What Dna Test Structure And Function Of The Dna Molecule
What Is Dna Meaning Dna Types Structure And Functions Dna is well suited to perform this biological function because of its molecular structure, and because of the development of a series of high performance enzymes that are fine tuned to interact with this molecular structure in specific ways. To grow, develop and carry on with its functions the cell has to read the genes in the dna and produce proteins and enzymes that are important for the cell’s structure and metabolism. this is done in two steps. first the information of the dna is copied to a fragment of rna (a molecule very similar to dna although it is usually single.
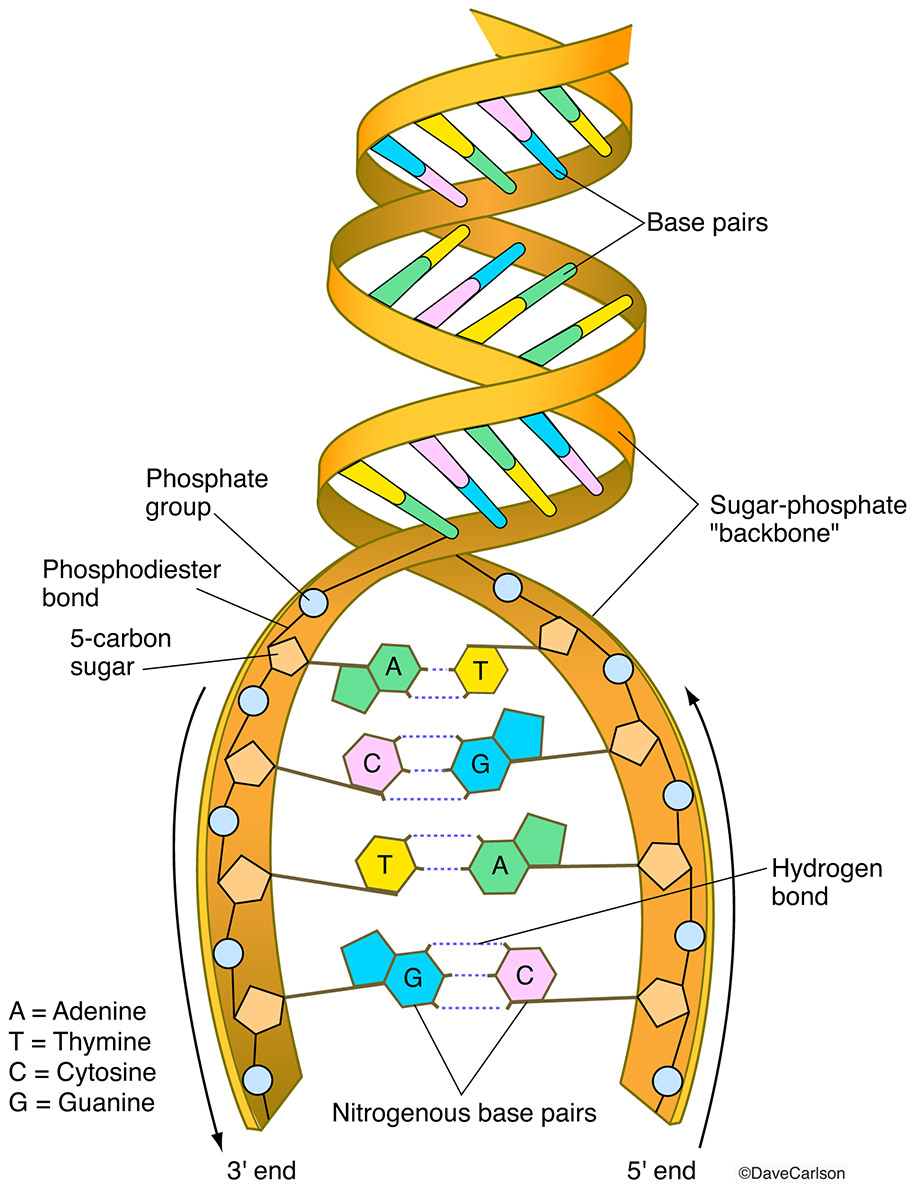
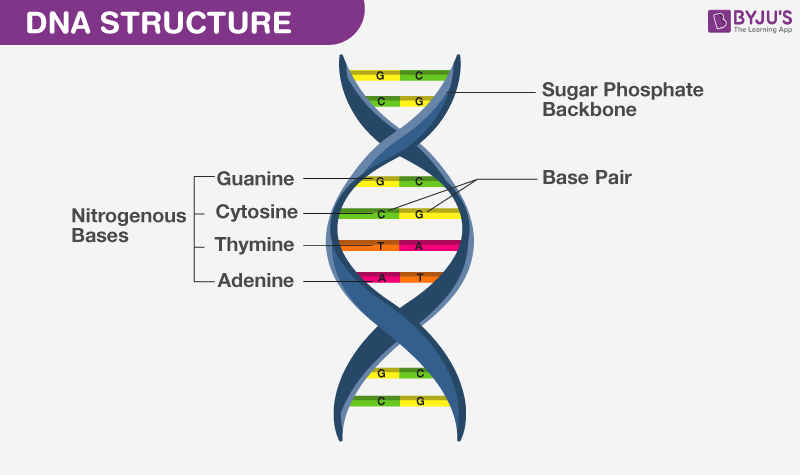
Dna Structure Carlson Stock Art Dna, organic chemical of complex molecular structure found in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. it codes genetic information for the transmission of inherited traits. the structure of dna was described in 1953, leading to further understanding of dna replication and hereditary control of cellular activities. Dna structure and functions. dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, a macromolecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms, from the tiniest microorganisms to the most complex multicellular humans. dna is a fundamental molecule that holds life’s blueprint. within a eukaryotic cell ( plant and animal), they are found inside. Dna: properties, structure, composition, types, functions. deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the heredity material found in humans and all living organisms. it is a double stranded molecule and has a unique twisted helical structure. dna is made up of nucleotides, each nucleotide has three components: a backbone made up of a sugar (deoxyribose. The structure and function of these molecules is determined by nucleotide sequences in dna. when a protein or rna molecule needs to be produced, the first step is transcription. like dna replication, this begins with the transient formation of a single stranded region.

The Chemical Structure Of Dna вђ Compound Interest Dna: properties, structure, composition, types, functions. deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the heredity material found in humans and all living organisms. it is a double stranded molecule and has a unique twisted helical structure. dna is made up of nucleotides, each nucleotide has three components: a backbone made up of a sugar (deoxyribose. The structure and function of these molecules is determined by nucleotide sequences in dna. when a protein or rna molecule needs to be produced, the first step is transcription. like dna replication, this begins with the transient formation of a single stranded region. The structure and function of dna. biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting dna as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. dna was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits, which resemble one another chemically. early in the 1950s, dna was first examined by x ray diffraction. Dna exists in many possible conformations that include a dna, b dna, and z dna forms, although only b dna and z dna have been directly observed in functional organisms. [14] the conformation that dna adopts depends on the hydration level, dna sequence, the amount and direction of supercoiling, chemical modifications of the bases, the type and concentration of metal ions , and the presence of.

The Cynical Tendency Making Choices The structure and function of dna. biologists in the 1940s had difficulty in accepting dna as the genetic material because of the apparent simplicity of its chemistry. dna was known to be a long polymer composed of only four types of subunits, which resemble one another chemically. early in the 1950s, dna was first examined by x ray diffraction. Dna exists in many possible conformations that include a dna, b dna, and z dna forms, although only b dna and z dna have been directly observed in functional organisms. [14] the conformation that dna adopts depends on the hydration level, dna sequence, the amount and direction of supercoiling, chemical modifications of the bases, the type and concentration of metal ions , and the presence of.
/dna-molecule--illustration-670895251-5a4e29e213f1290037183f8d.jpg)
Nucleic Acids Structure And Function

Comments are closed.