Transition Metals The Transition Metals A Level Chemistry Study

Transition Metals The Transition Metals A Level Chemistry Study Mind Defining transition metals. transition metals are found in the “d block” of the periodic table. the transition metals. the definition of transition metals is they have an incomplete d sub level in their atoms or ions. this means they can form one or more stable ions with a partially filled d sub shells. the transition metals. Transition metals. transition metals are found in the centre of the periodic table and are known as d block elements, which includes groups 3 to 12 of the periodic table. they exhibit properties unique to this set of elements: they are good conductors of heat and electricity, possess high densities and melting points, and are capable of forming.
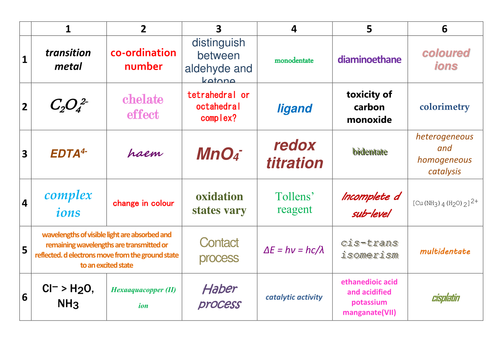
New Aqa A Level Chemistry Transition Metals 3 2 5 Learning Grid The reactions of eight major metal aqua ions have to be known for this a level specification: chromium(iii), manganese(ii), iron(ii), iron(iii), cobalt(ii), nickel(ii), copper(ii) and zinc(ii). these metal aqua ions react with sodium hydroxide and ammonia to form coloured precipitates. that can be used to identify the transition metal present. State the full electronic configuration of the manganese (iii) ion. answer. step 1: write out the electron configuration of the atom first: mn atomic number = 25. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 5. 2 2 6 2 6 2 5 = 25 electrons. step 2: subtract the appropriate number of electrons starting from the 4s subshell. mn (iii) = 22 electrons. Transition element ions can form complexes which consist of a central metal ion and ligands. copper (ii) and cobalt (ii) ions will be used as examples of the central metal ions, in the complex formation with water (h 2 o), ammonia (nh 3 ), hydroxide (oh ), and chloride (cl ) ligands. a copper (ii) ion has an electronic configuration of 1s 2. Transition element complexes form when electron rich species surround the positive metal ions and form co ordinate bonds with them. the electron rich species forming co ordinate bonds with the positive ions are called ligands. form coloured compounds. d orbitals in the metal ion can be split into high and low energies.

Comments are closed.