Triangle Angle Sum Theorem вђ Mrs Mayer S Math Class
Triangle Angle Sum Theorem вђ Mrs Mayer S Math Cl Mrs. mayer; philosophy of learning triangle angle sum theorem. notes. triangle angle sum theorem: the three interior angles of any triangle add up to 180 degrees. G.srt.7 – explain and use the relationship between the sine and cosine of complementary angles. g.srt.8 – use trigonometric ratios and the pythagorean theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems. apply trigonometry to general triangles; sections. review. pythagorean theorem & converse (review) triangle angle sum theorem (review).

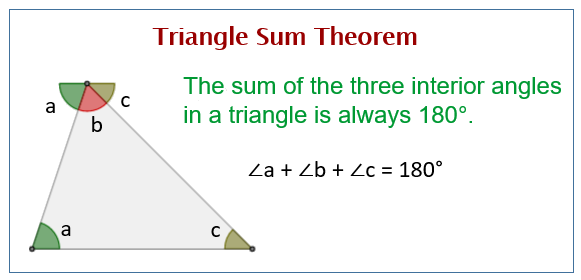
Triangle Sum Theorem вђ Definition Proof Examples Example 1: one of the acute angles of a right angled triangle is 45°. find the other angle using the triangle sum theorem. identify the type of triangle thus formed. solution: given, ∠1 = 90° (right triangle) and ∠2 = 45°. we know that the sum of the angles of a triangle adds up to 180°. Trigonometric ratios: ratios that relate the lengths of the sides of right triangles to their interior angles. sine: the sine ( sin) of an angle is equal to the length of the opposite (opp) side divided by the length of the hypotenuse (hypot). sin θ = opp hypot. cosine: the cosine ( cos) of an angle is equal to the length of the adjacent. A, b and c are the three vertices and ∠abc, ∠bca and ∠cab are three interior angles of ∆abc. theorem 1: angle sum property of triangle states that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180°. proof: consider a ∆abc, as shown in the figure below. to prove the above property of triangles, draw a line pq parallel to the side bc of. The angle sum property of a triangle theorem states that the sum of all three internal angles of a triangle is 180 ∘. it is also known as the angle sum theorem or triangle sum theorem. according to the angle sum theorem, in the above abc, m ∠ a m ∠ b m ∠ c = 180 ∘. example: in pqr, ∠ p = 60 ∘, ∠ q = 70 ∘.
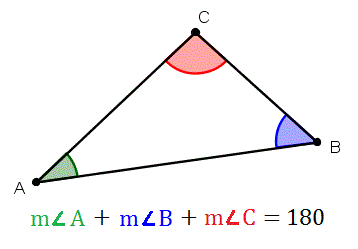
Triangle Angle Sum Theorem вђ Mrs Mayer S Math Cl A, b and c are the three vertices and ∠abc, ∠bca and ∠cab are three interior angles of ∆abc. theorem 1: angle sum property of triangle states that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180°. proof: consider a ∆abc, as shown in the figure below. to prove the above property of triangles, draw a line pq parallel to the side bc of. The angle sum property of a triangle theorem states that the sum of all three internal angles of a triangle is 180 ∘. it is also known as the angle sum theorem or triangle sum theorem. according to the angle sum theorem, in the above abc, m ∠ a m ∠ b m ∠ c = 180 ∘. example: in pqr, ∠ p = 60 ∘, ∠ q = 70 ∘. Let's have a look at the proof of the angle sum property of the triangle. the steps for proving the angle sum property of a triangle are listed below: step 1: draw a line pq that passes through the vertex a and is parallel to side bc of the triangle abc. step 2: we know that the sum of the angles on a straight line is equal to 180°. Hypothesis: from the triangle sum theorem, the sum of all three angles equals 180°. again, from the definition of an equilateral triangle, all angles are of equal measure. adding up all the angles, we get, ⇒ x x x = 180°. ⇒ 3x = 180°. ⇒ x = 60°. conclusion: each angle in an equilateral triangle measures 60°. what is the triangle.

Comments are closed.