What Is Coronary Artery Disease Mechanism Of Disease
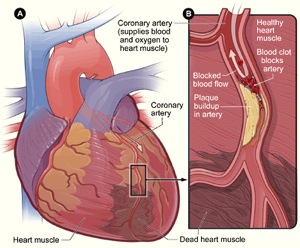
Coronary Artery Disease Cad Cardiac Surgery Michigan Medicine Coronary artery disease is a condition in which there is an inadequate supply of blood and oxygen to the myocardium. it results from occlusion of the coronary arteries and results in a demand supply mismatch of oxygen. it typically involves the formation of plaques in the lumen of coronary arteries that impede blood flow. it is the major cause of death in the us and worldwide. at the beginning. During the past decade, our understanding of the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease (cad) has undergone a remarkable evolution. we review here how these advances have altered our concepts of and clinical approaches to both the chronic and acute phases of cad. previously considered a cholesterol storage disease, we currently view atherosclerosis as an inflammatory disorder. the.
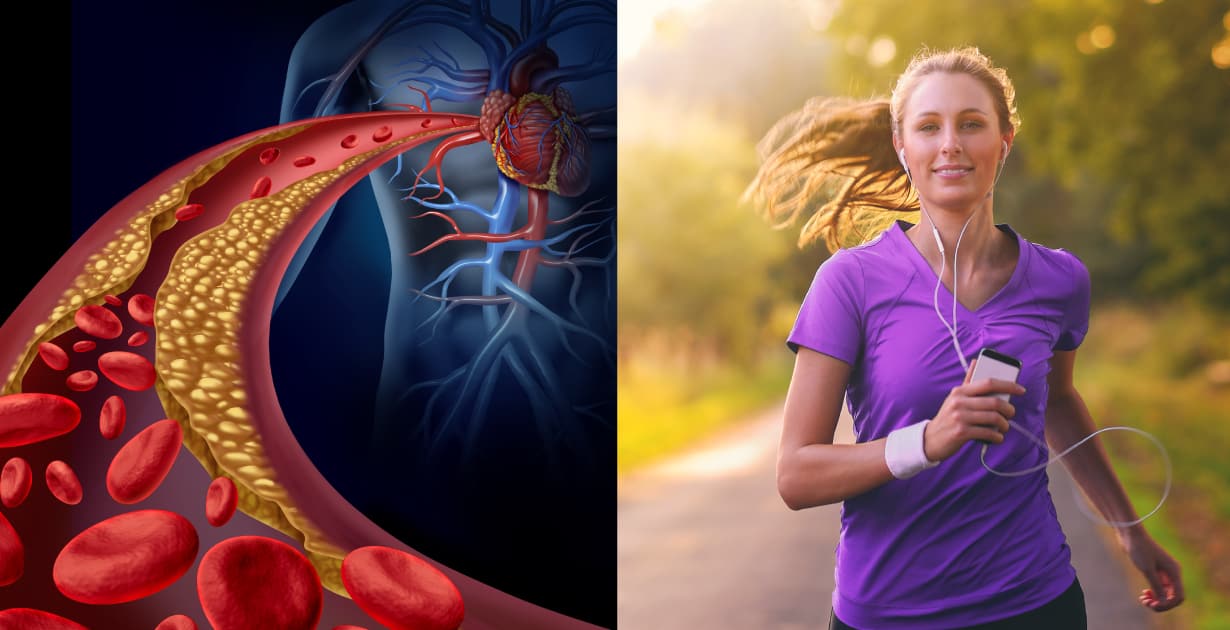

Coronary Artery Disease 6 Natural Ways To Help Relieve Cad Symptoms Abstract. in most developed countries, coronary artery disease (cad), mostly caused by atherosclerosis of coronary arteries, is one of the primary causes of death. from 1990s to 2000s, mortality caused by acute mi declined up to 50%. the incidence of cad is related with age, gender, economic, etc. atherosclerosis contains some highly. Recent research suggests that the beneficial effects of statins extend beyond their lipid lowering effects and likely also protects against atherosclerosis via lipid lowering independent mechanisms. 46,47 yu et al 48 tested a mouse model of spontaneous coronary artery atherosclerosis and showed that rosuvastatin treatment protected against. In most cases of ami and in a majority of cases of scd, the underlying pathology is acute intraluminal coronary thrombus formation within an epicardial coronary artery leading to total or near total acute coronary occlusion. this article summarizes our current understanding of the pathophysiology of these acute coronary syndromes and briefly. Usually, coronary artery disease is due to . coronary artery atherosclerosis: subintimal deposition of atheromas in large and medium sized coronary arteries. less often, coronary artery disease is due to. coronary artery spasm (see vasospastic angina) vascular endothelial dysfunction can promote atherosclerosis and contribute to coronary artery.
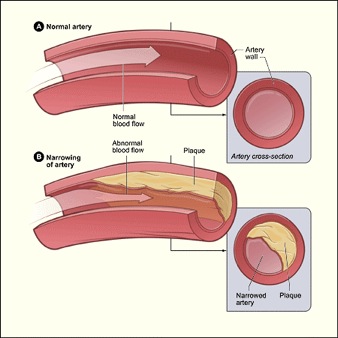
Coronary Artery Disease Cad Cardiac Surgery Michigan Medicine In most cases of ami and in a majority of cases of scd, the underlying pathology is acute intraluminal coronary thrombus formation within an epicardial coronary artery leading to total or near total acute coronary occlusion. this article summarizes our current understanding of the pathophysiology of these acute coronary syndromes and briefly. Usually, coronary artery disease is due to . coronary artery atherosclerosis: subintimal deposition of atheromas in large and medium sized coronary arteries. less often, coronary artery disease is due to. coronary artery spasm (see vasospastic angina) vascular endothelial dysfunction can promote atherosclerosis and contribute to coronary artery. Coronary artery disease symptoms may include: chest pain, called angina. you may feel squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in the chest. it may feel like somebody is standing on your chest. the chest pain usually affects the middle or left side of the chest. activity or strong emotions can trigger angina. In a prospective angiographic study involving patients undergoing percutaneous intervention for coronary artery disease, only half the subsequent events arose from lesions with sufficient stenosis.

Comments are closed.