Trigonometry Formulas Trigonometric Periodic Function Concept
Periodicity Of Trigonometric Functions Definition of a periodic function. a periodic function is a function that repeats its values at some regular interval, i.e., preserving its value when a fixed nonzero number (period of the function) is added to the argument: there is nonzero number t (period) that provides for meeting the equality across the entire range of definition of the. Periods of trigonometric function. the periodicity identities of trigonometric functions tell us that shifting the graph of a trigonometric function by a certain amount results in the same function. the \sin x sinx and \cos x cosx functions as well as their respective reciprocals \csc x cscx and \sec x secx all have a period of 2\pi, 2π, while.
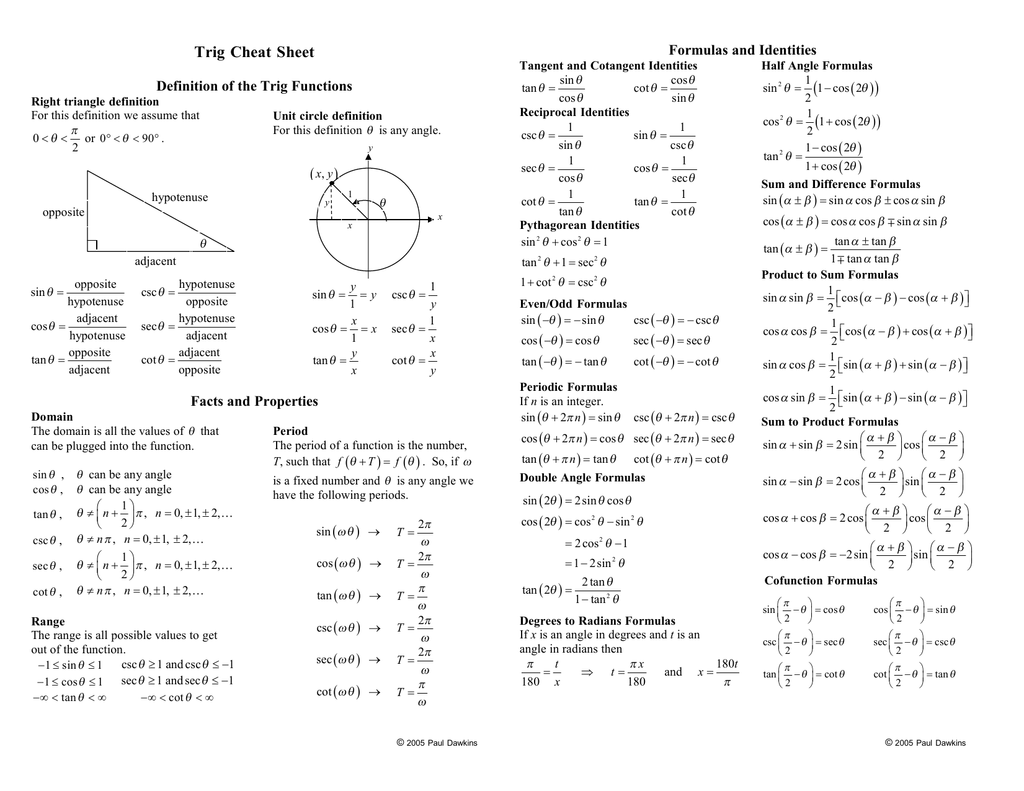
Trig Identities Table Of Trigonometric Identities Functions that have graphs shaped like sines or cosines are called sinusoidal. periodic function. the function y =f (x) y = f (x) is periodic if there is a smallest value of p p such that. f (x p) = f (x) f (x p) = f (x) for all x. x. the constant p p is called the period of the function. The cotangent function is the quotient of cosine and sine. its domain contains all angles \(\theta\) except the points \(\pi n, n \in \mathbb{z},\) where the sine function is equal to zero. the secant and cosecant are the reciprocal functions of cosine and sine, respectively. therefore, the secant function is periodic, with period \(2\pi:\). Skills. 1 graph periodic functions #1–6, 11–14, 27–28. 2 write equations for sinusoidal functions #7–12. 3 graph sinusoidal functions #13–18, 25–32. 4 find amplitude, period and midline #19–32. 5 fit a sinusoidal function to data or to a description #33–42. 6 find coordinates of points on a sinusoidal graph #43–48. Therefore, the formulas are correct: according to the definition of periodicity of a function, cos x is a periodic function with period Т = 2π (Т = 360°). completing n full circles by vector om counterclockwise forms angle α 2π n, and clockwise—angle α — 2π n. in both first and second cases, coordinates x and y of point m will.

Trigonometry Periodic Function Examples Youtube Skills. 1 graph periodic functions #1–6, 11–14, 27–28. 2 write equations for sinusoidal functions #7–12. 3 graph sinusoidal functions #13–18, 25–32. 4 find amplitude, period and midline #19–32. 5 fit a sinusoidal function to data or to a description #33–42. 6 find coordinates of points on a sinusoidal graph #43–48. Therefore, the formulas are correct: according to the definition of periodicity of a function, cos x is a periodic function with period Т = 2π (Т = 360°). completing n full circles by vector om counterclockwise forms angle α 2π n, and clockwise—angle α — 2π n. in both first and second cases, coordinates x and y of point m will. A periodic function is a function in which there is some positive constant k that for any x, f(x k) = f(x). this means that the function repeats itself in periods. the period of a function is the space over which you can basically cut and paste the graph horizontally. the domains of both sine and cosine are all real numbers and the ranges are. These concepts are especially important in the context of sine, cosine, and tangent functions, which are inherently periodic. identifying the period and frequency. the period of a trigonometric function is the smallest interval over which the function completes one full cycle. i look for the length of this interval on the function’s graph to.

Comments are closed.