What Are The Stages Of Play Jean юааpiagetюабтащs Theory Of Play Play

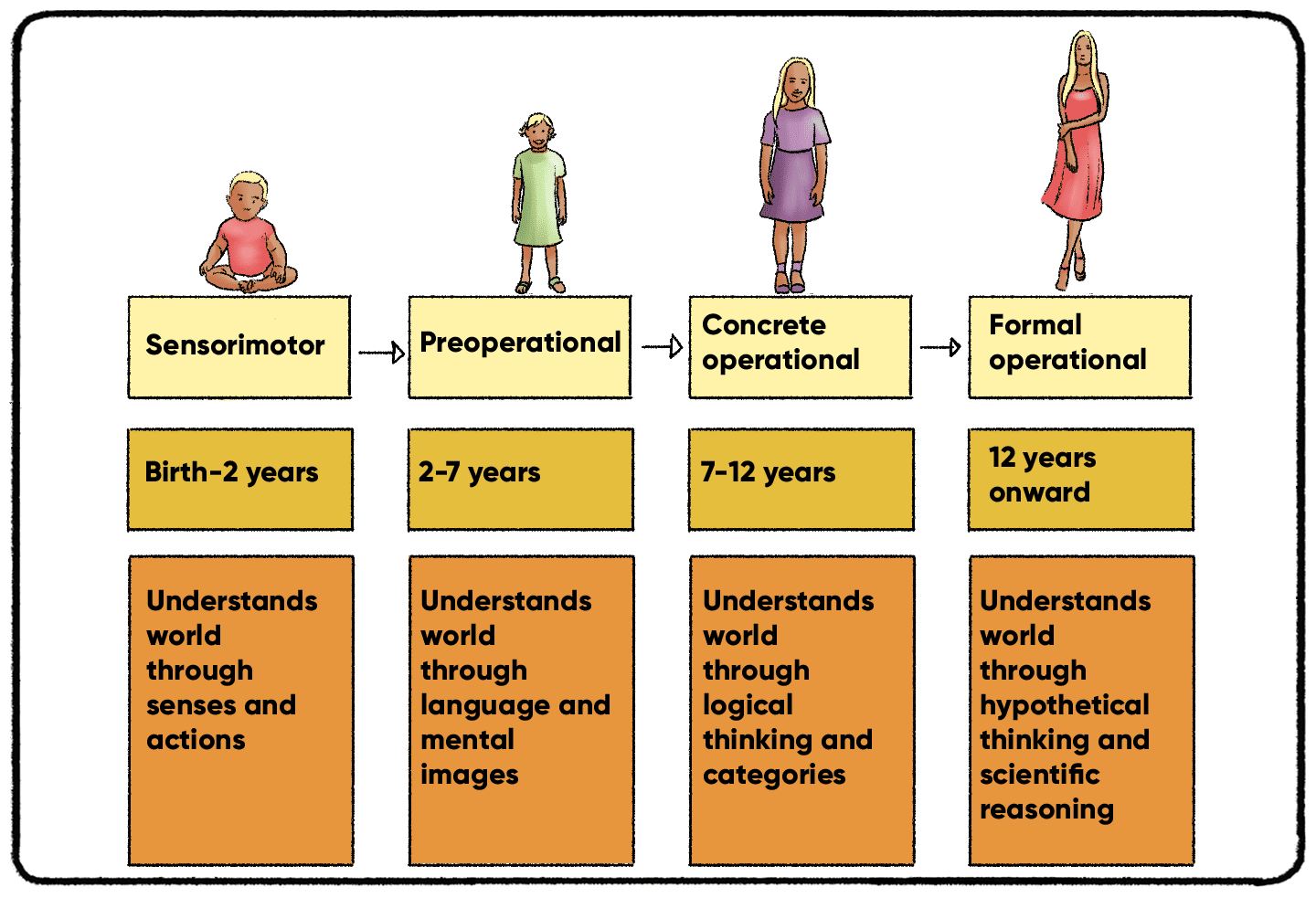
What Are The Stages Of Play Jean Piaget S Theory Of Play Atelier Piaget’s research led him to build his theory on four stages of cognitive development based on how children play, including the sensorimotor stage, the pre operational stage, the concrete operational stage, and the formal operational stage. the stages are broken down by age from birth to 2 years, 2 to 7 years, 7 to 11 years, and 11 years. Piaget’s theory is that together the four stages and their respective sub stages of ‘play’ help the child to develop their cognition, understanding what actions they can take in different situations, the effects of their actions are likely to have and whether those actions are right for the circumstance. of course, by the very basis of.

What Are The Stages Of Play Jean Piaget S Theory Of Play 55 Off Piaget’s research led him to build his theory on four stages of cognitive development based on the way children play including the sensorimotor stage, the pre operational stage, the concrete operational stage, and the formal operational stage. learn more. According to piaget, children engage in types of play that reflect their level of cognitive development: functional play, constructive play, symbolic fantasy play, and games with rules. ) gives you a clue about how children learn in those first two years of life. right from birth, babies use their. Theories of stages of play. the stages of play are anchored on three theories that show the correlation between a child’s environment and how they acquire knowledge as they grow. these theories will also show how children advance in play from simple body movements to more complex activities. 1. bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory. Vygotsky’s play theory highlights the significance of the zone of proximal development (zpd) and the role of more knowledgeable others (mkos) in scaffolding a child's learning. his theory emphasised the role of social interactions in learning. as a play based teacher, you no doubt encourage collaborative play.

Stages Of Play The Play Theories Of Parten And Piaget In 2022 Stages Theories of stages of play. the stages of play are anchored on three theories that show the correlation between a child’s environment and how they acquire knowledge as they grow. these theories will also show how children advance in play from simple body movements to more complex activities. 1. bronfenbrenner's ecological systems theory. Vygotsky’s play theory highlights the significance of the zone of proximal development (zpd) and the role of more knowledgeable others (mkos) in scaffolding a child's learning. his theory emphasised the role of social interactions in learning. as a play based teacher, you no doubt encourage collaborative play. Play theory. piaget (1951) argued that play is vital for children’s learning. play is an example of assimilation, and imitation is an example of accommodation. he argued that there are three types of games that children can play based on their cognitive development: practice games; symbolic games; games with rules. The first half of the twentieth century saw the emergence of two models that have shaped the theoretical foundations of most recent research on play and learning: piaget’s theory of cognitive development, which considers importance of play among other things, and vygotsky’s cultural historical approach, which considers play crucial in child’s development.

Developmental Stages Of Play Piaget вђ My Teaching Cupboard Play theory. piaget (1951) argued that play is vital for children’s learning. play is an example of assimilation, and imitation is an example of accommodation. he argued that there are three types of games that children can play based on their cognitive development: practice games; symbolic games; games with rules. The first half of the twentieth century saw the emergence of two models that have shaped the theoretical foundations of most recent research on play and learning: piaget’s theory of cognitive development, which considers importance of play among other things, and vygotsky’s cultural historical approach, which considers play crucial in child’s development.
Jean Piaget S Stages Of Cognitive Development I Tickle Right Atelier

Comments are closed.