What Is Chemical Equilibrium Explain With Example Class 10 Chemistry

What Is Chemical Equilibrium Explain With Example Class 10 Chemistry Problems on chemical equilibrium. 1. the equilibrium constant k p for the reaction n 2 (g) 3h 2 (g) ⇌ 2nh 3 (g) is 1.6 × 10 4 atm 2 at 400 o c. what will be the equilibrium constant of the chemical equilibrium at 500 o c if the heat of the reaction at this temperature range is 25.14 kcal? solution:. Equilibrium the state in which the measurable properties of the system such as pressure, density, colour or concentration do not undergo any further noticeable changes with time under a given set of conditions is said to be a state of equilibrium. to learn more about classification, example, description, characteristics and faqs of equilibrium, visit byju’s.
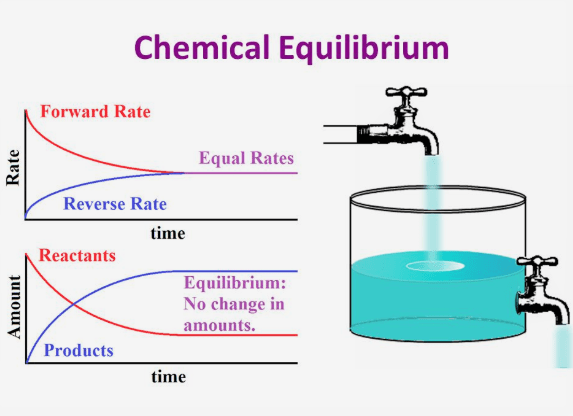
Physical Chemistry Which Graph Shows Chemical Equilib Vrogue Co Chemical equilibrium definition refers to the state of a system where the concentration of the reactant and the concentration of the products do not change with respect to time and the system does not display any further change in properties. chemical equilibrium is said to be achieved by the system when the rate of the forward reaction is. A given chemical reaction system is defined by a balanced net chemical equation which is conventionally written as. reactants→ products (11.1.1) (11.1.1) reactants → products. the first thing we need to know about a chemical reaction represented by a balanced equation is whether it can actually take place. Kc is the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of the molar concentrations. the equation kc = [ c ]c· [ d ]d [ a ]a· [ b ]b. or, kc = kf kb is the law of chemical equilibrium. the equilibrium constant is therefore related to the standard gibbs free energy change for the reaction which is stated by the equation –. §gº= rt ln k eq. Chemical equilibrium, condition in the course of a reversible chemical reaction in which no net change in the amounts of reactants and products occurs. a reversible chemical reaction is one in which the products, as soon as they are formed, react to produce the original reactants. at equilibrium, the two opposing reactions go on at equal rates.

Notes On Chemical Equilibrium Chemical Equilibrium Chemical Kc is the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of the molar concentrations. the equation kc = [ c ]c· [ d ]d [ a ]a· [ b ]b. or, kc = kf kb is the law of chemical equilibrium. the equilibrium constant is therefore related to the standard gibbs free energy change for the reaction which is stated by the equation –. §gº= rt ln k eq. Chemical equilibrium, condition in the course of a reversible chemical reaction in which no net change in the amounts of reactants and products occurs. a reversible chemical reaction is one in which the products, as soon as they are formed, react to produce the original reactants. at equilibrium, the two opposing reactions go on at equal rates. Chemical equilibrium is the condition of a system where the concentrations of the reactants and products do not change with time. also, the system does not show any change in its properties. during a reversible reaction, when the forward and reverse reaction rates become equal, the system achieves the state of chemical equilibrium. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. khan academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world class education for anyone, anywhere.

Comments are closed.