Using The Pythagorean Theorem To Find A Trigonometric Ratio

Find Trigonometric Values Using The Pythagorean Theorem Youtube Step 1: identify the given sides in the figure. find the missing side of the right triangle by using the pythagorean theorem. step 2: identify the formula of the trigonometric ratio asked in the. Trig triangle calculator.

Using The Pythagorean Theorem To Find A Trigonometric Ratio Practice The pythagorean identities are used to prove other trigonometric identities, find the value of a trigonometric ratio by using any other trigonometric ratio, and to solve the problems related to heights and distances. are pythagorean identities derived from pythagorean theorem? yes, pythagorean identities are derived from pythagorean theorem. How to use the pythagorean theorem to find a trigonometric ratio. For a complete list of timely math tutor videos by course: timelymathtutor. (you may have also recognized that this is a “pythagorean triple,” 6, 8, 10, instead of using the pythagorean theorem.) you can also find the third side using a trigonometric ratio. notice that the missing side, b, is adjacent to ∠ a, and the hypotenuse is given. therefore we can use the cosine function to find the length of b:.

Using The Pythagorean Theorem To Find A Trigonometric Ratio Practice For a complete list of timely math tutor videos by course: timelymathtutor. (you may have also recognized that this is a “pythagorean triple,” 6, 8, 10, instead of using the pythagorean theorem.) you can also find the third side using a trigonometric ratio. notice that the missing side, b, is adjacent to ∠ a, and the hypotenuse is given. therefore we can use the cosine function to find the length of b:. Example 2 (solving for a leg) use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 24 and x x are the legs. the hypotenuse is 26. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). a2 b2 = c2 x2 242 = 262 a 2 b 2 = c 2 x. Apply the pythagorean theorem to find the missing sides of a right triangle. apply the 30 ∘ 60 ∘ 90 ∘ 30 ∘ 60 ∘ 90 ∘ and 45 ∘ 45 ∘ 90 ∘ 45 ∘ 45 ∘ 90 ∘ right triangle relationships to find the missing sides of a triangle. apply trigonometric ratios to find missing parts of a right triangle.
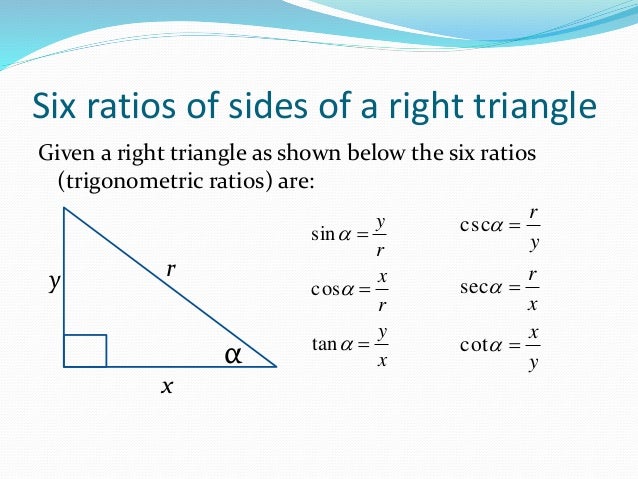
Angles Right Triangle Pythagorean Theorem Trigonometric Ratios Example 2 (solving for a leg) use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 24 and x x are the legs. the hypotenuse is 26. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). a2 b2 = c2 x2 242 = 262 a 2 b 2 = c 2 x. Apply the pythagorean theorem to find the missing sides of a right triangle. apply the 30 ∘ 60 ∘ 90 ∘ 30 ∘ 60 ∘ 90 ∘ and 45 ∘ 45 ∘ 90 ∘ 45 ∘ 45 ∘ 90 ∘ right triangle relationships to find the missing sides of a triangle. apply trigonometric ratios to find missing parts of a right triangle.

Comments are closed.