Worked Example Calculating Solubility From Kₛₚ Equilibrium Ap Chemistry Khan Academy

юааworkedюаб юааexampleюаб юааcalculatingюаб юааsolubilityюаб From юааkюабтвытвъ юааequilibriumюаб ю Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now! khanacademy.org science ap chemistry beta x2eef969c7. Watch this video to learn how to calculate the solubility of a salt from its solubility product constant, kₛₚ, using an example problem.

Introduction To Solubility Equilibria Equilibrium Ap Chemistry The solubility product constant, kₛₚ, is an equilibrium constant that reflects the extent to which an ionic compound dissolves in water. for compounds that d. Keep going! check out the next lesson and practice what you’re learning: khanacademy.org science ap chemistry beta x2eef969c74e0d802:equilibrium x. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. [instructor] the presence of a common ion can affect a solubility equilibrium. for example, let's say we have a saturated solution of lead ii chloride. lead ii chloride is a white solid, so here's the white solid on the bottom of the beaker. and the solid's at equilibrium with the ions in solution. so that would be pb2 and cl .
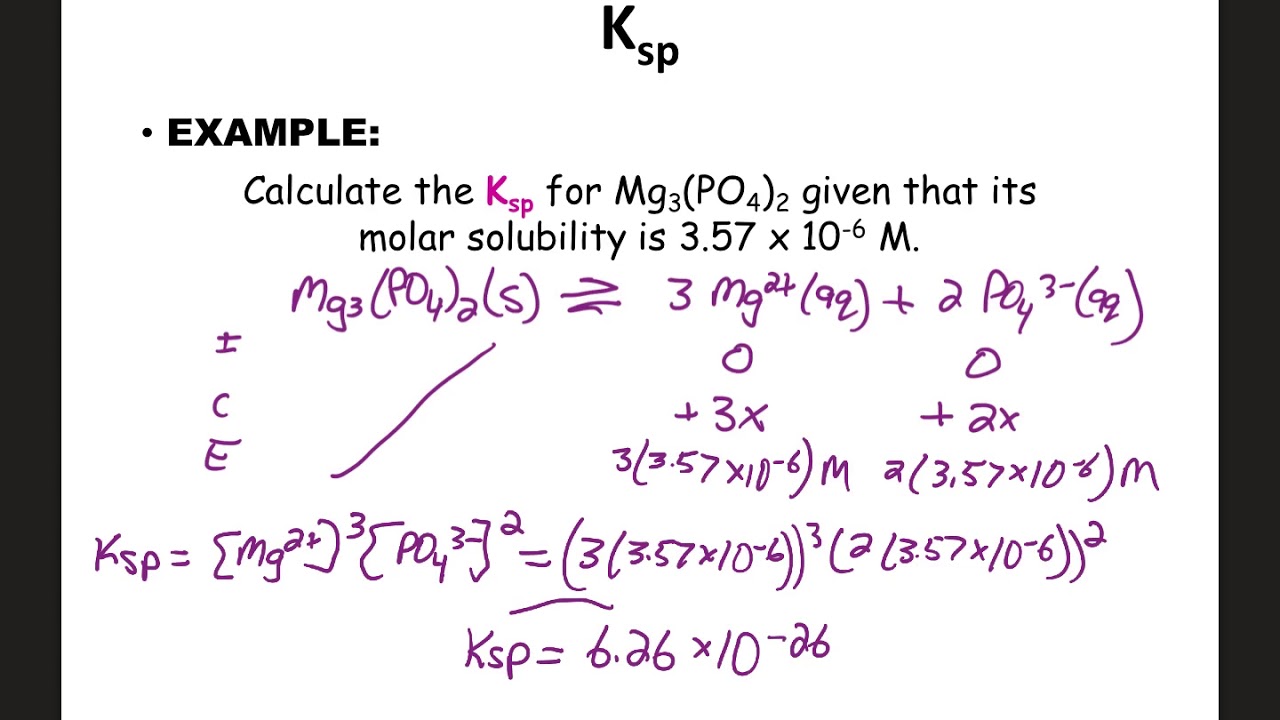
Solubility Equilibrium Notes Ap Youtube If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. [instructor] the presence of a common ion can affect a solubility equilibrium. for example, let's say we have a saturated solution of lead ii chloride. lead ii chloride is a white solid, so here's the white solid on the bottom of the beaker. and the solid's at equilibrium with the ions in solution. so that would be pb2 and cl . So the formation of a complex ion is a lewis acid base reaction. and notice the equilibrium constant for this. 1.6 times 10 to the seventh. kf is called the formation constant. this is a very high value for the equilibrium constant. so the equilibrium lies to the right, and this a stable complex ion. While other increase in solubility! aragonite is an example. example: the ksp for caco3 is 3.8 × 10 −9 @ 25 c. calculate the solubility of calcium carbonate in pure water in (a) moles per liter & (b) grams per liter: exercise 3 calculating solubility from ksp the ksp value for copper(ii) iodate, cu(io3)2, is 1.4 × 10 −7 at 25°c.

Comments are closed.