Triangle Sum Theorem Math Geometry Showme
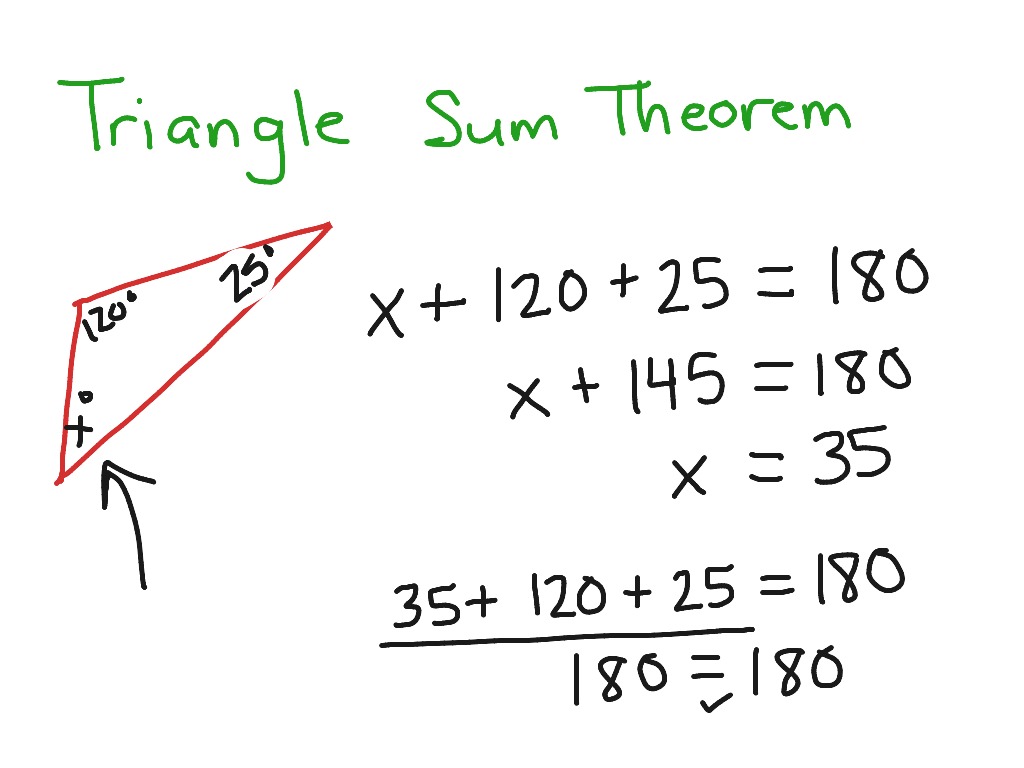
Triangle Sum Theorem Math Geometry Showme Triangle sum theorem by leeann hammett august 28, 2014 math; geometry; g.co.9; triangle sum theorem; you must be logged into showme. Example 1: one of the acute angles of a right angled triangle is 45°. find the other angle using the triangle sum theorem. identify the type of triangle thus formed. solution: given, ∠1 = 90° (right triangle) and ∠2 = 45°. we know that the sum of the angles of a triangle adds up to 180°.
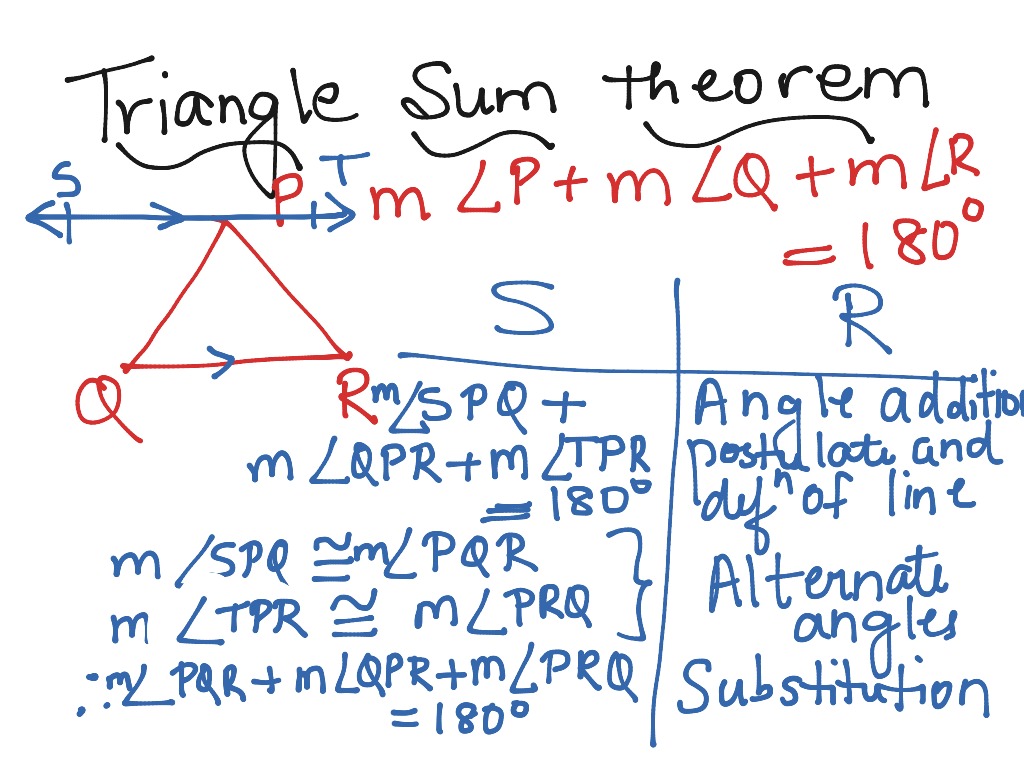
Triangle Sum Theorem By Ms Coral Math Showme Triangle sum theorem by mary gruver september 26, 2012. math; geometry; like 0. you should do so only if this showme contains inappropriate content. Hypothesis: from the triangle sum theorem, the sum of all three angles equals 180°. again, from the definition of an equilateral triangle, all angles are of equal measure. adding up all the angles, we get, ⇒ x x x = 180°. ⇒ 3x = 180°. ⇒ x = 60°. conclusion: each angle in an equilateral triangle measures 60°. what is the triangle. The sum of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°. the triangle sum theorem is also called the triangle angle sum theorem or angle sum theorem. example: find the value of x in the following triangle. solution: x 24° 32° = 180° (sum of angles is 180°) x 56° = 180°. x = 180° – 56° = 124°. A right angled triangle has one angle equal to 43°. what is the value of the other angles? solution: according to the triangle sum theorem, the interior angles of a triangle add up to 180° let us assume that the triangle is abc, where ∠abc = 90° (as the triangle is right angled) and ∠bca = 43° therefore, ∠abc ∠bca ∠cab = 180°.
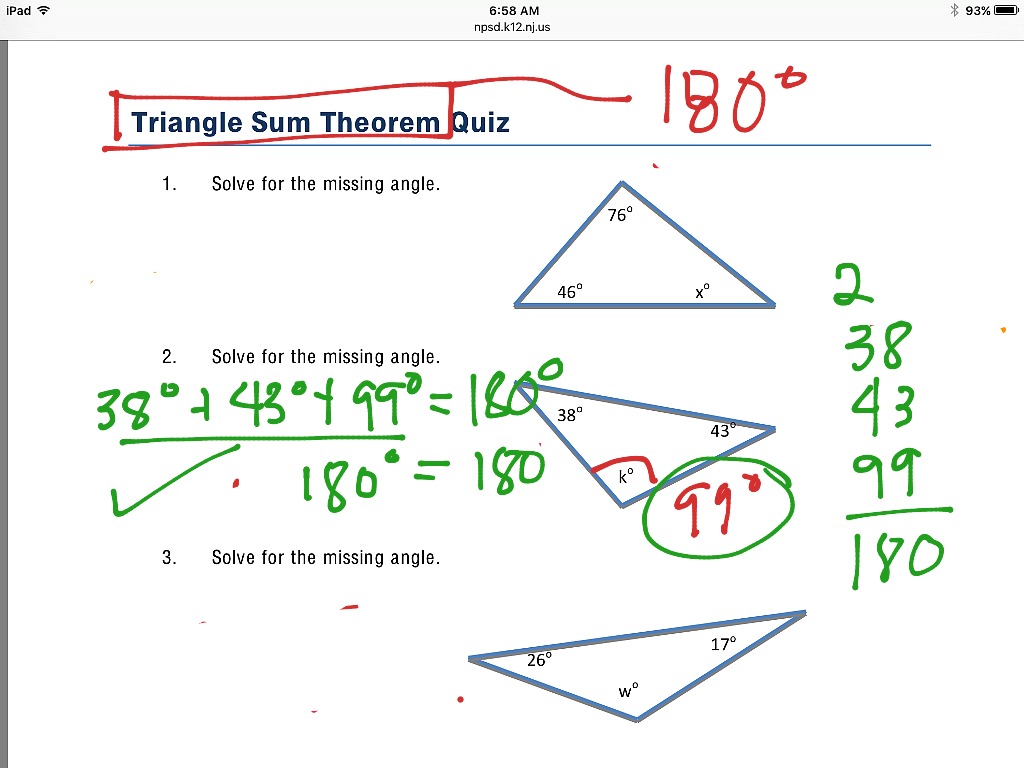
Triangle Sum Theorem Intro Math Geometry Angles 7th Grade Math The sum of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°. the triangle sum theorem is also called the triangle angle sum theorem or angle sum theorem. example: find the value of x in the following triangle. solution: x 24° 32° = 180° (sum of angles is 180°) x 56° = 180°. x = 180° – 56° = 124°. A right angled triangle has one angle equal to 43°. what is the value of the other angles? solution: according to the triangle sum theorem, the interior angles of a triangle add up to 180° let us assume that the triangle is abc, where ∠abc = 90° (as the triangle is right angled) and ∠bca = 43° therefore, ∠abc ∠bca ∠cab = 180°. There are two theorems that we can prove as a result of the triangle sum theorem and our knowledge of triangles. theorem #1: each angle in an equiangular triangle measures @$\begin {align*}60^\circ\end {align*}@$. theorem #2: the acute angles in a right triangle are always complementary. Triangle sum theorem. 1. start with Δabc Δ a b c. extend bc¯ ¯¯¯¯ b c ¯ to point d d. line bd b d will be a transversal. 2. draw line ec e c parallel to segment ab a b. draw transversal ac←→ a c ↔. 3. corresponding angles are congruent.
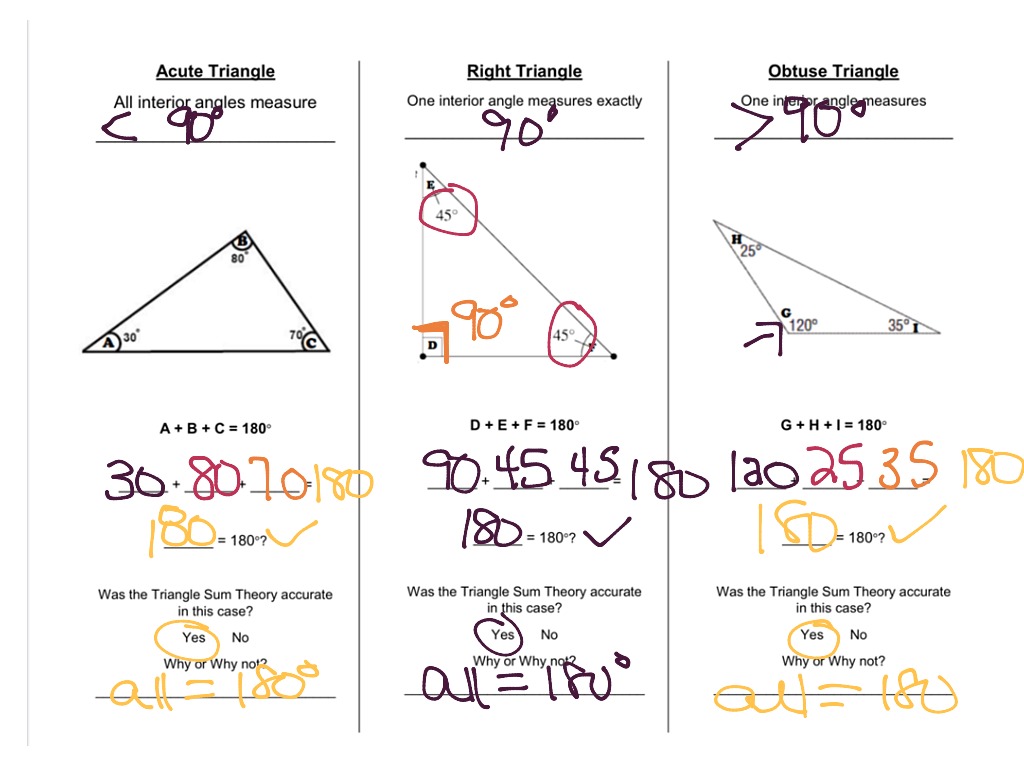
Triangle Sum Theorem Notes Math Showme There are two theorems that we can prove as a result of the triangle sum theorem and our knowledge of triangles. theorem #1: each angle in an equiangular triangle measures @$\begin {align*}60^\circ\end {align*}@$. theorem #2: the acute angles in a right triangle are always complementary. Triangle sum theorem. 1. start with Δabc Δ a b c. extend bc¯ ¯¯¯¯ b c ¯ to point d d. line bd b d will be a transversal. 2. draw line ec e c parallel to segment ab a b. draw transversal ac←→ a c ↔. 3. corresponding angles are congruent.
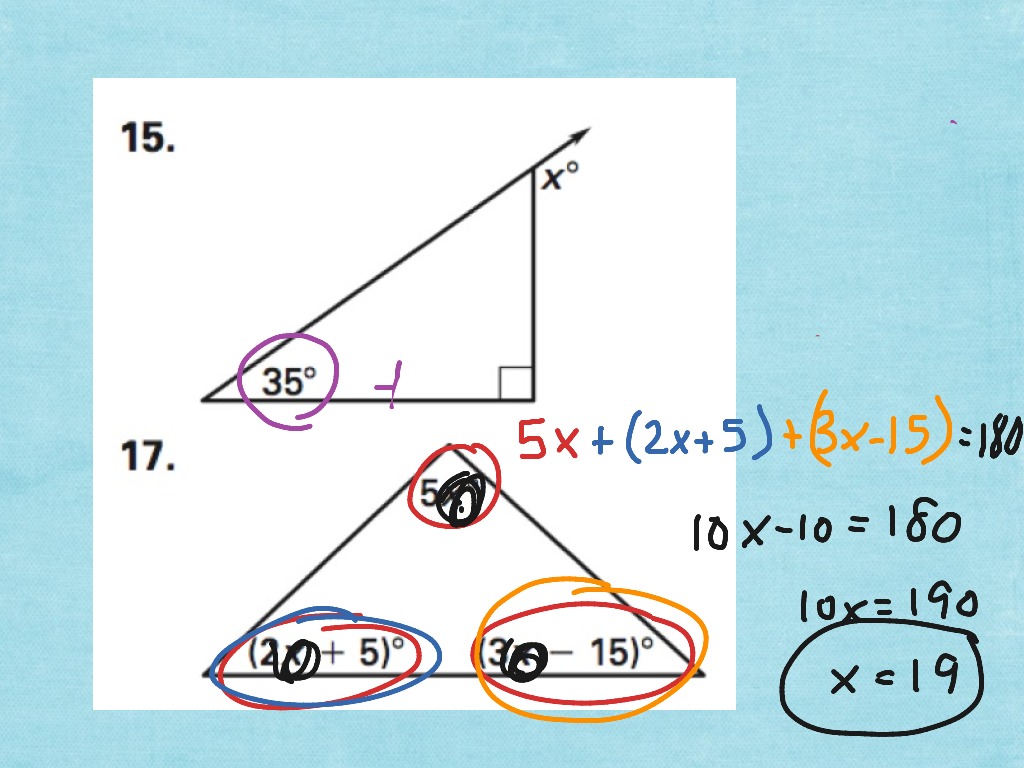
Topic Triangle Sum Theorem Showme Online Learning

Comments are closed.