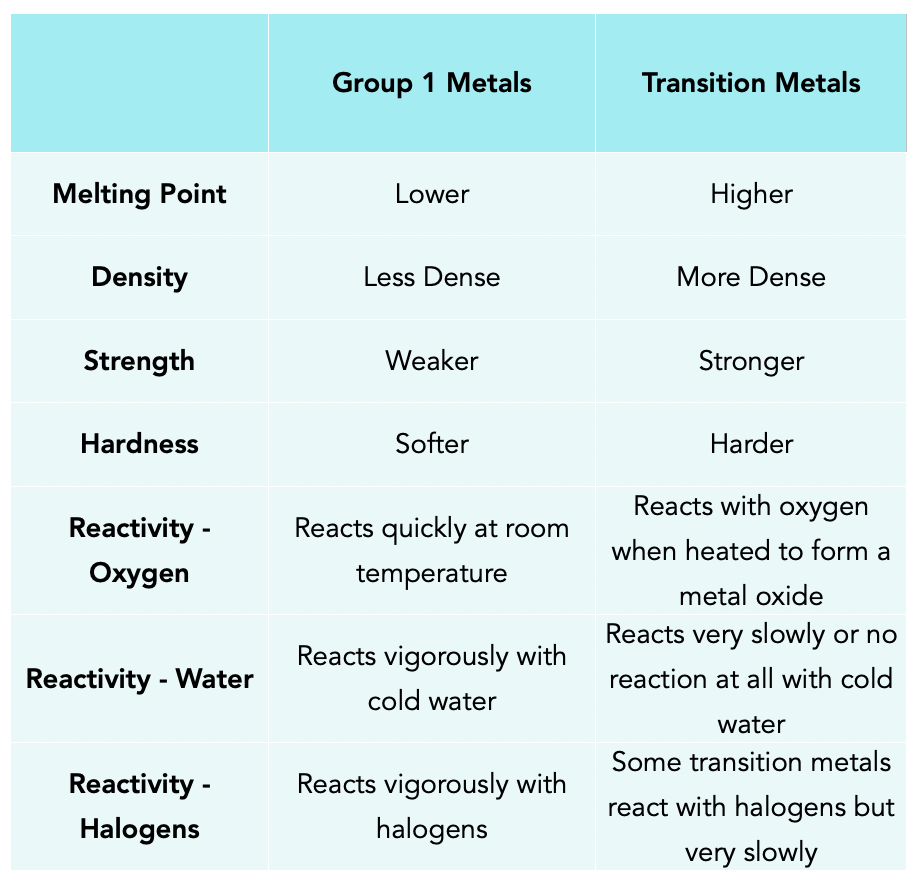
The Transition Metals Gcse Chemistry Study Mind Gcse; aqa; transition metals aqa physical properties of transition elements. the transition elements are metals. they have high melting points and densities, and are strong and hard. they form. Have catalytic activity as a pure metal, and as a compound. compared to aluminium and the group 1 and 2 metals, transition metals typically have higher melting points, and higher densities. iron (fe) as an example. iron follows these general rules for transition metals, and also has a very high melting point (1538°c) and a high density (7.87 g. Transition metals are also frequency used as catalysts, such as iron in the haber process and nickel used in the manufacture of margarine. the video below explains more about transition metals. the transition metals, this gcse chemistry (9 1) revision science section covers: the properties of transition metals. Have catalytic activity as a pure metal, and as a compound. compared to aluminium and the group 1 and 2 metals, transition metals typically have higher melting points, and higher densities. iron (fe) as an example. iron follows these general rules for transition metals, and also has a very high melting point (1538°c) and a high density (7.87 g.
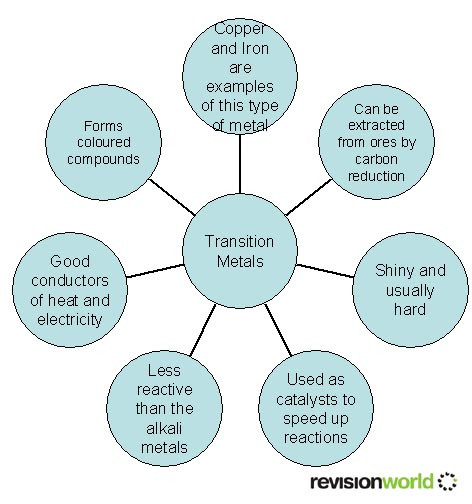
Transition Metals Chemistry Gcse Revision Transition metals are also frequency used as catalysts, such as iron in the haber process and nickel used in the manufacture of margarine. the video below explains more about transition metals. the transition metals, this gcse chemistry (9 1) revision science section covers: the properties of transition metals. Have catalytic activity as a pure metal, and as a compound. compared to aluminium and the group 1 and 2 metals, transition metals typically have higher melting points, and higher densities. iron (fe) as an example. iron follows these general rules for transition metals, and also has a very high melting point (1538°c) and a high density (7.87 g.

Comments are closed.