Welding Positions 1g 2g 3g 4g 5g 6g How To Learn Welding Positions

What Is 4f Welding Position Design Talk 6g uphill. 6g downhill. pipe and plate weld joint positions. normally there are six welding positions with certain numbers and letters i.e. 1g, 2g, 3g, 4g, 5g, and 6g 6gr. all the positions are used in various angles and shapes while performing welding. generally, the ways and ideas of welding are similar in different countries. 1g, 2g, 3g, 4g, 5g, 6g welding position explained. 1. flat welding (1g) 1g is flat welding. 1g welding. 1g welding characteristics: fusion welding of metal primarily relies on its own weight to flow into the molten pool. the shape and composition of the molten pool are simple to maintain and control. when welding metal with the same plate.

An Overview Of Positions For Pipe Welding 1g 2g 5g And 6g Application sectors of these positions. 1g, 2g, 3g and 4g plate welding positions uses in the fabrication and installation of tanks, vessel, structural, shipbuilding and aeronotics. 1g, 2g, 5g and 6g pipe welding positions are used in the fabrication and installation of piping and pipelines for industrila plants, oil and gas industry, chemical. Following are the numbers and letters used for the groove and fillet welding: for groove welding: 1g – flat welding position. 2g – horizontal welding position. 3g – vertical welding position. 4g – welding position overhead or overhead) 5g – uphill and downhill vertical welding position. The 4g and 3g welding positions share similarities, as both involve welding on vertical surfaces. however, the key difference lies in the direction of the weld bead movement. in the 3g position, the weld bead moves upward, while in the 4g position, it moves downward. the 4g position presents additional challenges due to the overhead orientation. There are six numbers. as you might expect, these are appropriately labeled 1 through 6. the number is, specifically, the position you’re using when you’re welding. they are: 1. flat. flat welding is welding below the torch. it’s among the most common, easiest to manage, and least complex of the welding positions.
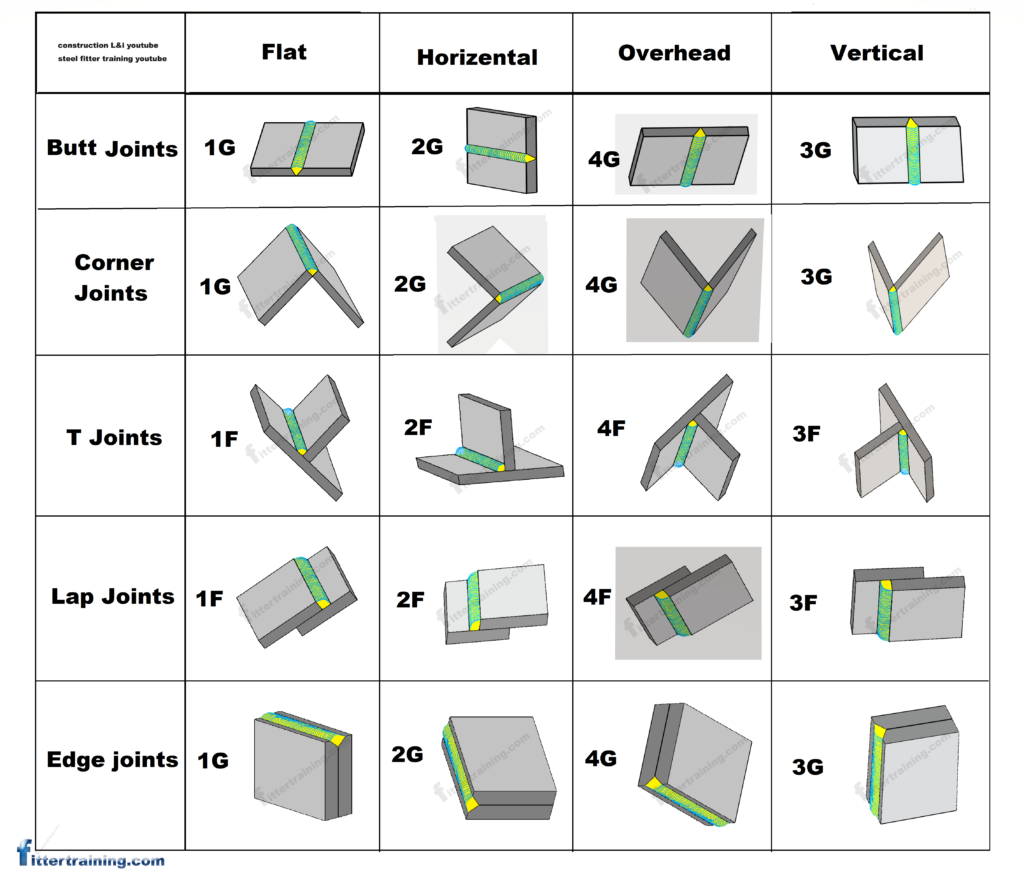
Welding 1g 2g 3g 4g 5g 6g The 4g and 3g welding positions share similarities, as both involve welding on vertical surfaces. however, the key difference lies in the direction of the weld bead movement. in the 3g position, the weld bead moves upward, while in the 4g position, it moves downward. the 4g position presents additional challenges due to the overhead orientation. There are six numbers. as you might expect, these are appropriately labeled 1 through 6. the number is, specifically, the position you’re using when you’re welding. they are: 1. flat. flat welding is welding below the torch. it’s among the most common, easiest to manage, and least complex of the welding positions. Welding positions and joint types 1g, 2g, 3g, 4g, 5g, and 6g. welding position has a significant impact on weld quality and difficulty. certain positions like flat (1g) are easier, as gravity helps hold the weld pool in place. positions like overhead (4g) are very challenging since the weld pool wants to drip down due to gravity. Overhead welding position (4g, 4f) these positions apply to groove welds (g) or fillet welds (f), with differences in joint configuration. in pipe welding, two additional positions, 5g and 6g, involve welding around vertically or inclined pipes using a combination of overhead, vertical, horizontal, and flat positions.

Comments are closed.