What Is Law Of Conservation Of Energy Derivation Examples
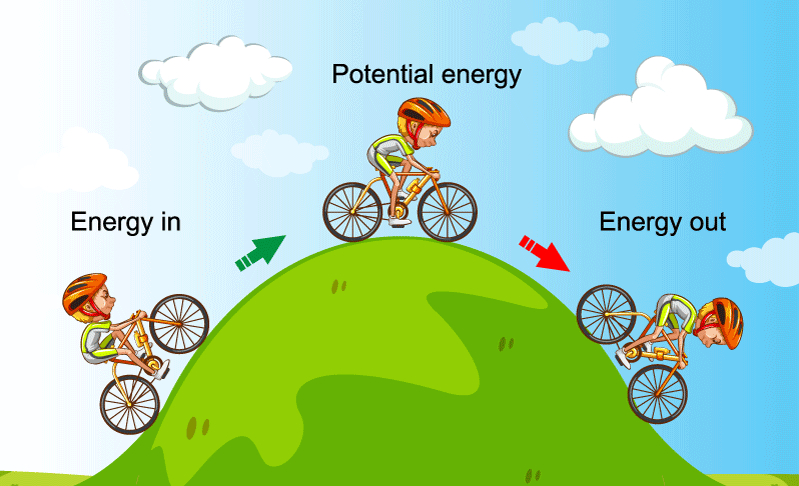
Law Of Conservation Of Energy Definition Derivation Examples Law of conservation of energy: definition, derivation &. The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. although, it may be transformed from one form to another. if you take all forms of energy into account, the total energy of an isolated system always remains constant. all the forms of energy follow the law of conservation of energy. in brief, the law.
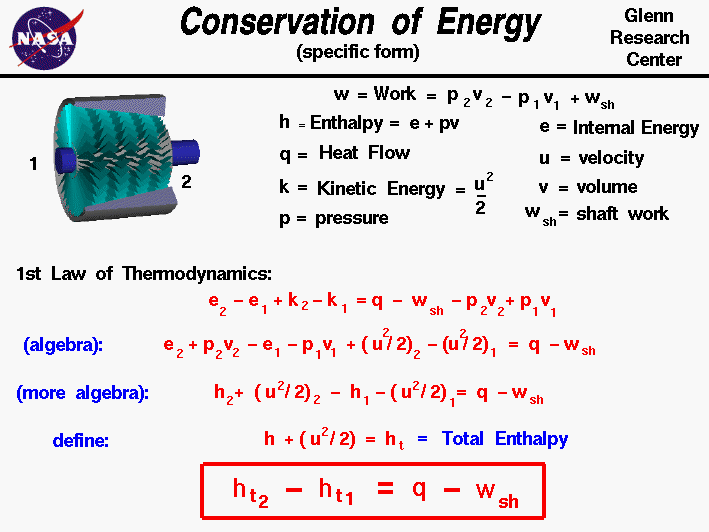
Conservation Of Energy The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in physics that asserts energy within a closed system remains constant, regardless of the transformations it undergoes. essentially, this law means that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. instead it merely shifts from one form to another. The conservation of energy law is one of the fundamental laws of all science disciplines. in several areas of science, energy conservation is applied to derive many essential equations. let us take the example of the first law of thermodynamics to understand this concept. consider a system that takes in heat and does valuable work. Hence, the light bulb is a prominent example of the law of conservation of energy. 2. collision. a moving object induces motion into a stationary object after hitting it. this is because the kinetic energy possessed by the moving object can not end abruptly. as per the law of conservation of energy, the energy can only be transferred and cannot. Law of conservation of energy states that in an isolated system, the total energy remains constant. energy can be converted from one form to the another. for example, in microphones, sound energy is converted to electrical energy. all the forms of energy available in the universe follows the law of conservation of energy.
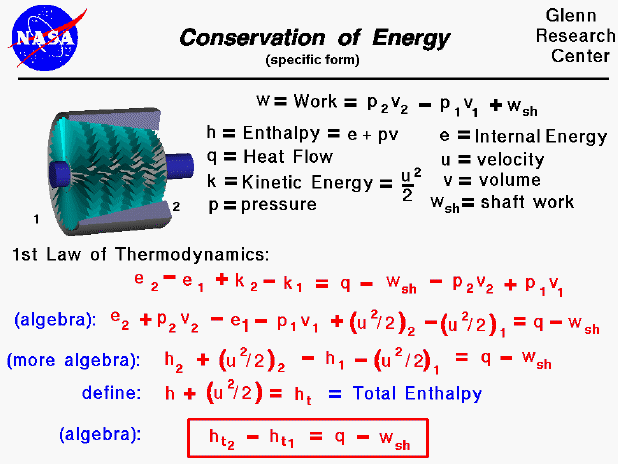
Conservation Of Energy Hence, the light bulb is a prominent example of the law of conservation of energy. 2. collision. a moving object induces motion into a stationary object after hitting it. this is because the kinetic energy possessed by the moving object can not end abruptly. as per the law of conservation of energy, the energy can only be transferred and cannot. Law of conservation of energy states that in an isolated system, the total energy remains constant. energy can be converted from one form to the another. for example, in microphones, sound energy is converted to electrical energy. all the forms of energy available in the universe follows the law of conservation of energy. The law of conservation of energy may be written: ke pe ie=e k e pe i e = e. where ke = kinetic energy = (1 2)m v2 , pe = potential energy (equal to m g h when gravity is the only force acting, but seen in other forms), ie = internal energy, and e = total energy = a constant. isolated systems can have mechanical energy converted to heat. The law of conservation of energy is a physical law that states that the total energy of an isolated system is a constant, although energy can change forms. in other words, energy is conserved over time. the law of conservation of energy is the first law of thermodynamics. french mathematician and philosopher Émilie du châtelet first proposed.
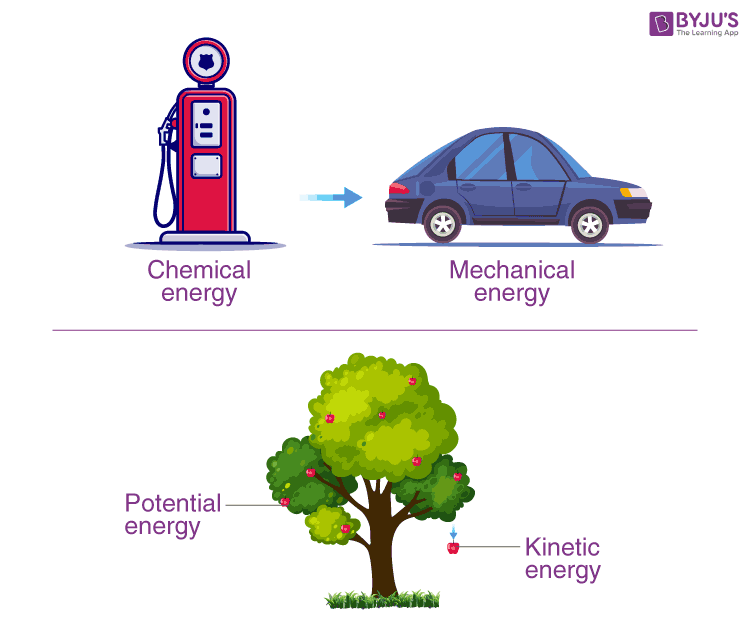
Law Of Conservation Of Energy Principle Of Conservation Of Energy The law of conservation of energy may be written: ke pe ie=e k e pe i e = e. where ke = kinetic energy = (1 2)m v2 , pe = potential energy (equal to m g h when gravity is the only force acting, but seen in other forms), ie = internal energy, and e = total energy = a constant. isolated systems can have mechanical energy converted to heat. The law of conservation of energy is a physical law that states that the total energy of an isolated system is a constant, although energy can change forms. in other words, energy is conserved over time. the law of conservation of energy is the first law of thermodynamics. french mathematician and philosopher Émilie du châtelet first proposed.

Comments are closed.