Trigonometric Formulas вђ Mathematics
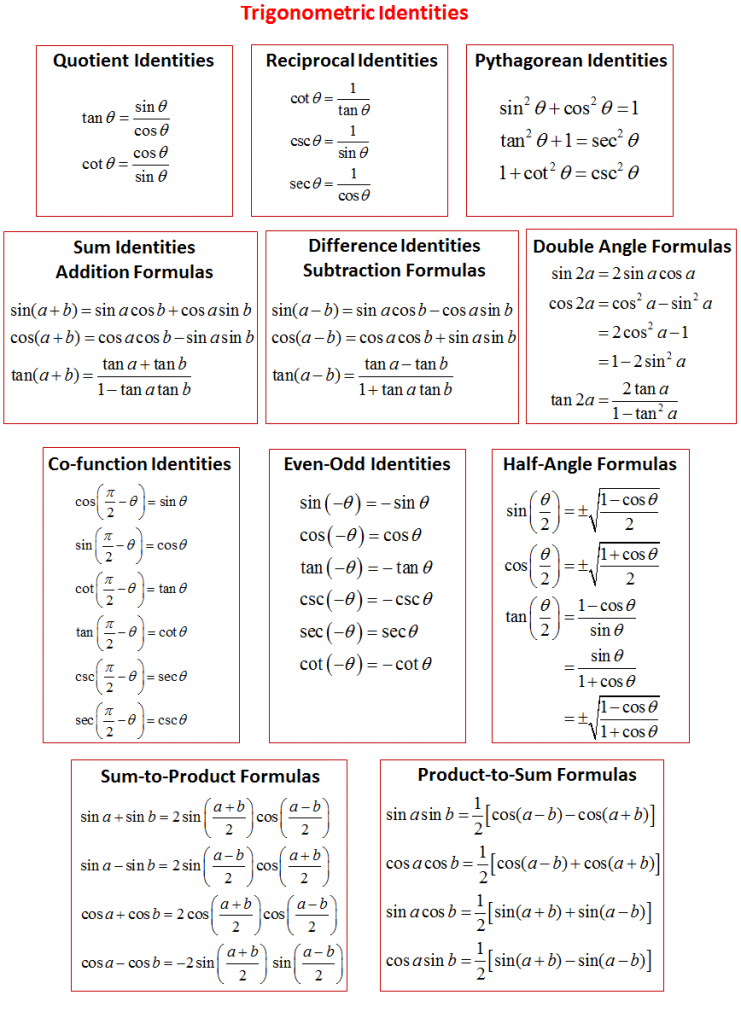
Trigonometric Functions With Their Formulas The six trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, secant, cosecant, tangent and cotangent. by using a right angled triangle as a reference, the trigonometric functions and identities are derived: sin θ = opposite side hypotenuse. cos θ = adjacent side hypotenuse. tan θ = opposite side adjacent side. Trigonometry formulas are sets of different formulas involving trigonometric identities, used to solve problems based on the sides and angles of a right angled triangle. additionally, there are many trigonometric identities and formulas that can be used to simplify expressions, solve equations, and evaluate integrals.
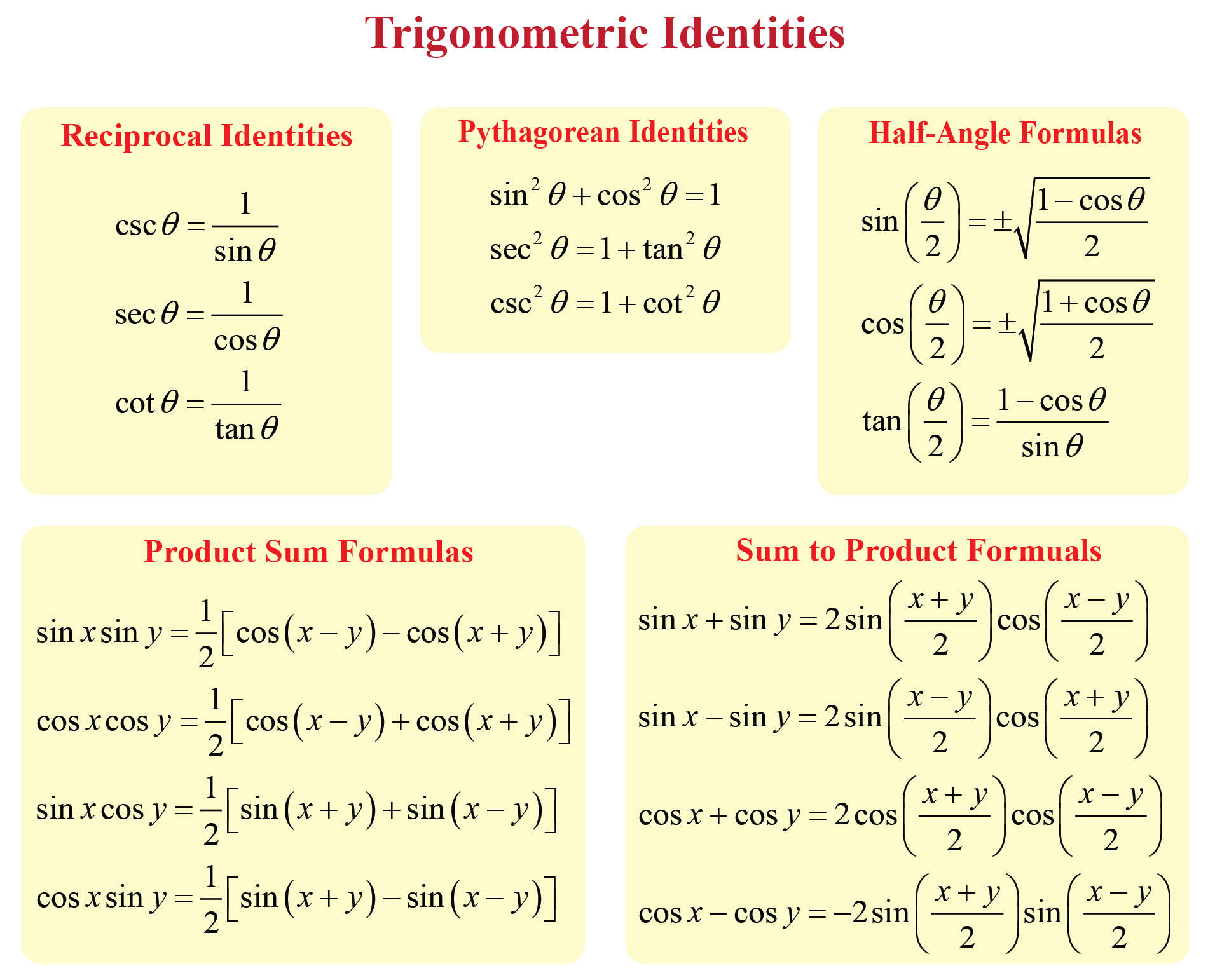
Trigonometry Formula Chart The pythagorean identities are based on the properties of a right triangle. cos2θ sin2θ = 1 (9.1.1) 1 cot2θ = csc2θ (9.1.2) 1 tan2θ = sec2θ (9.1.3) the even odd identities relate the value of a trigonometric function at a given angle to the value of the function at the opposite angle. Double angle and half angle formulas 26. sin(2 ) = 2 sin cos 27. cos(2 ) = cos2 sin2 28. tan(2 ) = 2 tan 1 2tan 29. sin 2 = r 1 cos 2 30. cos 2 = r 1 cos 2 31. tan 2 = 1 cos sin = sin 1 cos 32. tan 2 = r 1 cos 1 cos other useful trig formulas law of sines 33. sin = sin = sin law of cosines 34. a2 = b2 c2 2 b c cos b2 = a2 c2 2 a c cos c2 = a2. For the next trigonometric identities we start with pythagoras' theorem: the pythagorean theorem says that, in a right triangle, the square of a plus the square of b is equal to the square of c: dividing through by c2 gives. this can be simplified to: (a c)2 (b c)2 = 1. so (a c) 2 (b c) 2 = 1 can also be written:. These identities are useful whenever expressions involving trigonometric functions need to be simplified. an important application is the integration of non trigonometric functions: a common technique involves first using the substitution rule with a trigonometric function, and then simplifying the resulting integral with a trigonometric identity.

Trigonometry Ratios Formula Formula In Maths For the next trigonometric identities we start with pythagoras' theorem: the pythagorean theorem says that, in a right triangle, the square of a plus the square of b is equal to the square of c: dividing through by c2 gives. this can be simplified to: (a c)2 (b c)2 = 1. so (a c) 2 (b c) 2 = 1 can also be written:. These identities are useful whenever expressions involving trigonometric functions need to be simplified. an important application is the integration of non trigonometric functions: a common technique involves first using the substitution rule with a trigonometric function, and then simplifying the resulting integral with a trigonometric identity. Trigonometric identities are the equalities involving trigonometric functions and hold true for every value of the variables involved, in a manner that both sides of the equality are defined. some important identities in trigonometry are given as, sin θ = 1 cosec θ. cos θ = 1 sec θ. tan θ = 1 cot θ. The six basic trigonometric functions. trigonometric functions allow us to use angle measures, in radians or degrees, to find the coordinates of a point on any circle—not only on a unit circle—or to find an angle given a point on a circle. they also define the relationship between the sides and angles of a triangle.

Comments are closed.