What Happens To Your Brain During A Migraine вђ Translingual
Headaches And Migraine Don T Suffer In Silence Active Health Download now language: english level: b2 number of pages: 3 worksheet time: 60' this lesson plan is dedicated to doctors, pharmacists, therapists, psychologists, med students, or anybody else who would like to discover the medical english vocabulary. the worksheet is divided into 3 parts: vocabulary, comprehension and. Once released, they travel to the outer layer of your brain–the meninges–which results in inflammation and swelling of blood vessels, causing an increase in blood flow around the brain. this is likely the cause of the throbbing, pulsing pain most people experience during migraine. while the pain may be originating from the surface of your.

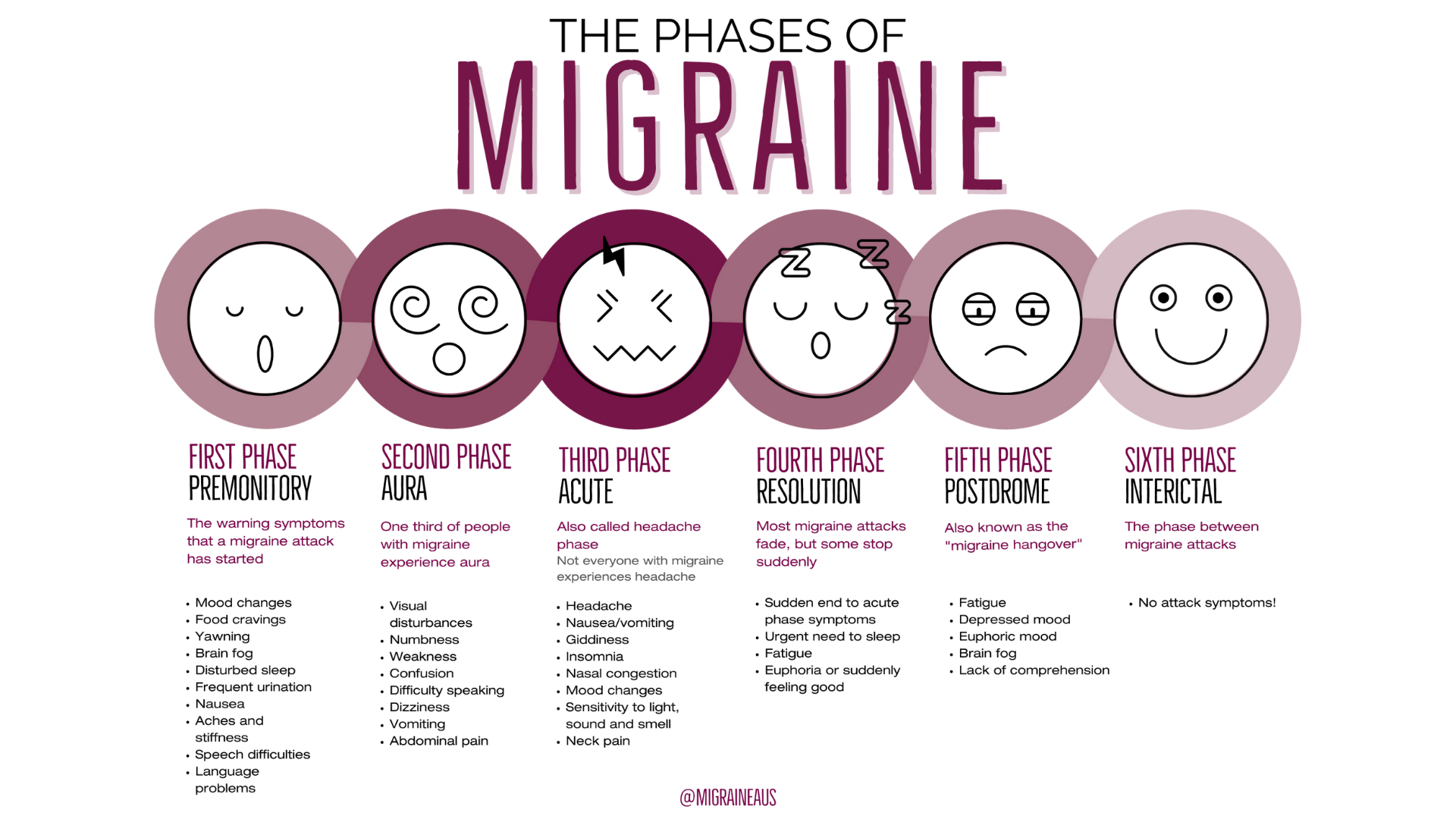
Science Explains What Happens In The Brain During A Migraine What happens to your brain during a migraine? a throbbing, pounding headache. bright zigzagging lines across your field of vision. sensitivity to light, lingering fatigue, disrupted sleep. while an incapacitating headache is one of the most common symptoms, a migraine can include any of these experiences. so what exactly is a migraine?. Premonition phase: a shift in mood or behavior could occur hours or days before the headache. aura phase: one third of people who have migraine headaches report an unusual “feeling” or aura before the headache. the aura phase is characterized by visual, sensory, or motor symptoms that appear just before the headache. Migraine is often used as shorthand for a severe headache, but the term “migraine” actually refers to a neurological condition that affects about 39 million people in the united states. Chronic migraine is a highly disabling disease with a great impact on socioeconomic functioning and quality of life of migraine patients. chronic migraine usually evolves from episodic migraine that gradually increases in attack frequency, supporting the view of migraine as a spectrum disorder. pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for.

What Happens To Your Brain During A Migraine Migraine is often used as shorthand for a severe headache, but the term “migraine” actually refers to a neurological condition that affects about 39 million people in the united states. Chronic migraine is a highly disabling disease with a great impact on socioeconomic functioning and quality of life of migraine patients. chronic migraine usually evolves from episodic migraine that gradually increases in attack frequency, supporting the view of migraine as a spectrum disorder. pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for. Aspirin. for people with mild migraine, non specific anti inflammatory medications such as high dose aspirin, or standard dose non steroidal medications (nsaids) can be very helpful. their. One aspect of migraine pain theory explains that migraine pain happens due to waves of activity by groups of excitable brain cells. these trigger chemicals, such as serotonin, to narrow blood vessels. serotonin is a chemical necessary for communication between nerve cells. it can cause narrowing of blood vessels throughout the body.

Comments are closed.