Trauma Nc Complex Mental Health And Intellectual Developmental
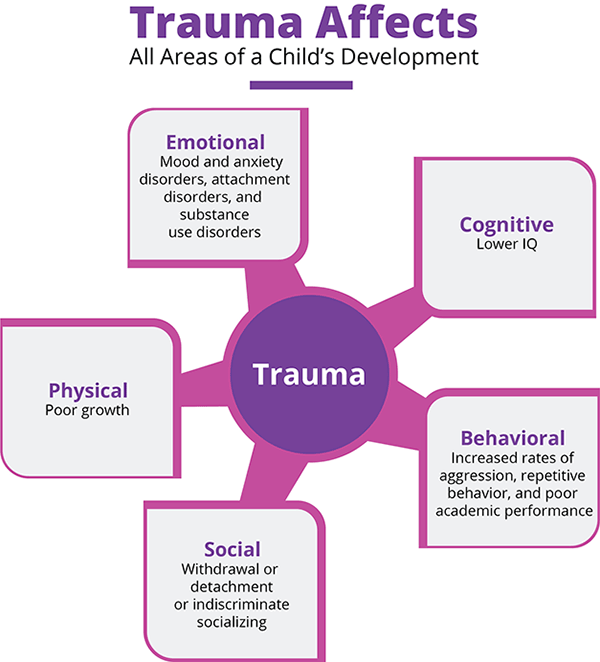
Trauma Nc Complex Mental Health And Intellectual Developmental Trauma occurs when an individual either experiences or witnesses a real or perceived threat to their emotional and or physical well being and the intensity of this experience negatively impacts the individual. trauma does not necessarily have to be a particular event. it can also result from chronic neglect of basic needs, whether emotional or. Behavioral health springboard unc school of social work tate turner kuralt building 325 pittsboro street cb# 3550 chapel hill, nc 27599 3550 contact us | phone: 919 843 6083 | fax: 919 962 6562.
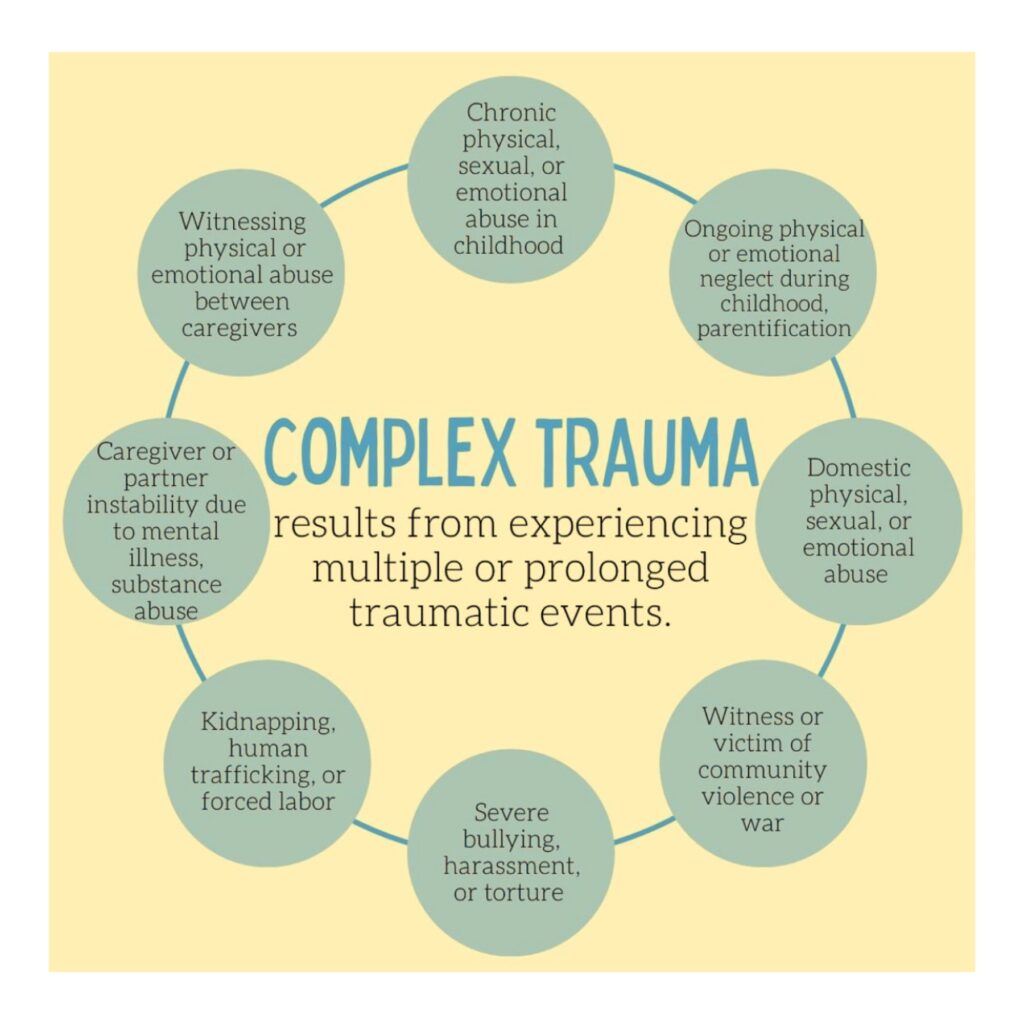
Complex Trauma Behavioral health springboard unc school of social work tate turner kuralt building 325 pittsboro street cb# 3550 chapel hill, nc 27599 3550 contact us | phone: 919 843 6083 | fax: 919 962 6562. Provides information on the impact that trauma may have on youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities (idd).this fact sheet offers providers information on idd and trauma, communication and trauma related behavior, idd and systems of care, screening and assessment for youth with idd, diagnostic criteria, treatment, and resilience and recovery for youth with idd who have experienced. Translating trauma informed care principles into practice (with a focus on dual diagnosis and complex behavior) (link is external) — webinar (3:42:48) that covers trauma informed principles, vicarious trauma, and self care (pennsylvania department of human services, 2022) children with intellectual and developmental disabilities can. The impact of trauma on youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a fact sheet for providers approximately one in six youth between the ages of 3 and 17 in the united states have an intellectual or developmental disability, as signified by major delays or difficulty in functioning in one or more key developmental areas.

Assessment Of Complex Trauma By Mental Health Professionals The Translating trauma informed care principles into practice (with a focus on dual diagnosis and complex behavior) (link is external) — webinar (3:42:48) that covers trauma informed principles, vicarious trauma, and self care (pennsylvania department of human services, 2022) children with intellectual and developmental disabilities can. The impact of trauma on youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a fact sheet for providers approximately one in six youth between the ages of 3 and 17 in the united states have an intellectual or developmental disability, as signified by major delays or difficulty in functioning in one or more key developmental areas. Developmental trauma (dt) refers to the complex and pervasive exposure to life threatening events that occurs through sensitive periods of infant and child development, disrupts interpersonal attachments, compromises an individual's safety and security operations, alters foundational capacities for cognitive, behavioral, and emotional control. 1) believing and validating their child’s experience, 2) tolerating the child’s affect, and. 3) managing their own emotional response. the connection between a parent and child is broken when a parent denies the child’s experiences. in such cases, the child is forced to act “as if” the trauma did not occur.

How Childhood Trauma Affects Mental Health Recovery Ranger Developmental trauma (dt) refers to the complex and pervasive exposure to life threatening events that occurs through sensitive periods of infant and child development, disrupts interpersonal attachments, compromises an individual's safety and security operations, alters foundational capacities for cognitive, behavioral, and emotional control. 1) believing and validating their child’s experience, 2) tolerating the child’s affect, and. 3) managing their own emotional response. the connection between a parent and child is broken when a parent denies the child’s experiences. in such cases, the child is forced to act “as if” the trauma did not occur.
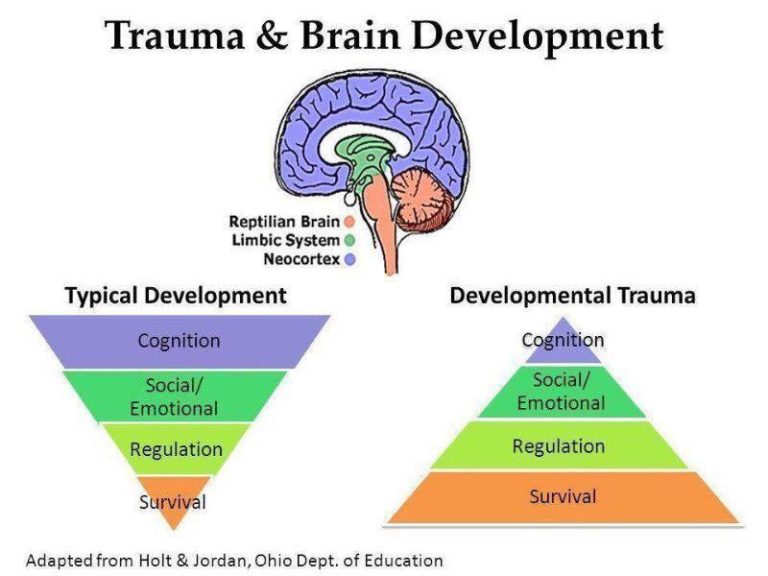
Trauma And The Brain Diagram

Comments are closed.