Which Is Lighter Hydrogen Or Helium Science Behind It By Er Sir

Chapter 7 Hydrogen Solutions For Class 8 Viraf J Dalal Simplified #sciencebehndit #hydrogengas #lightergaswhy hydrogen gas is not used in balloons ?which one is lighter hydrogen or helium ?which is best conductor of electri. Answer. in order to get a floating balloon you want a gas which is as light as possible. helium is quite a lot lighter than air: it's about an eighth of the density of air. hydrogen is about a sixteenth the density of air, so it'll float in air and will in fact float upwards. you'd have thought that hydrogen would be a better gas as it would.

Why Do We Need Lighter Hydrogen Tanks Lighter than air gases, such as hydrogen and helium, have unique properties that make them buoyant in the earth's atmosphere. while hydrogen is flammable, helium is safer and commonly used. other lesser known gases, like methane, ammonia, and neon, also defy gravity. these gases offer possibilities and challenges for industries like aviation. Hot air balloons. hot air balloons were the first lta vehicles to be developed. these simple forms of lighter than air flight technology have two main parts: the envelope: a large balloon shaped bag made of lightweight fabric. it is sewn together in panels which are joined to make strips called gores; and. For some applications, h2 h 2 is more appropriate. for example, weather balloons often use hydrogen due to cost, with side benefits being lower density and lower diffusion rates across the membrane; flammability is not a major concern. since helium is on shortage, fewer and fewer places use it any more for balloons. That means the net force on a hydrogen balloon is greater. the difference in the net force is small. hydrogen is h2 h 2, which has atomic mass 2, while air is mostly n2 n 2, which has atomic mass 28, so the hydrogen balloon has a net force of about (28 2) 28 = .93 the weight of the air it displaces. helium is mostly helium 4, so the net force.

Get Answer Both Hydrogen Gas And Helium Gas Are Lighter Than Air For some applications, h2 h 2 is more appropriate. for example, weather balloons often use hydrogen due to cost, with side benefits being lower density and lower diffusion rates across the membrane; flammability is not a major concern. since helium is on shortage, fewer and fewer places use it any more for balloons. That means the net force on a hydrogen balloon is greater. the difference in the net force is small. hydrogen is h2 h 2, which has atomic mass 2, while air is mostly n2 n 2, which has atomic mass 28, so the hydrogen balloon has a net force of about (28 2) 28 = .93 the weight of the air it displaces. helium is mostly helium 4, so the net force. Hydrogen and helium are the most commonly used lift gases. although helium is twice as heavy as (diatomic) hydrogen, they are both significantly lighter than air. the lifting power in air of hydrogen and helium can be calculated using the theory of buoyancy as follows: thus helium is almost twice as dense as hydrogen. The helium balloon then experiences an upward force (buoyancy force) that is equal to the weight of the air it has displaced. this buoyancy force is greater than the force of gravity pulling the balloon downward, allowing it to float. the importance of lightness: helium is lighter than air, which is why it is often used to fill balloons.

Solved Since Helium Is Lighter Than Air It Is Difficult To Chegg Hydrogen and helium are the most commonly used lift gases. although helium is twice as heavy as (diatomic) hydrogen, they are both significantly lighter than air. the lifting power in air of hydrogen and helium can be calculated using the theory of buoyancy as follows: thus helium is almost twice as dense as hydrogen. The helium balloon then experiences an upward force (buoyancy force) that is equal to the weight of the air it has displaced. this buoyancy force is greater than the force of gravity pulling the balloon downward, allowing it to float. the importance of lightness: helium is lighter than air, which is why it is often used to fill balloons.
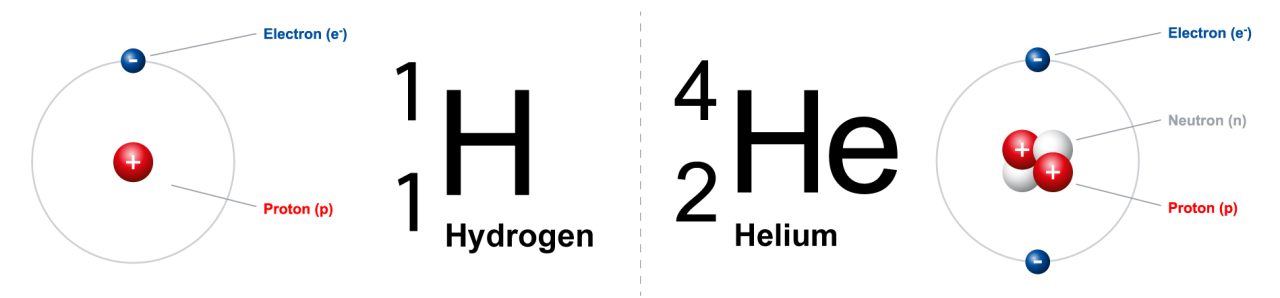
Confusion Versus Clarity Understanding The Difference Between Helium

Comments are closed.