Vertices Of A Triangle вђ Definition Formula Theorem Examples

Vertices Of A Triangle вђ Definition Formula Theorem Examples In geometry, a vertex (plural vertices) is a point where two straight lines intersect. a triangle is formed by the intersection of three line segments. each side of a triangle has two endpoints, with the endpoints of all three sides meeting at three different points in a plane, forming a triangle. the three different intersecting points or. Solution: according to the midsegment theorem, the length of the midsegment is half the length of the third side. a b = 1 2 × x z. 3 x − 1 = 1 2 × 34. 3 x − 1 = 17. 3 x = 18. x = 6 feet. 4. if abc is an equilateral triangle with a midsegment of length 12 units then find the perimeter of the triangle abc.
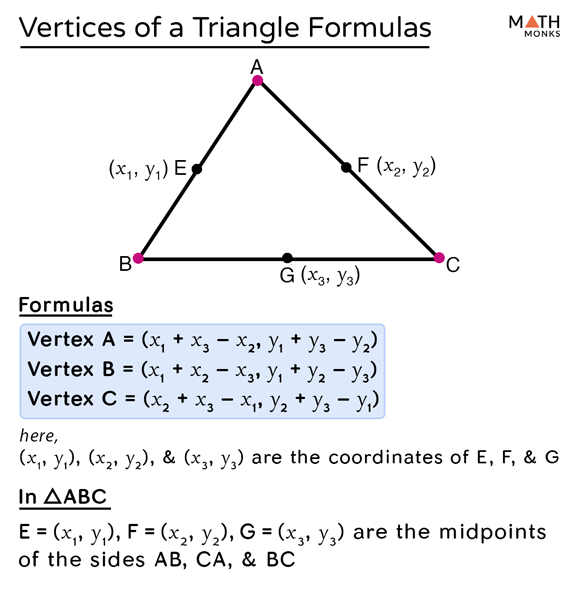
Vertices Of A Triangle Examples of polyhedrons are cube, prism, pyramid and so on. the relationship between vertices, edges and faces for polyhedrons can be given by euler’s formula. euler’s formula says, in a polyhedron, the number of vertices (v) and faces (f) together is exactly two more than the number of edges (e). v f = 2 e. Worked examples of pythagoras theorem: example 4. the two short sides of a right triangle are 5 cm and 12cm. find the length of the third side. solution. given, a = 5 cm. b = 12 cm. c = ? from the pythagoras theorem formula; c 2 = a 2 b 2, we have; c 2 = a 2 b 2. c 2 =12 2 5 2. c 2 = 144 25. √c 2 = √169. c = 13. therefore, the third. Properties of a triangle. the sum of all three interior angles of a triangle is always equal to 180⁰. the sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side. the area of a triangle is equal to half of the product of its base and height. A triangle with three vertices p, q, and r is represented as pqr. the most commonly seen examples of triangles are the signboards and sandwiches that are in the shape of a triangle. let us read more about the triangle shape, the definition of a triangle, the parts of a triangle, the kinds of triangles and the properties of triangles on this page.

Solved Consider The Triangle With Vertices 0 0 5 0 And Chegg Properties of a triangle. the sum of all three interior angles of a triangle is always equal to 180⁰. the sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side. the area of a triangle is equal to half of the product of its base and height. A triangle with three vertices p, q, and r is represented as pqr. the most commonly seen examples of triangles are the signboards and sandwiches that are in the shape of a triangle. let us read more about the triangle shape, the definition of a triangle, the parts of a triangle, the kinds of triangles and the properties of triangles on this page. A right triangle's hypotenuse. the hypotenuse is the largest side in a right triangle and is always opposite the right angle. (only right triangles have a hypotenuse ). the other two sides of the triangle, ac and cb are referred to as the 'legs'. in the triangle above, the hypotenuse is the side ab which is opposite the right angle, ∠c ∠ c . The pythagorean theorem can be summarized in a short and compact equation as shown below. for a given right triangle, it states that the square of the hypotenuse, in right a triangle, the square of longest side known as the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. the pythagorean theorem guarantees that if we know.

Comments are closed.