Vygotsky S Theory Of Cognitive Development а µа ѕа а аґ а аґќа ёа аґђ а аґ а

D0 C2 C8 Cb Bd Cc B0 E64 B1 D8 D0 De3 2 D5 Dc D1 A7 Ca B7 C9 Cf B5 Vygotsky’s theory comprises concepts such as culture specific tools, private speech, and the zone of proximal development. vygotsky believed cognitive development is influenced by cultural and social factors. he emphasized the role of social interaction in the development of mental abilities e.g., speech and reasoning in children. Taking up vygotsky’s theories, memory development in a 2 year old, a 3 year old, and a 5 year old cannot simply be measured by “how much” memory is “added” at each developmental stage. in the systemic framework, the structure of memory for a 5 year old is qualitatively different from the memory of a 3 year old. therefore, instead of.

Https Storage Yandexcloud Net Vigbo Gallery Gallery Photo 664667b5 Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like vygotsky's theory stresses the of cognitive development. a) egocentricity b) neuroplasticity c) physiology d) social context, research shows that young children use private speech (see textbook p. 323) a) because they have difficulty with perspective taking. b) to help them guide their own learning and problem solving. Central to vygotsky's theory of cognitive development is the idea that children make sense of their world: by interacting with more experienced people who mediate their understandings. after explaining what sines and cosines are, a high school math teacher shows students how they might use these concepts in constructing a large building. Vygotsky (1978) states: “every function in the child’s cultural development appears twice: first, on the social level, and later, on the individual level; first, between people (interpsychological) and then inside the child (intrapsychological). this applies equally to voluntary attention, to logical memory, and to the formation of concepts. Vygotsky’s theory. in vygotsky’s (1934 1987) theory of cognitive development, inner speech is the outcome of a developmental process. vygotsky assumed that understanding how such a phenomenon emerges over the life span is necessary for full comprehension of its subjective qualities and functional characteristics.

студенты вгика приняли участие в международной акции код доступа Vygotsky (1978) states: “every function in the child’s cultural development appears twice: first, on the social level, and later, on the individual level; first, between people (interpsychological) and then inside the child (intrapsychological). this applies equally to voluntary attention, to logical memory, and to the formation of concepts. Vygotsky’s theory. in vygotsky’s (1934 1987) theory of cognitive development, inner speech is the outcome of a developmental process. vygotsky assumed that understanding how such a phenomenon emerges over the life span is necessary for full comprehension of its subjective qualities and functional characteristics. Piaget said there were a number of stages that we went through: 1. sensorimotor stage: from birth to age two (using our senses, e.g., sucking); 2. preoperational stage: from beginning to speak to the age of seven (starting to use symbols and thinking is egocentric) 3. concrete operational stage: from ages seven to eleven. This paper turns to the contributions that russian psychologist lev vygotsky and his adherents have made to our understanding of emotional development in early childhood. following several main ways that his developmental theory described development through play, it proposes an extra social–individual dialectical relationship to explain.
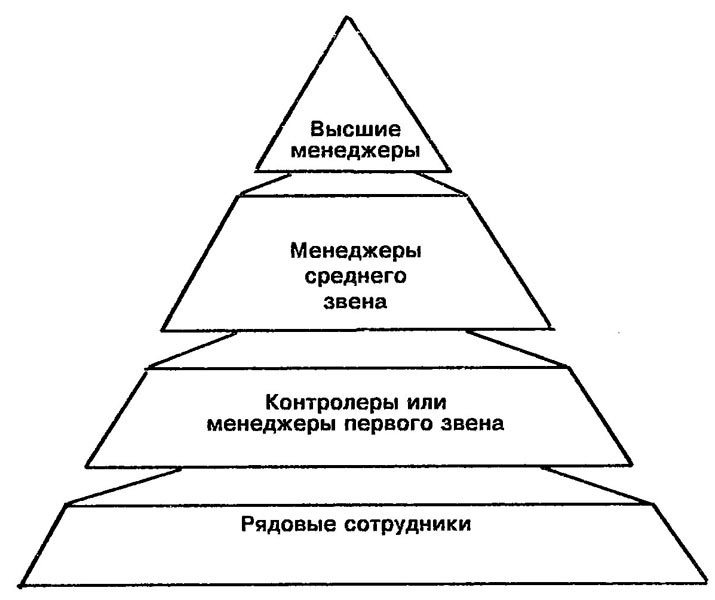
менеджер Piaget said there were a number of stages that we went through: 1. sensorimotor stage: from birth to age two (using our senses, e.g., sucking); 2. preoperational stage: from beginning to speak to the age of seven (starting to use symbols and thinking is egocentric) 3. concrete operational stage: from ages seven to eleven. This paper turns to the contributions that russian psychologist lev vygotsky and his adherents have made to our understanding of emotional development in early childhood. following several main ways that his developmental theory described development through play, it proposes an extra social–individual dialectical relationship to explain.

Comments are closed.